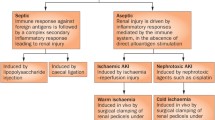
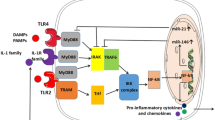
Abstract
Kidney ischemia–reperfusion injury (IRI) engages both the innate and adaptive immune responses. Cellular mediators of immunity, such as dendritic cells, neutrophils, macrophages, natural killer T, T, and B cells, contribute to the pathogenesis of renal injury after IRI. Postischemic kidneys express increased levels of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells and toll-like receptors on tubular epithelial cells. Soluble components of the immune system, such as complement activation proteins and cytokines, also participate in injury/repair of postischemic kidneys. Experimental studies on the immune response in kidney IRI have resulted in better understanding of the mechanisms underlying IRI and led to the discovery of novel therapeutic and diagnostic targets.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jang HR, Rabb H (2009) The innate immune response in ischemic acute kidney injury. Clin Immunol 130:41–50
Kelly KJ, Williams WW Jr, Colvin RB et al (1996) Intercellular adhesion molecule-1-deficient mice are protected against ischemic renal injury. J Clin Invest 97:1056–1063
Sutton TA, Mang HE, Campos SB, Sandoval RM, Yoder MC, Molitoris BA (2003) Injury of the renal microvascular endothelium alters barrier function after ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F191–F198
Brodsky SV, Yamamoto T, Tada T et al (2002) Endothelial dysfunction in ischemic acute renal failure: rescue by transplanted endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F1140–F1149
Liu M, Chien CC, Grigoryev DN, Gandolfo MT, Colvin RB, Rabb H (2009) Effect of T cells on vascular permeability in early ischemic acute kidney injury in mice. Microvasc Res 77:340–347
Wolfs TG, Buurman WA, van Schadewijk A et al (2002) In vivo expression of Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 by renal epithelial cells: IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha mediated up-regulation during inflammation. J Immunol 168:1286–1293
Kim BS, Lim SW, Li C et al (2005) Ischemia–reperfusion injury activates innate immunity in rat kidneys. Transplantation 79:1370–1377
Shigeoka AA, Holscher TD, King AJ et al (2007) TLR2 is constitutively expressed within the kidney and participates in ischemic renal injury through both MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways. J Immunol 178:6252–6258
Leemans JC, Stokman G, Claessen N et al (2005) Renal-associated TLR2 mediates ischemia/reperfusion injury in the kidney. J Clin Invest 115:2894–2903
Wu H, Chen G, Wyburn KR et al (2007) TLR4 activation mediates kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 117:2847–2859
Rosenberger C, Griethe W, Gruber G et al (2003) Cellular responses to hypoxia after renal segmental infarction. Kidney Int 64:874–886
Matsumoto M, Makino Y, Tanaka T et al (2003) Induction of renoprotective gene expression by cobalt ameliorates ischemic injury of the kidney in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1825–1832
Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S et al (2006) Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1970–1978
Nangaku M, Eckardt KU (2007) Hypoxia and the HIF system in kidney disease. J Mol Med 85:1325–1330
Thornton MA, Winn R, Alpers CE, Zager RA (1989) An evaluation of the neutrophil as a mediator of in vivo renal ischemic–reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 135:509–515
Hayama T, Matsuyama M, Funao K et al (2006) Beneficial effect of neutrophil elastase inhibitor on renal warm ischemia–reperfusion injury in the rat. Transplant Proc 38:2201–2202
Roelofs JJ, Rouschop KM, Leemans JC et al (2006) Tissue-type plasminogen activator modulates inflammatory responses and renal function in ischemia reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:131–140
Mizuno S, Nakamura T (2005) Prevention of neutrophil extravasation by hepatocyte growth factor leads to attenuations of tubular apoptosis and renal dysfunction in mouse ischemic kidneys. Am J Pathol 166:1895–1905
Rouschop KM, Roelofs JJ, Claessen N et al (2005) Protection against renal ischemia reperfusion injury by CD44 disruption. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:2034–2043
De Greef KE, Ysebaert DK, Dauwe S et al (2001) Anti-B7-1 blocks mononuclear cell adherence in vasa recta after ischemia. Kidney Int 60:1415–1427
Jo SK, Sung SA, Cho WY, Go KJ, Kim HK (2006) Macrophages contribute to the initiation of ischaemic acute renal failure in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:1231–1239
Ko GJ, Boo CS, Jo SK, Cho WY, Kim HK (2008) Macrophages contribute to the development of renal fibrosis following ischaemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:842–852
Zhang ZX, Wang S, Huang X et al (2008) NK cells induce apoptosis in tubular epithelial cells and contribute to renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Immunol 181:7489–7498
Ascon DB, Lopez-Briones S, Liu M et al (2006) Phenotypic and functional characterization of kidney-infiltrating lymphocytes in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. J Immunol 177:3380–3387
Li L, Huang L, Sung SS et al (2007) NKT cell activation mediates neutrophil IFN-gamma production and renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Immunol 178:5899–5911
