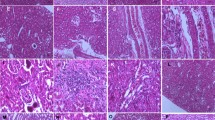
Abstract
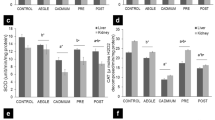
Increased intake of Cd results in its retention and in peroxidative damage in soft tissues. Coadministration of antioxidants, viz., glutathione (GSH), α-tocopherol, and Se, restricted the uptake and distribution of Cd in liver and kidney of rats. Moreover, no rise in malondialdehyde was recorded. Although possible antioxidative mechanisms manifested by GSH, α-tocopherol, and Se have been discussed, it is hypothesized that GSH functions as a Cd chelator. Glutathione yielded favorable effects in comparison to Se and α-tocopherol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Friberg, C. G. Elinder, T. Kjellstrom, and G. F. Nordberg,Cadmium and Health. A Toxicological and Epidemiological Appraisal, CRC, Boca Raton, FL (1986).
M. Webb, Binding of cadmium ions by rat liver and kidney,Biochem. Pharmacol. 21, 2751 (1972).
F. A. Probst, W. F. Bousquet, and T. S. Miya, Correlation of hepatic metallo thionein concentrations with acute cadmium toxicity in the mouse,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 39, 61 (1977).
S. V. S. Rana, V. P. Agrawal, and N. G. Bharadwaj, Cadmium and Zinc induced changes in the liver and kidney of rats,Int. J. Tiss. Reac. 2, 57–64 (1980).
R. W. Chen, P. A. Wanger, W. G. Hockstra, and H. E. Ganather, Affinity labelling studies with cadmium induced testicular injury in the rats.J. Reprod. Fertility 38, 293 (1974).
P. D. Whanger, Selenium versus metal toxicity in animals, in “Proc. Symposium Selenium, Tellurium in the environment,” Industrial Health Foundation: Pittsburgh, P A, pp. 234 (1976).
H. D. Stove, Biliary excretion of cadmium by rats, effects of zinc, cadmium and selenium pretreatments,J. Toxicol Environ Health 2, 45–53 (1976).
B. A. Arrick, C. F. Nathan, and Z. A. Cohn, Glutathione metabolism as a determinant of therapeutic efficacy. A review:Cancer Res. 44, 4334 (1984).
N. H. Stacey, The amelioration of cadmium induced injury in isolated hepatocytes by reduced glutathione,Toxicology 42, 85 (1986).
G. A. Pascoe and D. J. Reed, Cell calcium, vitamin E and thiol redox system in cytotoxicity,Tree Radical & Biol. and Med. 6, 209 (1989).
M. Sato, K. Yamanobe, and Y. Nagai, Sex related differences in cadmium induced lipid peroxidation in the rat,Life Sci. 33, 903–908 (1983).
S. Gabor, Z. Anca, and E. Bordas, Cadmium induced lipid peroxidation in kidney and testes. Effect of Zinc and Copper,Rev. Roum. Biochim. 15, 113–117 (1978).
S. V. S. Rana, V. P. Agrawal, and N. G. Bharadwaj, The effects of dietary Cd & Zn on lipids proteins and carbohyderates in rats.Arch. Inds. Hyg. Toxicol. 32, 157–161 (1981).
Z. A. Placer, L. L. Cushman, and B. C. Johnson, Estimation of the product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl-dialdehyde) in biochemical systems,Analyt. Biochem 16, 359 (1966).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall, Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent,J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951).
G. L. Ellman, Tissue sulphahydryl groups,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70–77 (1959).
S. Ohmori, M. IKeda, E. Kasaharae, H. Hyodoh, and K. Hirota, A colorimetric determination of total-glutathione based on its C-terminal glycineresidue and its application to blood liver and yeast,Chem. Pharm. Bul. 29, 1355–1360 (1986).
R. A. Fisher,Statistical Methods for Research Workers, 11th ed., Oliver and Boyd, London (1950).
D. D. Perrin and A. E. Watt, Complex formation of Zinc and Cadmium with glutathione.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 230, 96 (1971).
