Abstract
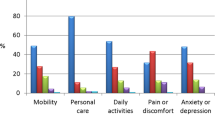
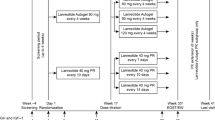
Background: Normalization of IGF-I in patients with acromegaly is associated with a decrease in mortality. Pegvisomant may be more effective in lowering IGF-I than octreotide. Subjects and methods: The efficacy and safety of pegvisomant and octreotide long-acting release (LAR) were compared in 118 patients with acromegaly in this 52-week, multicenter, open-label, randomized study. The primary end-point was IGF-I normalization at week 52. Secondary end-points included mean changes from baseline in IGF-I, IGF binding protein 3, acromegaly signs and symptom scores, ring size, acromegaly quality of life questionnaire scores, and safety. Results: Fifty-six patients received pegvisomant and 57 received octreotide LAR. IGF-I normalized in 51% of pegvisomant patients and 34% treated with octreotide LAR (p=0.09, ns). Patients with baseline IGF-I ≥2xupper limit of normal had a higher rate of IGF-I normalization with pegvisomant vs octreotide LAR (p=0.05). Among the patients who did not achieve a normalized IGF-I, pegvisomant-treated patients were more likely to be receiving <30 mg of study drug (71% vs 16%). Treatment-related adverse events were mild-to-moderate in both groups. Mean fasting glucose decreased in diabetic and non-diabetic patients on pegvisomant whereas octreotide LAR was associated with an increase at week 52 (p=0.005 and p=0.003 between groups, respectively). Mean change in tumor volume during treatment was similar between groups. Conclusions: Pegvisomant and octreotide LAR were equally effective in normalizing IGF-I in the overall population, and pegvisomant was more effective in patients with higher baseline IGF-I levels. Pegvisomant had a more favorable effect on parameters of glycemic control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danzig J. Acromegaly. BMJ 2007, 335: 824–5.
Melmed S. Medical progress: acromegaly. N Engl J Med 2006, 355: 2558–73.
Melmed S, Casanueva F, Cavagnini F, et al. Consensus statement: medical management of acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 2005, 153: 737–40.
Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G. Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev 2004, 25: 102–52.
Ahmed S, Elsheikh M, Stratton IM, Page RC, Adams CB, Wass JA. Outcome of transphenoidal surgery for acromegaly and its relationship to surgical experience. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1999, 50: 561–7.
Sheaves R, Jenkins P, Blackburn P, et al. Outcome of transsphenoidal surgery for acromegaly using strict criteria for surgical cure. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1996, 45: 407–13.
Swearingen B, Barker FG, 2nd, Katznelson L, et al. Long-term mortality after transsphenoidal surgery and adjunctive therapy for acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998, 83: 3419–26.
Losa M, Gioia L, Picozzi P, et al. The role of stereotactic radiotherapy in patients with growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008, 93: 2546–52.
Petit JH, Biller BM, Coen JJ, et al. Proton stereotactic radiosurgery in management of persistent acromegaly. Endocr Pract 2007, 13: 726–34.
Freda PU, Katznelson L, van der Lely AJ, Reyes CM, Zhao S, Rabinowitz D. Long-acting somatostatin analog therapy of acromegaly: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90: 4465–73.
Melmed S, Sternberg R, Cook D, et al. A critical analysis of pituitary tumor shrinkage during primary medical therapy in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90: 4405–10.
Tolis G, Angelopoulos NG, Katounda E, et al. Medical treatment of acromegaly: comorbidities and their reversibility by somatostatin analogs. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83: 249–57.
Freda PU. Somatostatin analogs in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002, 87: 3013–8.
Ezzat S, Redelmeier DA, Gnehm M, Harris AG. A prospective multicenter octreotide dose response study in the treatment of acromegaly. J Endocrinol Invest 1995, 18: 364–9.
Flogstad AK, Halse J, Bakke S, et al. Sandostatin LAR in acromegalic patients: long-term treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997, 82: 23–8.
Lancranjan I, Atkinson AB. Results of a European multicentre study with Sandostatin LAR in acromegalic patients. Sandostatin LAR Group. Pituitary 1999, 1: 105–14.
