Abstract
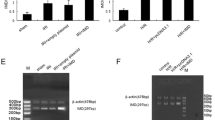
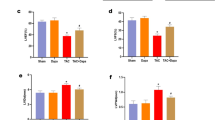
Intermedin (IMD) is a novel member of the calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family. We aimed to explore whether the cardioprotective effect of IMD is mediated by inhibiting myocardial endoplasmic reticulum (sarcoplasmic reticulum) stress (ERS). In vitro, IMD1–53 (10−9, 10−8, and 10−7 mol/l) directly inhibited the upregulation of ERS markers such as glucose-regulated protein 78, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein, and caspase-12 induced by the ERS inducers tunicamycin (Tm, 10 mg/ml) or dithiothreitol (DTT, 2 mmol/l) in cardiac tissue. IMD1–53 also inhibited Tm- or DTT-induced upregulation of cleaved activating transcription factor 6 and 4. These inhibitory effects of IMD1–53 were abolished by the IMD receptor antagonist IMD17–47 (10−6 mol/l) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002 (10 μmol/l). However, preincubation with PD98059 (20 μmol/l), an extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase inhibitor, and H89 (10 μmol/l), a protein kinase A inhibitor, could not block the ERS-inhibiting effects of IMD1–53. Furthermore, in an in vivo model of myocardium ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) in rats, administration of IMD1–53 (20 nmol/kg, intravenously) greatly attenuated ERS and ameliorated myocardium impairment induced by I/R. IMD1–53 could exert its cardioprotective effect by inhibiting myocardial ERS, which might be mediated by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufman RJ (2002) Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest 110:1389–1398
Boyce M, Yuan J (2006) Cellular response to endoplasmic reticulum stress: a matter of life or death. Cell Death Differ 13:363–373
Duan XH, Qi YF, Tang CS (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and cardiovascular diseases. Geriatr Cardiol 6:49–55
Liu XH, Zhang ZY, Sun S, Wu XD (2008) Ischemic postconditioning protects myocardium from ischemia/reperfusion injury through attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Shock 30:422–427
Ma QB, Gao W, Guo YH, Zhao CY, Xue L, Tang CS (2005) Hypoxia/reoxygenation induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocyte. J Peki Univ (health sciences) 37:386–388
Martindale JJ, Fernandez R, Thuerauf D, Whittaker R, Gude N, Sussman MA, Glembotski CC (2006) Endoplasmic reticulum stress gene induction and protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury in the hearts of transgenic mice with a tamoxifen- regulated form of ATF6. Circ Res 98:1186–1193
Qi X, Vallentin A, Churchill E, Mochly-Rosen D (2007) deltaPKC participates in the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced response in cultured cardiac myocytes and ischemic heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:420–428
Shintani-Ishida K, Nakajima M, Uemura K, Yoshida K (2006) Ischemic preconditioning protects cardiomyocytes against ischemic injury by inducing GRP78. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:1600–1605
Roh J, Chang CL, Bhalla A, Klein C, Hsu SY (2004) Intermedin is a calcitonin/calcitonin gene-related peptide family peptide acting through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor/receptor activity-modifying protein receptor complexes. J Biol Chem 279:7264–7274
Takei Y, Inoue K, Ogoshi M, Kawahara T, Bannai H, Miyano S (2004) Identification of novel adrenomedullin in mammals: a potent cardiovascular and renal regulator. FEBS Lett 556:53–58
Bell D, McDermott BJ (2008) Intermedin (adrenomedullin-2): a novel counter-regulatory peptide in the cardiovascular and renal systems. Br J Pharmacol 153:S247–S262
Grossini E, Molinari C, Mary DA, Uberti F, Caimmi PP, Vacca G (2009) Intracoronary intermedin 1–47 augments cardiac perfusion and function in anesthetized pigs: role of calcitonin receptors and {beta}-adrenoreceptor-mediated nitric oxide release. J Appl Physiol 107:1037–1050
Jolly L, March JE, Kemp PA, Bennett T, Gardiner SM (2009) Mechanisms involved in the regional haemodynamic effects of intermedin (adrenomedullin 2) compared with adrenomedullin in conscious rats. Br J Pharmacol 157:1502–1513
