Abstract
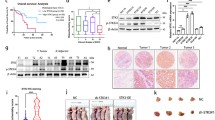
Rho family members are known to regulate malignant transformation and motility of cancer cells, but the clinicopathological significance of RhoC remains unclear yet in the case of gastric cancer. In this study, we evaluated the protein expression level of RhoC in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Results showed that only weak staining of RhoC was detected in 3 of 33 non-tumorous cases by immunohistochemistry. The expression of RhoC was significantly higher in gastric cancer tissues (23/42, 54.8%) than in non-tumorous tissues (p < 0.01). Further analysis demonstrated that RhoC had high specificity (80.0%) in detecting gastric carcinomas with metastatic potential. RhoC was positively expressed in 18 out of 20 metastases (90.0%), even higher than that in primary gastric cancer tissues. Western blot showed that RhoC was up-regulated in five different gastric cancer cell lines but not expressed in SV40-transformed immortal gastric epithelial cell GES-1. Overexpression of RhoC GTPase in GES-1 cells could produce the motile and invasive phenotype but did not alter the monolayer growth rate. To further study the functions of RhoC, we took the powerful siRNA technology to knock down the expression of RhoC in SGC7901 cells. It was shown that down-regulation of RhoC did not affect the proliferation of SGC7901 cells. However, interference of RhoC expression could inhibit migration, invasion, and anchorage-independent growth of SGC7901 cells. In conclusion, RhoC may play a very important role in the metastasis of gastric carcinoma. Therapeutic strategies targeting RhoC and RhoC-mediated pathways may be a novel approach for treating metastasis of gastric cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SiRNA:
-
small interfering RNA
References
Alberts SR, Cervantes A, van de Velde CJ (2003) Gastric cancer: epidemiology, pathology and treatment. Ann Oncol 14(2):ii31–36
Roder DM (2002) The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 5(1):5–11
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420(6916):629–635
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) Rho-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev 2:133–142
Fritz G, Just I, Kaina B (1999) Rho GTPases are over-expressed in human tumors. Int J Cancer 819(5):682–687
Kamai T, Arai K, Tsujii T, Honda M, Yoshida K (2001) Overexpression of RhoA mRNA is associated with advanced stage in testicular germ cell tumour. BJU Int 87(3):227–231
Kamai T, Tsujii T, Arai K et al (2003) Significant association of Rho/ROCK pathway with invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9(7):2632–2641
Horiuchi A, Imai T, Wang C et al (2003) Up-regulation of small GTPases, RhoA and RhoC, is associated with tumor progression in ovarian carcinoma. Lab Invest 83(6):861–870
Kamai T, Yamanishi T, Shirataki H, Takagi K, Asami H, Ito Y, Yoshida K (2004) Overexpression of RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 GTPases is associated with progression in testicular cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10(14):4799–4805
Adnane J, Muro-Cacho C, Mathews L, Sebti SM, Munoz-Antonia T (2002) Suppression of rho B expression in invasive carcinoma from head and neck cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 8(7):2225–2232
Jiang K, Delarue FL, Sebti SM (2004) EGFR, ErbB2 and Ras but not Src suppress RhoB expression while ectopic expression of RhoB antagonizes oncogene-mediated transformation. Oncogene 23(5):1136–1145
Prendergast GC (2001) Actin’ up: RhoB in cancer and apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer 1(2):162–168
Clark EA, Golub TR, Lander ES, Hynes RO (2000) Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 406(6795):532–535
Liu N, Bi F, Pan Y et al (2004) Reversal of the malignant phenotype of gastric cancer cells by inhibition of RhoA expression and activity. Clin Cancer Res 10(18):6239–6247 (Pt 1)
Xue Y, Bi F, Zhang X, Zhang S, Pan Y, Liu N, Shi Y, Yao X, Zheng Y, Fan D (2006) Role of Rac1 and Cdc42 in hypoxia induced p53 and von Hippel–Lindau suppression and HIF1alpha activation. Int J Cancer 118(12):2965–2972
Wherlock M, Mellor H (2002) The Rho GTPase family: a Racs to Wrchs story. J Cell Sci 115(2):239–240
van Golen KL, Bao LW, Pan Q, Miller FR, Wu ZF, Merajver SD (2002) Mitogen activated protein kinase pathway is involved in RhoC GTPase induced motility, invasion and angiogenesis in inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 19(4):301–311
