Summary
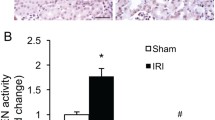
The effects of SB203580 (SB) with different concentrations at different time points on renal function, apoptosis, P38MAPK activity and the expression, as well as the P38MAPK substrates in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury were investigated. Forty-nine rats were divided into 7 groups at random (n=7 in each group) according to the durations of ischemia/reperfusion injury and the time of medication. Based on the orthogonal Latin side, the rats were injected, by caudal vein, with the same volume but different dosages of SB. BUN and Scr were determined. The apoptosis was detected with TUNEL kit. The protein was assayed qualitatively and semi-quantitatively by Western blot. The results showed that SB could significantly reduce the increased Scr and BUN, the apoptosis of renal tubular epithelia and the activation of P38MAPK all caused by renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.05). And the effect was most predominant when SB was given 3 h before renal ischemia. This suggested that SB could significantly alleviate renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Administration of SB 3 h before ischemia at the concentration of 5 μmol/L could obtain an optimal effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Y, Li X M, Wang H Y. IL-1β pass through the signal of JNK/P38 channel adjusting renal membrane cell express α- SM. Physiol Newspaper 2002, 54(3): 244–250
Di Mari J F, Davos R, Safirstein R Let al. MAPK activation determines renal epithelial cell survival during oxidative injury. Am J Physiol, 1999, 277 (Pt2): F195-F203
Li R S, Sun X L, Liu X C. The relation between cell signal molecular P38MAPK and cell apoptosis in ischemic/reperfused kidney. Clin J Nephrol (Chinese), 2003, 19: 180–181
Prichett W, Hand A, Sheilds Jet al. Mechanism of action of bicyclic imidazoles defines a translational regulatory pathway for tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Inflamm, 1995, 45: 97–105
Lali F V, Hunt A E, Foxwell B Met al. The pyridinyl imidarol inhibitor SB203580 blocks phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase activity, protein kinase B phosphorylation and retinoblastoma hyperphosphorylation in interleukin-stimulated T cells independently of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275: 7395–7402
Ito T, Kozawa O, Tanabe Ket al. P38MAP kinase is required for vasopressin-stimulated HSP27 induction in aortic smooth muscle cells. Hepertension, 2002, 35(2): 673–683
Ohanian, Jacqueile, Cunlifeet al. Activated of P38 Mitogen-Actly protein kinase by Endothelin and noraderna-line in small Arterles, Regulation by Calcium Inflax and Tyuslre Klnase, and their role in contraction arterisclerosis thrombosis δ. Vascular Biol, 2002, 21 (12): 1921–1927
Mackay K, Mochly-Rosen D. An inhibitor of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase protects neonatal cardiac myocytes from ischemia. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274: 6272–6279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
LI Rongshan, male, born in 1963, Professor
This project was supported by a grant from Natural Sciences Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 20001072).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rongshan, L., Tao, D., Xiaocheng, L. et al. Influence of SB203580 on cell apoptosis and P38MAPK in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 26, 50–52 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828037
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02828037