Abstract
Purpose
Our aim is to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of interspinous spacers versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) for degenerative lumbar spinal diseases.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane Library through September 2015. Included studies were performed according to eligibility criteria. Data of complication rate, post-operative back visual analogue scale (VAS) score, Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) score, estimated blood loss (EBL), operative time, length of hospital stay (LOS), range of motion (ROM) at the surgical, proximal and distal segments were extracted and analyzed.
Results
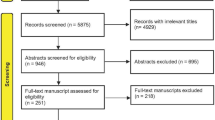
Ten studies were selected from 177 citations. The pooled data demonstrated the interspinous spacers group had a lower estimated blood loss (weighted mean difference [WMD]: −175.66 ml; 95 % confidence interval [CI], −241.03 to −110.30; p < 0.00001), shorter operative time (WMD: −55.47 min; 95%CI, −74.29 to −36.65; p < 0.00001), larger range of motion (ROM) at the surgical segment (WMD: 3.97 degree; 95%CI, −3.24 to −1.91; p < 0.00001) and more limited ROM at the proximal segment (WMD: −2.58 degree; 95%CI, 2.48 to 5.47; p < 0.00001) after operation. Post-operative back VAS score, ODI score, length of hospital stay, complication rate and ROM at the distal segment showed no difference between the two groups.
Conclusions
Our meta-analysis suggested that interspinous spacers appear to be a safe and effective alternative to PLIF for selective patients with degenerative lumbar spinal diseases. However, more randomized controlled trials (RCT) are still needed to further confirm our results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cole CD, McCall TD, Schmidt MH, Dailey AT (2009) Comparison of low back fusion techniques: transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) or posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) approaches. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2:118–126. doi:10.1007/s12178-009-9053-8
Wilke HJ, Drumm J, Haussler K, Mack C, Steudel WI, Kettler A (2008) Biomechanical effect of different lumbar interspinous implants on flexibility and intradiscal pressure. Eur Spine J 17:1049–1056. doi:10.1007/s00586-008-0657-2
Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Alfieri A (2014) Controversies about interspinous process devices in the treatment of degenerative lumbar spine diseases: past, present, and future. BioMed Res Int 2014:975052. doi:10.1155/2014/975052
Verhoof OJ, Bron JL, Wapstra FH, van Royen BJ (2008) High failure rate of the interspinous distraction device (X-Stop) for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis caused by degenerative spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J 17:188–192. doi:10.1007/s00586-007-0492-x
Puzzilli F, Gazzeri R, Galarza M, Neroni M, Panagiotopoulos K, Bolognini A, Callovini G, Agrillo U, Alfieri A (2014) Interspinous spacer decompression (X-STOP) for lumbar spinal stenosis and degenerative disk disease: a multicenter study with a minimum 3-year follow-up. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 124:166–174. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.07.004
Furlan AD, Pennick V, Bombardier C, van Tulder M (2009) 2009 updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Back Review Group. Spine 34:1929–1941. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181b1c99f
Zhao-hui C, Qiang FU, Cong W et al (2010) Posterior single segment fusion or non-fusion in treatment of lumbar spinal disease: a comparative study. Orthop J China 18:629–632
Zeng Z, Guo Z, Zhu Z et al (2013) Posterior single segment fusion or non - fusion in treatment of lumbar spinal disease: a comparative study. Orthop J China 21:34–36
Kong D-S, Kim E-S, Eoh W (2007) One-year outcome evaluation after interspinous implantation for degenerative spinal stenosis with segmental instability. J Korean Med Sci 22:330–335
Hongsheng LIN, Guowei Z, Hao WU, Ning LIU, Zhengang ZHA et al (2011) Treatment of single degenerative disc disease with Coflex interspinous implant and posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a comparative analysis. J Sun Yat-sen Univ Med Sci 32:364–369
Liang C, Chang Y, Zhan S, Wang Y, Ke Y, Yin D, Xiao D, Zheng X et al (2014) A comparative study between single lever Coflex implantation and lumbar fusion in treating single-level degenerative lumbar spinal disorders. Chin J Clin Anat 32:98–101
Li Z, Qian J, Li C et al (2010) Comparison of short term outcome in the treatment of degenerative lumbar stenosis with Coflex implant versus laminectomy and posterior interbody fusion along with pedicle screw system. Orthop J China 18:888–891
Jin LIU, Hao LIU, Tao LI, Jiancheng Z, Yueming S, Limin LIU, Quan G et al (2011) Coflex interspinous dynamic reconstruction and 360 degrees fusion for single level lumbar degenerative disease: a cost-utility analysis. Chin J Evid Based Med 11:893–898
Jiangming YU, Yunrong ZHU, Peng XU et al (2011) A comparative study of Coflex interspinous internal fixation versus posterior interbody fusion used in the surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Orthop J China 19:885–888
Davis RJ, Errico TJ, Bae H, Auerbach JD (2013) Decompression and Coflex interlaminar stabilization compared with decompression and instrumented spinal fusion for spinal stenosis and low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis two-year results from the prospective, randomized, multicenter, food and drug administration investigational device exemption trial. Spine 38:1529–1539
Awei F, Zhong R, Wang L, Liu S, Cui S, Pan X, Sun H, Huang Y et al (2014) Analysis of adjacent segment disease after different lumbar instrumented fusion by using magnetic resonance T1p. J Sun Yat-sen Univ Med Sci 35:545–551
Bohm PE, Anderson KK, Friis EA, Arnold PM (2015) Grade 1 spondylolisthesis and interspinous device placement: removal in six patients and analysis of current data. Surg Neurol Int 6:54. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.154461
Moojen WA, Arts MP, Bartels RH, Jacobs WC, Peul WC (2011) Effectiveness of interspinous implant surgery in patients with intermittent neurogenic claudication: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J 20:1596–1606. doi:10.1007/s00586-011-1873-8
Bastian L, Lange U, Knop C, Tusch G, Blauth M (2001) Evaluation of the mobility of adjacent segments after posterior thoracolumbar fixation: a biomechanical study. Eur Spine J 10:295–300
Park P, Garton HJ, Gala VC, Hoff JT, McGillicuddy JE (2004) Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine 29:1938–1944
Ren C, Song Y, Liu L, Xue Y (2014) Adjacent segment degeneration and disease after lumbar fusion compared with motion-preserving procedures: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol Orthop Traumatol 24(Suppl 1):S245–S253. doi:10.1007/s00590-014-1445-9
Zhao H, Guo M, Mei Y et al (2012) Coflex versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of lumbar spine degenerative diseases: a meta analysis. Orthop J China 20:2129–2134
Wu AM, Zhou Y, Li QL, Wu XL, Jin YL, Luo P, Chi YL, Wang XY (2014) Interspinous spacer versus traditional decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 9:e97142. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0097142
Deyo RA, Martin BI, Ching A, Tosteson AN, Jarvik JG, Kreuter W, Mirza SK (2013) Interspinous spacers compared with decompression or fusion for lumbar stenosis: complications and repeat operations in the medicare population. Spine 38:865–872. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31828631b8
DiPaola CP, Molinari RW (2008) Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 16:130–139
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to Taifeng Zhou and Chong Chen for valuable discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Luo, J., Huang, J. et al. Interspinous spacers versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spinal diseases: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 40, 1135–1142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3139-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3139-x