Conclusion
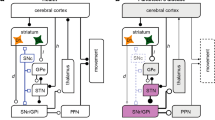
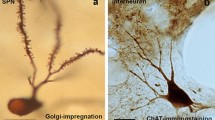
The data reviewed here demonstrate a capacity for neuronal plasticity in the aged human brain, even when affected by neurodegenerative disorders. However, given their location and environment, these morphological changes may have beneficial or deleterious consequences. In Parkinson disease, the changes observed in the substantia nigra are likely involved in compensatory mechanisms that may delay the appearance of the clinical symptoms, where as the synaptic plasticity in the striatum may aggravate the behavioral disturbances. Finally, it is likely that such synaptic plasticity requires a highly differentiated set of trophic molecules during the evolution of the pathological process. Further knowledge of these molecules is needed, however, before their use can be envisaged as possible therapeutic agents aimed at correcting the behavioral deficits owing to the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglade P., Tsuji S., Hirsch E. C., Javoy-Agid F., and Agid Y. (1993) Ultrastructural relations between nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons and cholinergic nerve endings in the human brain.Histol. Histopathol. 8, 501–504.
Anglade P., Tsuji P., Agid Y., and Hirsch H. C. (1995a) Plasticity of nerve afferents to nigrostriatal neurons in Parkinson’s disease.Ann. Neurol. 37, 265–272.
Anglade P., Mouatt-Prigent A., Agid Y., and Hirsch E. C. (1995b) Synaptic plasticity in the striatum of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Submitted.
Blaha C. D. and Winn P. (1993) Modulation of dopamine efflux in the striatum following cholinergic stimulation of the substantia nigra in intact and pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus-lesioned rats.J. Neurosci. 13, 1035–1044.
Bolam J. P. and Smith Y. (1990) The GABA and substance P input to dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the rat.Brain Res. 529, 57–78.
Bolam J. P., Francis C. M., and Henderson Z. (1991) Cholinergic input to dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra: a double immunocytochemical study.Neuroscience 41, 483–494.
Calverley R. K. S. and Jones D. G. (1990) Contributions of dendritic spines and perforated synapses to synaptic plasticity.Brain Res. Rev. 15, 215–249.
Cotman C. W. and Anderson K. J. (1988) Synaptic plasticity and functional stabilization in the hippocampal formation: possible role in Alzheimer’s disease.Adv. Neurol. 47, 313–336.
Girault J.-A., Halpain S., and Greengard P. (1990) Excitatory aminoacid antagonist and Parkinson’s disease.Trends Neurosci. 13, 225–227.
Grofova I., Deniau J. M., and Kitai S. T. (1982) Morphology of the substantia nigra pars reticulata projection neurons intracellularly labeled with HRP.J. Comp. Neurol. 208, 352–368.
Hernandez-Lopez S., Gongora-Alfaro J. L., Martinez-Fong D., and Aceves J. (1992) A cholinergic input to the substantia nigra pars compacta increases striatal dopamine metabolism measured by in vivo voltametry.Brain Res. 598, 114–120.
Hornykiewicz O. (1993) Parkinson’s disease and the adaptative capacity of the nigrostriatal dopamine system: possible neurochemical mechanism.Adv. Neurol. 60, 140–147.
Ingham C. A., Hood S. H., van Maldegem B., Weenick A., and Arbuthnott G. W. (1993) Morphological changes in the rat neostriatum after unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine injections into the nigrostriatal pathway.Exp. Brain Res. 93, 17–27.
Javoy F., Agid Y., Bouvet D., and Glowinski J. (1974) Changes in neostriatal DA metabolism after carbachol or atropine microinjections in the substantia nigra.Brain Res. 68, 253–260.
Kerns J. M., Sierens D. K., Kao L. C., Klawans H. L., and Carvey P. M. (1992) Synaptic plasticity in the rat striatum following chronic haloperidol treatment.Clin. Neuropharmacol. 15, 488–500.
Leenders K. L., Salmon E. P., Tyrell P., Perani D., Brooks D. J., Sager H., Jones T., Marsden C. D., and Frackowiak R. S. J. (1990) The nigrostriatal dopaminergic system assessed in vivo by positron emission tomography in healthy volunteer subjects and patients with Parkinson’s disease.Arch. Neurol. 47, 1290, 1291.
Meshul C. K., Stallbaumer R. K., Taylor B., and Janowsky A. (1994) Haloperidolinduced morophological changes in the striatum are associated with glutamate synapses.Brain Res. 648, 181–195.
Reid M. S., Herrera-Marschitz M., Hökfelt T., Ohlin M., and Ungerstedt U. (1988) Differential modulation of striatal dopamine release by intranigral injection of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), dynorphin A and substance P.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 147, 411–420.
Reid M. S., Herrera-Marschitz M., and Ungerstedt U. (1990) Effects of intranigral substance P and neurokinin A on striatal dopamine release-II. Interactions with bicuculline and naloxone.Neuroscience 36, 659–667.
Rinne U. K., Laihinen A., Rinne J. O., Nagren K., Bergman J., and Ruotsalainen U. (1990) Positron emission tomography demonstrates dopamine D2 receptor supersensitivity in the striatum with early Parkinson’s disease.Movt. Disord. 5, 55–59.
Smith A. D. and Bolam J. P. (1990) The neural network of the basal ganglia as revealed by the study of synaptic connections of identified neurones.Trends Neurosci. 13, 259–265.
Vijayan V. J. and Cotman C. M. (1987) Hydrocortisone administration alters glial reacation to entorhinal lesion in the rat dentate gyrus.Exp. Neurol. 96, 307–320.
Walters J. R., Bergstrom D. A., Carlson J. H., Chase T. N., and Braun A. R. (1987) D1 dopamine receptor activation required for postsynaptic expression of D2 agonist effects.Science 236, 719–722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anglade, P., Tsuji, S., Agid, Y. et al. Neuronal plasticity and Parkinson disease. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 24, 251–255 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02962152
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02962152