Abstract
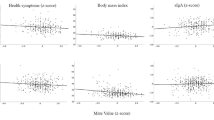
The construct of explanatory style has been related to numerous aspects of human psychology, including health. Our research has focused on the effects of various psychological variables on the immune system, in particular Immunoglobulin A (IgA). We had participants fill out the Attributional Style Questionnaire (ASQ), the predominant measure of explanatory style, and assayed saliva samples for secretory IgA. No relationship was observed between overall ASQ score and IgA, or composite optimism score and IgA. However we observed significant negative correlations between both the composite pessimism score and IgA, as well as the hopelessness score and IgA. Pessimistic explanatory style may therefore be related to immune system deficits and poor health.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson, L. Y., Seligman, M. E. P., and Teasdale, J. D. (1979). Learned helplessness in humans: Critique and reformulation.Journal of Abnormal Psychology 87:49–74.
Brennan, F. X., and Charnetski, C. J. (2000). The effect of Muzak on Immunoglobulin A (IgA) and stress in a work setting.Psychological Reports. 87:218–222.
Brennan, F. X., Job, R. F. S., Watkins, L. R., and Maier, S. F. (1992). Total plasma cholesterol levels are increased following only three sessions of tailshock.Life Sciences 50:945–50.
Buchanan, G. M., and Seligman, M. E. P., (Eds) (1995).Explanatory Style. Hillsdale NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum & Associates.
Burns, M. O., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1989) Explanatory style across the life span: evidence for stability over 52 years.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 56:471–7.
Charnetski, C. J., Brennan, F. X., and Harrison, J. F. (1998). Effect of music and auditory stimuli on secretory Immunoglobulin A (IgA).Perceptual and Motor Skills 87:1163–1170.
Charnetski, C. J., and Brennan, F. X. (1999). Sexual frequency and Immunoglobulin A (IgA). Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Eastern Psychological Association, Providence, R.I.
Charnetski, C. J., Strand, G. C., Olexa, M. L., Turosczi, L. J., and Rinehart, J. M. (1989). The effect of music modality on immunoglobulin A (IgA).Journal of the Pennsylvania Academy of Science 63:73–76.
Cohen, S. (1996). Psychological stress, immunity, and upper respiratory infections.Current Directions in Psychological Science 5:86–90.
Dillon, K.M., Minchoff B. and Baker, K.H. (1985). Positive emotional states and enhancement of the immune system. Int J Psychiatry Med 15:13–8.
Green, M. L., Green, R. G., and Santoro, W. (1988). Daily relaxation modifies serum and salivary immunoglobulins and psychophysiologic symptom severity.Biofeedback and Self Regulation 13:187–99.
Kamen-Siegel, L., Rodin, J., Seligman, M. E. P., and Dwyer, J. (1991). Explanatory style and cell-mediated immunity in elderly men and women.Health Psychology 10:229–35.
Kuby, J. (1992).Immunology. New York: Freeman.
Maier, S. F., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1976). Learned helplessness: Theory and Evidence.Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 105:3–46.
Mancini, G., Carbonara, A. O., and Heremans, J. F. (1965). Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion.Immunochemistry 2:623–625.
McClelland, D. C., Alexander, C., and Marks, E. (1980). The need for power, stress, immune function, and illness among male prisoners.Journal of Abnormal Psychology 10:93–102.
Ogra, P. L. (1985). Local immune responses.British Medical Bulletin 41:28.
Overmier, J. B., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1967). Effects of inescapable shock on subsequent escape and avoidance learning.Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 63:23–33.
Peterson, C., Maier, S. F., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1993).Learned Helplessness: A Theory for the Age of Personal Control. New York: Oxford University Press.
Peterson, C., Seligman, M. E. P., and Vaillant, G. E. (1988). Pessimistic explanatory style is a risk factor for physical illness: a thirty-five-year longitudinal study.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 55:23–7.
Peterson, C., Semmel, A., von Baeyer, C., Abramson, L. Y., Metalsky, G. I., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1982). The attributional style questionnaire.Cognitive Therapy and Research 6:287–299.
Peterson, C. (1988). Explanatory style as a risk factor for illness.Cognitive Therapy and Research 12:119–132.
Rider, M. S., Achterberg, J., Lawlis, G. F., Goven, A., Toledo, R., and Butler, J. R. (1990). Effect of immune system imagery on secretory IgA.Biofeedback and Self Regulation 15:317–33.
Rosselini, R. A., and Seligman, M. E. P. (1978). Role of shock intensity in the learned helplessness paradigm. AnimalLearning and Behavior 6:143–146.
Seligman, M. E. P., and Maier, S. F. (1967). Failure to escape traumatic shock.Journal of Experimental Psychology 74:1–9.
Seligman, M. E. P. (1981). A learned helplessness point of view. In:Behavior Therapy for depression: Present Status and Future Directions L. P. Rehm, (Ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Seligman, M. E. P. (1990).Learned Optimism. New York: Knopf.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brennan, F.X., Charnetski, C.J. Explanatory style and immunoglobulin A (IgA). Integrative Physiological and Behavioral Science 35, 251–255 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688787
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02688787