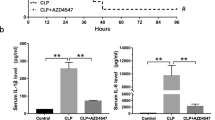
Abstract
Sepsis, a leading cause of death in hospitalized patients, is characterized by lethal systemic inflammatory responses. JAK2 is an essential tyrosine kinase modulating immune responses. However, the implications of JAK2 in infectious disorders remain undetermined. Here, we report that JAK2 inhibitors rescue animals from polymicrobial sepsis in a clinically relevant time frame. JAK2 inhibition with AG490 prevents NF-κB activation, modulates macrophage activation, and restrains the production of inflammatory cytokines. The inhibition of JAK2 blunted TNF production in both macrophages and splenocytes in a concentration-dependent manner. JAK2 inhibition specifically prevents LPS-induced STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation without affecting serine phosphorylation in macrophages. JAK2 inhibitor prevents the activation of the canonical p65RelA/p50NF-κB1 pathway but not the other NF-κB proteins. In vivo, JAK2 inhibition restrains serum TNF levels by modulating TNF production in the lung and the spleen and protects mice from lethal endotoxemia in a concentration-dependent manner. AG490 also inhibits extracellular release of HMGB1 from macrophages and prevents an increase in serum HMGB1 levels during sepsis. JAK2 inhibition started at 24 h after the onset of sepsis rescued the mice from polymicrobial sepsis. Our study is the first experimental evidence that JAK2 inhibitors may provide a pharmacological advantage for the treatment of sepsis in a clinically relevant time frame.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR (2001) Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29:1303–1310
Ulloa L, Brunner M, Ramos L, Deitch EA (2009) Scientific and clinical challenges in sepsis. Curr Pharm Des 15:1918–1935
Ulloa L, Tracey KJ (2005) The "cytokine profile": a code for sepsis. Trends Mol Med 11:56–63
Tracey KJ, Fong Y, Hesse DG, Manogue KR, Lee AT, Kuo GC, Lowry SF, Cerami A (1987) Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature 330:662–664
Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA (2003) Novel strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat Med 9:517–524
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, Manogue KR, Faist E, Abraham E, Andersson J, Andersson U, Molina PE, Abumrad NN, Sama A, Tracey KJ (1999) HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 285:248–251
Ulloa L, Messmer D (2006) High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein: friend and foe. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:189–201
Lotze MT, Tracey KJ (2005) High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat Rev Immunol 5:331–342
Wang H, Liao H, Ochani M, Justiniani M, Lin X, Yang L, Al-Abed Y, Wang H, Metz C, Miller EJ, Tracey KJ, Ulloa L (2004) Cholinergic agonists inhibit HMGB1 release and improve survival in experimental sepsis. Nat Med 10:1216–1221
Ulloa L (2005) The vagus nerve and the nicotinic anti-inflammatory pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:673–684
Huston JM, Ochani M, Rosas-Ballina M, Liao H, Ochani K, Pavlov VA, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ashok M, Czura CJ, Foxwell B, Tracey KJ, Ulloa L (2006) Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J Exp Med 203:1623–1628
de Jonge WJ, van der Zanden EP, The FO, Bijlsma MF, van Westerloo DJ, Bennink RJ, Berthoud HR, Uematsu S, Akira S, van den Wijngaard RM, Boeckxstaens GE (2005) Stimulation of the vagus nerve attenuates macrophage activation by activating the Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 6:844–851
de Jonge WJ, Ulloa L (2007) The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 151:915–929
Meydan N, Grunberger T, Dadi H, Shahar M, Arpaia E, Lapidot Z, Leeder JS, Freedman M, Cohen A, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Roifman CM (1996) Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor. Nature 379:645–648
Ruetten H, Thiemermann C (1997) Effects of tyrphostins and genistein on the circulatory failure and organ dysfunction caused by endotoxin in the rat: a possible role for protein tyrosine kinase. Br J Pharmacol 122:59–70
Lee JY, Sullivan KE (2001) Gamma interferon and lipopolysaccharide interact at the level of transcription to induce tumor necrosis factor alpha expression. Infect Immun 69:2847–2852
