Abstract
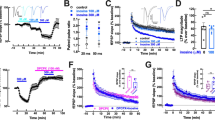
Rat striatal and hippocampal slices, preincubated with [3H] dopamine (DA) {or [3H] noradrenaline (NA)} and [14C] choline, were superfused continuously and stimulated electrically. 2-chloroadenosine (2-CADO 0.001–100 μM), a non-selective adenosine receptor agonist, produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of the electrically evoked DA and acetylcholine (ACh) release from the striatal slices and of the electrically evoked NA and ACh release from the hippocampal slices. 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX 3, 30 and 200 nM), a selective adenosine A1 receptor antagonist, caused a concentration-dependent, parallel, rightward shift of the 2-CADO concentration-response curve, consistent with competitive antagonism. The pA2 values ranged between 8.4 and 8.8. In the case of ACh release from the hippocampus, but in no other case, was there an increase in release of radioactivity at low concentrations of 2-CADO in the presence of DPCPX. The stimulation in the hippocampus could be blocked by a selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist KF 17837. By itself KF 17837 (0.1–100 μM) had no effect on electrically evoked NA release from hippocampal slices, but decreased electrically evoked ACh release. This inhibition was counteracted by DPCPX (1 μM).
These results show that, under the conditions used, DA release in the striatum, and NA release in the hippocampus, as well as ACh release from the striatum are regulated by adenosine A1 but not by adenosine A2A receptors. By contrast, ACh release from the hippocampus is tonically regulated both by adenosine A1 receptors, which inhibit release, and by adenosine A2A receptors which stimulate release.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 April 1996 / Accepted: 30 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, S., Fredholm, B. Adenosine A2A receptor stimulation increases release of acetylcholine from rat hippocampus but not striatum, and does not affect catecholamine release. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 355, 48–56 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00004917
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00004917