Newman CB, Melmed S, Snyder PJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of long-term octreotide therapy of acromegaly: results of a multicenter trial in 103 patients—a clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995, 80: 2768–75.
Vance ML, Harris AG. Long-term treatment of 189 acromegalic patients with the somatostatin analog octreotide. Results of the International Multicenter Acromegaly Study Group. Arch Intern Med 1991, 151: 1573–8.
Lamberts SW, van der Lely AJ, de Herder WW, Hofland LJ. Octreotide. N Engl J Med 1996, 334: 246–54.
Ronchi CL, Varca V, Beck-Peccoz P, et al. Comparison between six-year therapy with long-acting somatostatin analogs and successful surgery in acromegaly: effects on cardiovascular risk factors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 121–8.
Colao A, Arnaldi G, Beck-Peccoz P, et al. Pegvisomant in acromegaly: why, when, how. J Endocrinol Invest 2007, 30: 693–9.
Kopchick JJ, Parkinson C, Stevens EC, Trainer PJ. Growth hormone receptor antagonists: discovery, development, and use in patients with acromegaly. Endocr Rev 2002, 23: 623–46.
Trainer PJ, Drake WM, Katznelson L, et al. Treatment of acromegaly with the growth hormone-receptor antagonist pegvisomant. N Engl J Med 2000, 342: 1171–7.
van der Lely AJ, Hutson RK, Trainer PJ, et al. Long-term treatment of acromegaly with pegvisomant, a growth hormone receptor antagonist. Lancet 2001, 358: 1754–9.
Elmlinger MW, Kuhnel W, Weber MM, Ranke MB. Reference ranges for two automated chemiluminescent assays for serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3). Clin Chem Lab Med 2004, 42: 654–64.
Barkan AL, Burman P, Clemmons DR, et al. Glucose homeostasis and safety in patients with acromegaly converted from long-acting octreotide to pegvisomant. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005, 90: 5684–91.
Webb SM, Prieto L, Badia X, et al. Acromegaly Quality of Life Questionnaire (ACROQOL) a new health-related quality of life questionnaire for patients with acromegaly: development and psychometric properties. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002, 57: 251–8.
Brabant G, von zur Muhlen A, Wuster C, et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor I reference values for an automated chemiluminescence immunoassay system: results from a multicenter study. Horm Res 2003, 60: 53–60.
Colao A, Pivonello R, Auriemma RS, et al. Efficacy of 12-month treatment with the GH receptor antagonist pegvisomant in patients with acromegaly resistant to long-term, high-dose somatostatin analog treatment: effect on IGF-I levels, tumor mass, hypertension and glucose tolerance. Eur J Endocrinol 2006, 154: 467–77.
Drake WM, Rowles SV, Roberts ME, et al. Insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance improve in patients with acromegaly converted from depot octreotide to pegvisomant. Eur J Endocrinol 2003, 149: 521–7.
Klijn JG, Lamberts SW, de Jong FH, van Dongen KJ, Birkenhager JC. Interrelationships between tumour size, age, plasma growth hormone and incidence of extrasellar extension in acromegalic patients. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980, 95: 289–97.
Biering H, Saller B, Bauditz J, et al. Elevated transaminases during medical treatment of acromegaly: a review of the German pegvisomant surveillance experience and a report of a patient with histologically roven chronic mild active hepatitis. Eur J Endocrinol 2006, 154: 213–20.
Feenstra J, van Aken MO, de Herder WW, Feelders RA, van der Lely AJ. Drug-induced hepatitis in an acromegalic patient during combined treatment with pegvisomant and octreotide long-acting repeatable attributed to the use of pegvisomant. Eur J Endocrinol 2006, 154: 805–6.
Schreiber I, Buchfelder M, Droste M, et al; German Pegvisomant Investigators. Treatment of acromegaly with the GH receptor antagonist pegvisomant in clinical practice: safety and efficacy evaluation from the German Pegvisomant Observational Study. Eur J Endocrinol 2007, 156: 75–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghigo, E., Biller, B.M.K., Colao, A. et al. Comparison of pegvisomant and long-acting octreotide in patients with acromegaly naïve to radiation and medical therapy. J Endocrinol Invest 32, 924–933 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345774
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345774