Abstract
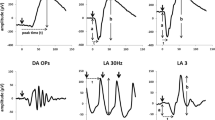
Suprathreshold photopic oscillatory potentials recorded with a DTL electrode were compared to those obtained with a Lovac corneal electrode. The overall oscillatory potential response (sum of oscillatory potentials) recorded with the DTL electrode was half of that obtained with the Lovac electrode. However, there was no evidence of a selective attenuation (or amplification) of any given oscillatory potential with the DTL electrode. Similarly, the oscillatory potential relative amplitude ratios and the peak times of the oscillatory potentials were identical for both electrodes. Our findings clearly indicate that the DTL electrode is adequate to record the high-frequency oscillatory potentials. Given the low cost and ease of use, as well as the disposable nature of the DTL electrode, we believe that electroretinographic specialists should seriously consider a wider utilization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coupland SG. Electrodes for clinical electrophysiological testing. In: Heckenlively JR, Arden GB, eds. Principles and practice of clinical electrophysiology of vision. St. Louis: Mosby, 1991: 177–82.
Gjötterberg M. Electrodes for electroretinography: A comparison of four different types. Arch Ophthalmol 1986; 104: 569–70.
Berninger T, Arden GB. The pattern electroretinogram. In: Heckenlively JR, Arden GB, eds. Principles and practice of clinical electrophysiology of visions. St. Louis: Mosby, 1991: 291–300.
Coupland SG, Janaky M. ERG electrode in pediatric patients: Comparison of DTL fiber, PVA-gel, and non-corneal skin electrodes. Doc Ophthalmol 1989; 71: 427–33.
Dawson WW, Trick GL, Litzkow CA. Improved electrode for electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1979; 18: 988–91.
Arden GB, Carter RM, Hogg C, Margolis S. A gold foil electrode: Extending the horizons for clinical electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1979; 18: 421–6.
Marmor MF, Arden GB, Nilsson SEG, Zrenner E. Standard for clinical electroretinography. Arch Ophthalmol 1989; 107: 816–9.
Prager TC, Saad N, Schweitzer C, Garcia CA, Arden GB. Electrode comparison in pattern electroretinography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1992; 33: 390–4.
Kothe AC, Lovasik JV, Coupland SG. Variability in clinically measured photopic oscillatory potentials. Doc Ophthalmol 1989; 71: 381–95.
Lachapelle P. Analysis of the photopic electroretinogram recorded before and after dark adaptation. Can J Ophthalmol 1987; 22: 354–61.
Lachapelle P. The effect of a slow flicker on the human photopic oscillatory potentials. Vision Res 1991; 31: 1851–7.
Lachapelle P, Benoit J, Blain L, Guité P, Roy M-S. The oscillatory potentials in response to stimuli of photopic intensities delivered in dark-adaptation: An explanation for the conditioning flash effect. Vision Res 1990; 30: 503–13.
Odom JV, Maida TM, Dawson WW, Hobson R. Pattern electroretinogram: Effects of reference electrode position. Doc Ophthalmol 1987; 65: 297–306.
Dawson WW, Trick GL, Maida TM. Evaluation of the DTL corneal electrode. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 1982; 31: 81–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lachapelle, P., Benoit, J., Little, J.M. et al. Recording the oscillatory potentials of the electroretinogram with the DTL electrode. Doc Ophthalmol 83, 119–130 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206210
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01206210