Abstract.
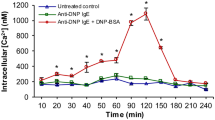
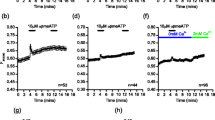
Mast cell activation involves the rapid release of inflammatory mediators, including histamine, from intracellular granules. The cells are capable of regranulation and multiple rounds of activation. The goal of this study was to determine if there are changes in the content of pre-formed mast cell mediators after a round of activation. After 24 h, the histamine content of bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMC), but not that of peritoneal mast cells, exceeded the amount in resting cells. Accumulation of histamine in BMMC peaked at 72 h of activation, and returned toward preactivation levels by 96 h. The increase in histamine content was accompanied by an increase in the gene expression of histidine decarboxylase. No increases in β hexosaminidase or murine mast cell protease-6 were observed. These findings indicate that BMMC respond to activation by increasing total cell-associated histamine content. This increase may be important to the response of these cells upon subsequent exposure to antigens.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 29 February 2008; received after revision 25 March 2008; accepted 26 March 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fitz, L.J., Brennan, A., Wood, C.R. et al. Activation-induced cellular accumulation of histamine in immature but not mature murine mast cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65, 1585–1595 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8106-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8106-2