Abstract.
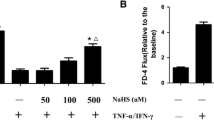
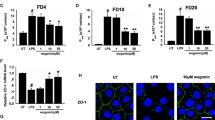
Tight junctions (TJs) create a paracellular permeability barrier. Although reactive oxygen species have been implicated as mediators of inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases, their influence on the function of colonic epithelial TJs remains unknown. Oxidative stress-mediated colonic epithelial permeability was significantly attenuated by a p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase inhibitor, SB203580. Although the amount of TJ proteins was not altered, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) changed the localization of claudin-4 protein from an NP-40 insoluble fraction to a soluble fraction and from an apical TJ to lateral membrane. The p38 MAP kinase inactivator Wip1 significantly attenuated phosphorylation of p38 MAP kinase, and oxidative stress mediated permeability. H2O2-induced changes in claudin-4 localization were abolished by SB203580 pretreatment as well as Wip1-expressing adenovirus infection. This is the first study to demonstrate that exogenous Wip1 functions to protect oxidative stress-mediated colonic mucosal permeability and that H2O2-induced claudin-4 dislocalization is abolished by Wip1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 14 June 2007; received after revision 8 October 2007; accepted 8 October 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshima, T., Sasaki, M., Kataoka, H. et al. Wip1 protects hydrogen peroxide-induced colonic epithelial barrier dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 3139–3147 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7268-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7268-7