Lee HT, Kim M, Kim N, FTt Billings, D’Agati VD, Emala CW Sr (2007) Isoflurane protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury and modulates leukocyte infiltration in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F713–F722
Burne MJ, Daniels F, El Ghandour A et al (2001) Identification of the CD4(+) T cell as a major pathogenic factor in ischemic acute renal failure. J Clin Invest 108:1283–1290
Day YJ, Huang L, Ye H, Li L, Linden J, Okusa MD (2006) Renal ischemia–reperfusion injury and adenosine 2A receptor-mediated tissue protection: the role of CD4+ T cells and IFN-gamma. J Immunol 176:3108–3114
Yokota N, Burne-Taney M, Racusen L, Rabb H (2003) Contrasting roles for STAT4 and STAT6 signal transduction pathways in murine renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F319–F325
Wang S, Diao H, Guan Q et al (2008) Decreased renal ischemia–reperfusion injury by IL-16 inactivation. Kidney Int 73:318–326
Ascon M, Ascon DB, Liu M et al (2008) Renal ischemia–reperfusion leads to long term infiltration of activated and effector-memory T lymphocytes. Kidney Int 75:526–535
Burne-Taney MJ, Ascon DB, Daniels F, Racusen L, Baldwin W, Rabb H (2003) B cell deficiency confers protection from renal ischemia reperfusion injury. J Immunol 171:3210–3215
Dong X, Swaminathan S, Bachman LA, Croatt AJ, Nath KA, Griffin MD (2007) Resident dendritic cells are the predominant TNF-secreting cell in early renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 71:619–628
Schlichting CL, Schareck WD, Weis M (2006) Renal ischemia–reperfusion injury: new implications of dendritic cell–endothelial cell interactions. Transplant Proc 38:670–673
Loverre A, Capobianco C, Stallone G et al (2007) Ischemia–reperfusion injury-induced abnormal dendritic cell traffic in the transplanted kidney with delayed graft function. Kidney Int 72:994–1003
Thurman JM, Ljubanovic D, Royer PA et al (2006) Altered renal tubular expression of the complement inhibitor Crry permits complement activation after ischemia/reperfusion. J Clin Invest 116:357–368
Thurman JM, Royer PA, Ljubanovic D et al (2006) Treatment with an inhibitory monoclonal antibody to mouse factor B protects mice from induction of apoptosis and renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:707–715
de Vries B, Walter SJ, Peutz-Kootstra CJ, Wolfs TG, van Heurn LW, Buurman WA (2004) The mannose-binding lectin-pathway is involved in complement activation in the course of renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 165:1677–1688
de Vries B, Kohl J, Leclercq WK et al (2003) Complement factor C5a mediates renal ischemia–reperfusion injury independent from neutrophils. J Immunol 170:3883–3889
Zhou W, Farrar CA, Abe K et al (2000) Predominant role for C5b-9 in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest 105:1363–1371
Donnahoo KK, Meng X, Ayala A, Cain MP, Harken AH, Meldrum DR (1999) Early kidney TNF-alpha expression mediates neutrophil infiltration and injury after renal ischemia–reperfusion. Am J Physiol 277:R922–R929
Haq M, Norman J, Saba SR, Ramirez G, Rabb H (1998) Role of IL-1 in renal ischemic reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:614–619
Daemen MA, de Vries B, van’t Veer C, Wolfs TG, Buurman WA (2001) Apoptosis and chemokine induction after renal ischemia–reperfusion. Transplantation 71:1007–1011
Miura M, Fu X, Zhang QW, Remick DG, Fairchild RL (2001) Neutralization of Gro alpha and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 159:2137–2145
Fiorina P, Ansari MJ, Jurewicz M et al (2006) Role of CXC chemokine receptor 3 pathway in renal ischemic injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:716–723
Furuichi K, Gao JL, Murphy PM (2006) Chemokine receptor CX3CR1 regulates renal interstitial fibrosis after ischemia–reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol 169:372–387
Oh DJ, Dursun B, He Z et al (2008) Fractalkine receptor (CX3CR1) inhibition is protective against ischemic acute renal failure in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F264–F271
Deng J, Kohda Y, Chiao H et al (2001) Interleukin-10 inhibits ischemic and cisplatin-induced acute renal injury. Kidney Int 60:2118–2128
Lemos FB, Ijzermans JN, Zondervan PE et al (2003) Differential expression of heme oxygenase-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in cadaveric and living donor kidneys after ischemia–reperfusion. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:3278–3287
Sandovici M, Henning RH, van Goor H, Helfrich W, de Zeeuw D, Deelman LE (2008) Systemic gene therapy with interleukin-13 attenuates renal ischemia–reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 73:1364–1373
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Maria Teresa Gandolfo for the helpful suggestions with the manuscript. HR is supported by the US National Institutes of Health, US National Kidney Foundation, and Talecris Biotech., Inc. grants. BAW is supported by AHA, ROTRF, and Talecris Biotech., Inc. grants. HRJ is supported by the Korea Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, H.R., Ko, G.J., Wasowska, B.A. et al. The interaction between ischemia–reperfusion and immune responses in the kidney. J Mol Med 87, 859–864 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0491-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0491-y