G. Bellomo, F. Mirabelli, D. Di monte, P. Richelmi, H. Thor, C. Orrenius, and S. Orrenius, Formation and reduction of glutathione mixed disulfides during oxidative stress,Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 1313 (1987).
N. S. Kosower and E. M. Kosower, Glutathione & Cell membrane thiol status, inFunctions of Glutathione: Biochemical Physiological Toxicological and Clinical Aspects, A. Larrson, S. Orrenius, A. Holmgren, and B. Mannervik, eds., Raven, New York, pp. 307–315 (1983).
P. Graf and H. Sies, Hepatic uptake of cadmium and its biliary release as affected by dithioery thritol and glutathione,Biochem. Pharmacol. 33, 401 (1984).
M. Shimizu and S. Morita, Effects of feeding & fasting on hepatolobular distribution of glutathione and cadmium induced hepato toxicity,Toxicology 75, 97–107 (1992).
S. Horiuchi, M. Inoue, and Y. Morino, γ-glutamyltrans peptidase: Sidedness of its active site on renal brush border membrane,Eur. J. Biochem. 87, 429–437 (1978).
J. S. Cornell and A. Meister, Glutathione and γ-glutamyl cycle enzymes in crypt and villus tip cells of rat jejunal mucosa,Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 420–422 (1976).
S. V. S. Rana, and P. R. Boora, Antiperoxidative mechanism offered by selenium against liver injury caused by cadmium and mercury in rat.Bull. Env. Cont. Toxicol. 48, 120–124 (1992).
H. Iwata, T. Masukawa, H. Kitto, and M. Hiyashi, Involvement of tissue sulphydryl in the formation of a complex of methyl mercury with selenium,Biochem. Pharmacol. 30, 3159–3163 (1981).
T. Masukawa, H. Kitto, M. Hayashi, and H. Iwata, Formation and possible role of bis (methyl mercuric) selenide in rats treated with methyl mercury and selenite,Biochem. Pharmacol. 31, 75–78 (1982).
R. Reiter and A. Wendel, Selenium and drugs metabolism III relation of glutathione peroxidase and other hepatic enzyme modulations to dietary supplements,Biochem. Pharmacol. 34, 2287–2290 (1985).
G. S. Shukla, T. Hussain, R. S. Srivastava, and S. V. Chandra, Glutathione peroxidase catalase in liver, kidney, testes and brain regions of rats following cadmium exposure and subsequent withdrawl,Industrial Health 27, 59–69 (1989).
G. W. Burton and K. V. Ingold, Autoxidation of biological molecules. The antioxidant activity of Vitamin E and related chain breaking phènolic antioxidantsin vitro, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 103, 6472 (1981).
D. C. Liebler, D. S. Kling, and D. J. Reed, Antioxidant protection of phospholipid bilayers by α-tocopherol,J. Biol. Chem. 261, 12,114–12,119 (1986).
O. Levander, Lead toxicity and nutritional deficiencies,Env. Health Perspect. 29, 115–125 (1979).
D. Barltrop and H. E. Khoo, Nutritional determinants of lead absorption,Trace Substances in Environmental Health, IX, D. D. Hemphill, ed., University of Missouri Press, Columbia, MO, pp. 369–376 (1975).
D. J. Reed, G. A. Pascoe, and K. Olafsdottir, Some aspects of cell defense mechanism of glutathione and vitamin E during cell injury,Arch. Toxicol. Supp. 11, 34–38 (1987).
J. Isaacs and F. Binkley, Glutathione dependent control of protein disulfide-sulphydryl content by subcellular fractions of hepatic tissue,Biochem. et Biophys. Acta 497, 192–204 (1977).
N. S. Kosower and E. M. Kosower, The glutathione status of cells,Intl. Review of Cytology 54, 109–160 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, S.V.S., Verma, S. Protective effects of GSH, vitamin E, and selenium on lipid peroxidation in cadmium-fed rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 51, 161–168 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785435
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785435