Hui L, Yao Y, Wang S, Yu Y, Dong N, Li H, Sheng Z (2009) Inhibition of Janus kinase 2 and signal transduction and activator of transcription protect against cecal ligation and puncture-induced multiple organ damage. J Trauma 66:859–865
Liu H, Yao YM, Yu Y, Dong N, Yin HN, Sheng ZY (2007) Role of Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in regulation of expression and inflammation-promoting activity of high mobility group box protein 1 in rat peritoneal macrophages. Shock 27:55–60
Kim JH, Kim SJ, Lee IS, Lee MS, Uematsu S, Akira S, Oh KI (2009) Bacterial endotoxin induces the release of high mobility group box 1 via the IFN-beta signaling pathway. J Immunol 182:2458–2466
Parrish WR, Rosas-Ballina M, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Ochani M, Ochani K, Yang LH, Hudson L, Lin X, Patel N, Johnson SM, Chavan S, Goldstein RS, Czura CJ, Miller EJ, Al-Abed Y, Tracey KJ, Pavlov VA (2008) Modulation of TNF release by choline requires alpha7 subunit nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated signaling. Mol Med 14:567–574
Rosas-Ballina M, Goldstein RS, Gallowitsch-Puerta M, Yang L, Valdes-Ferrer SI, Patel NB, Chavan S, Al-Abed Y, Yang H, Tracey KJ (2009) The selective alpha7 agonist GTS-21 attenuates cytokine production in human whole blood and human monocytes activated by ligands for TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR9, and RAGE. Mol Med 15:195–202
Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA (2001) Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature 412:641–647
Ghaffari S, Kitidis C, Fleming MD, Neubauer H, Pfeffer K, Lodish HF (2001) Erythropoiesis in the absence of janus-kinase 2: BCR-ABL induces red cell formation in JAK2(-/-) hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 98:2948–2957
Liu H, Ma Y, Cole SM, Zander C, Chen KH, Karras J, Pope RM (2003) Serine phosphorylation of STAT3 is essential for Mcl-1 expression and macrophage survival. Blood 102:344–352
Li Q, Van Antwerp D, Mercurio F, Lee KF, Verma IM (1999) Severe liver degeneration in mice lacking the IkappaB kinase 2 gene. Science 284:321–325
Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT, Ghosh S, Baltimore D (1995) Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature 376:167–170
Doi TS, Marino MW, Takahashi T, Yoshida T, Sakakura T, Old LJ, Obata Y (1999) Absence of tumor necrosis factor rescues RelA-deficient mice from embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2994–2999
Tanaka M, Fuentes ME, Yamaguchi K, Durnin MH, Dalrymple SA, Hardy KL, Goeddel DV (1999) Embryonic lethality, liver degeneration, and impaired NF-kappa B activation in IKK-beta-deficient mice. Immunity 10:421–429
Mantell LL, Parrish WR, Ulloa L (2006) HMGB1 as a therapeutic target for infectious and inflammatory disorders. Shock 25:4–11
Qin S, Wang H, Yuan R, Li H, Ochani M, Ochani K, Rosas-Ballina M, Czura CJ, Huston JM, Miller E, Lin X, Sherry B, Kumar A, Larosa G, Newman W, Tracey KJ, Yang H (2006) Role of HMGB1 in apoptosis-mediated sepsis lethality. J Exp Med 203:1637–1642
Crandall M, Shapiro MB, West MA (2009) Does splenectomy protect against immune-mediated complications in blunt trauma patients? Mol Med 15:263–267
Eskandari MK, Bolgos G, Miller C, Nguyen DT, DeForge LE, Remick DG (1992) Anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody therapy fails to prevent lethality after cecal ligation and puncture or endotoxemia. J Immunol 148:2724–2730
Calandra T, Echtenacher B, Roy DL, Pugin J, Metz CN, Hultner L, Heumann D, Mannel D, Bucala R, Glauser MP (2000) Protection from septic shock by neutralization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Nat Med 6:164–170
Yan JJ, Jung JS, Lee JE, Lee J, Huh SO, Kim HS, Jung KC, Cho JY, Nam JS, Suh HW, Kim YH, Song DK (2004) Therapeutic effects of lysophosphatidylcholine in experimental sepsis. Nat Med 10:161–167
Acknowledgments
L.U. is supported by the faculty program of the Department of Surgery of the New Jersey Medical School and grants from the U.S. Army Medical Research Command [USAMRMC#05308004], the American Heart Association [AHA06352230N], and the NIH [RO1-GM084125].
Conflict of interest
G.P, B. C., and L.U. are applying for patents as inventors on technology related to the topic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peña, G., Cai, B., Deitch, E.A. et al. JAK2 inhibition prevents innate immune responses and rescues animals from sepsis. J Mol Med 88, 851–859 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0628-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-010-0628-z