del Peso L, Hernandez-Alcoceba R, Embade N, Carnero A, Esteve P, Paje C, Lacal JC (1997) Rho proteins induce metastatic properties in vivo. Oncogene 15(25):3047–3057
Kjoller L, Hall A (1999) Signaling to Rho GTPases. Exp Cell Res 253(1):166–179 (Nov 25)
Suwa H, Ohshio G, Imamura T, Watanabe G, Arii S, Imamura M, Narumiya S, Hiai H, Fukumoto M (1998) Overexpression of the rhoC gene correlates with progression of ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Br J Cancer 77(1):147–152
Wang W, Yang LY, Yang ZL, Huang GW, Lu WQ (2003) Expression and significance of RhoC gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 9(9):1950–1953
Crnogorac-Jurcevic T, Efthimiou E, Nielsen T, Loader J, Terris B, Stamp G, Baron A, Scarpa A, Lemoine NR (2002) Expression profiling of microdissected pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Oncogene 21(29):4587–4594
van Golen KL, Davies S, Wu ZF, Wang Y, Bucana CD, Root H, Chandrasekharappa S, Strawderman M, Ethier SP, Merajver SD (1999) A novel putative low-affinity insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, LIBC (lost in inflammatory breast cancer), and RhoC GTPase correlate with the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Clin Cancer Res 5(9):2511–2519
Kleer CG, Griffith KA, Sabel MS, Gallagher G, van Golen KL, Wu ZF, Merajver SD (2005) RhoC-GTPase is a novel tissue biomarker associated with biologically aggressive carcinomas of the breast. Breast Cancer Res Treat 93(2):101–110
Shikada Y, Yoshino I, Okamoto T, Fukuyama S, Kameyama T, Maehara Y (2003) Higher expression of RhoC is related to invasiveness in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 9(14):5282–5286
Faried A, Faried LS, Kimura H, Nakajima M, Sohda M, Miyazaki T, Kato H, Usman N, Kuwano H (2006) RhoA and RhoC proteins promote both cell proliferation and cell invasion of human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cancer 42(10):1455–1465
Ikoma T, Takahashi T, Nagano S, Li YM, Ohno Y, Ando K, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H, Kosai K (2004) A definitive role of RhoC in metastasis of orthotopic lung cancer in mice. Clin Cancer Res 10(3):1192–1200
Mukai M, Endo H, Iwasaki T, Tatsuta M, Togawa A, Nakamura H, Inoue M (2006) RhoC is essential for TGF-beta1-induced invasive capacity of rat ascites hepatoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346(1):74–82
Hakem A, Sanchez-Sweatman O, You-Ten A, Duncan G, Wakeham A, Khokha R, Mak TW (2005) RhoC is dispensable for embryogenesis and tumor initiation but essential for metastasis. Genes Dev 19(17):1974–1979
Simpson KJ, Dugan AS, Mercurio AM (2004) Functional analysis of the contribution of RhoA and RhoC GTPases to invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 64(23):8694–8701
Bellovin DI, Simpson KJ, Danilov T, Maynard E, Rimm DL, Oettgen P, Mercurio AM (2006) Reciprocal regulation of RhoA and RhoC characterizes the EMT and identifies RhoC as a prognostic marker of colon carcinoma. Oncogene 25:6959–6967
Pille JY, Denoyelle C, Varet J, Bertrand JR, Soria J, Opolon P, Lu H, Pritchard LL, Vannier JP, Malvy C, Soria C, Li H (2005) Anti-RhoA and anti-RhoC siRNAs inhibit the proliferation and invasiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Ther 11(2):267–274
van Golen KL, Wu ZF, Qiao XT, Bao LW, Merajver SD (2000) RhoC GTPase, a novel transforming oncogene for human mammary epithelial cells that partially recapitulates the inflammatory breast cancer phenotype. Cancer Res 60(20):5832–5838
Reddig PJ, Juliano RL (2005) Clinging to life: cell to matrix adhesion and cell survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24(3):425–439
Wang LH (2004) Molecular signaling regulating anchorage-independent growth of cancer cells. Mt Sinai J Med 71(6):361–367
Acknowledgements
We thank technicians Taidong Qiao and Zheng Chen for their excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the National Outstanding Youth Foundation (Grant 30325039) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 30400535).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
N. Liu and G. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Zhang, G., Bi, F. et al. RhoC is essential for the metastasis of gastric cancer. J Mol Med 85, 1149–1156 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0217-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0217-y