Abstract.
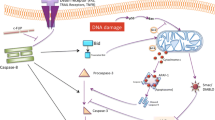
Doxycycline (Dc) has been demonstrated to inhibit cell growth and induce apoptosis in tumor cells, although its mechanism of action is not fully understood. The present study demonstrates that apoptosis can be induced in HeLa cells. Western blot data demonstrated that cytochrome c (Cyt c), Smac (the second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase), calpain I, caspase-9, −3 and −8 were involved in the apoptotic process, while the pan caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk almost completely inhibited Dc-induced apoptosis. We further demonstrated that the release of mitochondrial proteins and the activation of calpains occurred upstream of the caspase cascade, in which caspase-9 was activated in response to the release of Cyt c, that caspase-8 activation was caspase and calpain dependent, and that caspase-3 was activated mainly by caspase-8 and −9. Caspase-8 played important roles in the activation of caspase-3 and induction of apoptosis, whereas the role of the caspase-9 was limited.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 26 November 2005; received after revision 14 February 2006; accepted 1 March 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Liu, T., Xie, J. et al. Mitochondria and calpains mediate caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by doxycycline in HeLa cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 949–957 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5565-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5565-6