Abstract.
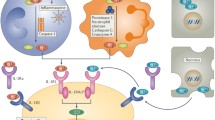
The inflammatory cytokine cascade plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Recently, a novel human cytokine, interleukin-32, was reported to induce tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Interleukin-32 is expressed primarily in lymphoid tissues and leukocytes, but also in stimulated epithelial cells and synovial fibroblasts. Although the interleukin-32 receptor has not been reported, interleukin-32 can induce other inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6 from monocytes/macrophages in vitro and in vivo, and it synergizes with signals from pattern-recognition receptors. Notably, in the inflamed synovial tissues from rheumatoid arthritis patients, interleukin-32 is prominently expressed and correlates with the severity of arthritis and the expression of other cytokines, including TNF-α and interleukin-1. In experimental mice models of arthritis, joint injection of interleukin-32 induces joint inflammation, and overexpression of interleukin-32β in hematopoietic cells exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis. Interleukin-32 can thus be seen to play an important role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 16 April 2007; received after revision 5 June 2007; accepted 19 June 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoda, H., Fujio, K. & Yamamoto, K. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Interleukin-32. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 2671 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7186-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7186-8