Yang JH, Cai Y, Duan XH, Ma CG, Wang X, Tang CS, Qi YF (2009) Intermedin 1–53 inhibits rat cardiac fibroblast activation induced by angiotensin II. Regul Pept 158:19–25
Pearson LJ, Yandle TG, Nicholls MG, Evans JJ (2009) Intermedin (adrenomedullin-2): a potential protective role in human aortic endothelial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 23:97–108
Smith RS Jr, Gao L, Bledsoe G, Chao L, Chao J (2009) Intermedin is a new angiogenic growth factor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H1040–H1047
Bell D, Zhao Y, McCoy FP, Devine A, McDermott BJ (2008) Expression of the counter-regulatory peptide intermedin is augmented in the presence of oxidative stress in hypertrophied cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 21:409–420
Hagiwara M, Bledsoe G, Yang ZR, Smith RS Jr, Chao L, Chao J (2008) Intermedin ameliorates vascular and renal injury by inhibition of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1735–F1743
Pfeil U, Aslam M, Paddenberg R, Quanz K, Chang CL, Park JI, Gries B, Rafiq A, Faulhammer P, Goldenberg A, Papadakis T, Noll T, Hsu SY, Weissmann N, Kummer W (2009) Intermedin/adrenomedullin-2 is a hypoxia-induced endothelial peptide that stabilizes pulmonary microvascular permeability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 297:L837–L845
Jia YX, Yang JH, Pan CS, Geng B, Zhang J, Xiao Y, Zhao J, Gerns H, Yang J, Chang JK et al (2006) Intermedin1-53 protects the heart against isoproterenol-induced ischemic injury in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 549:117–123
Yang JH, Jia YX, Pan CS, Zhao J, Ouyang M, Yang J, Chang JK, Tang CS, Qi YF (2005) Effects of intermedin (1–53) on cardiac function and ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:713–719
Song JQ, Teng X, Cai Y, Tang CS, Qi YF (2009) Activation of Akt/GSK-3beta signaling pathway is involved in intermedin(1–53) protection against myocardial apoptosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Apoptosis 14:1061–1069
Zhang HY, Jiang W, Liu JY, Li Y, Chen CL, Xin HB, Huang DJ (2009) Intermedin is upregulated and has protective roles in a mouse ischemia/reperfusion model. Hypertens Res 32:861–868
Webster KW, Discher DJ, Bishopric NH (1995) Cardioprotection in in vitro model of hypoxic preconditioning. J Mol Cell Cardiol 27:453–458
Teng X, Qi YF, Tang CS (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and heart diseases. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 40:106–110
Zhang GG, Teng X, Liu Y, Cai Y, Zhou YB, Duan XH, Song JQ, Shi Y, Tang CS, Yin XH et al (2009) Inhibition of endoplasm reticulum stress by ghrelin protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat heart. Peptides 30:1109–1116
Glembotski CC (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the heart. Circ Res 101:975–984
Chauhan M, Yallampalli U, Reed L, Yallampalli C (2006) Adrenomedullin 2 antagonist infusion to rats during midgestation causes fetoplacental growth restriction through apoptosis. Biol Reprod 75:940–947
Gibbons C, Dackor R, Dunworth W, Fritz-Six K, Caron KM (2007) Receptor activity-modifying proteins: RAMPing up adrenomedullin signaling. Mol Endocrinol 21:783–796
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Exton JH (2004) Critical role of endogenous Akt/IAPs and MEK1/ERK pathways in counteracting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 279:49420–49429
Mao W, Iwai C, Liu J, Sheu SS, Fu M, Liang CS (2008) Darbepoetin alfa exerts a cardioprotective effect in autoimmune cardiomyopathy via reduction of ER stress and activation of the PI3K/Akt and STAT3 pathways. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45:250–260
Hyoda K, Hosoi T, Horie N, Okuma Y, Ozawa K, Nomura Y (2004) PI3K-Akt inactivation induced CHOP expression in endoplasmic reticulum-stressed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 340:286–290
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Tsuchiya K, Shibata T, Seiwa E (2004) Translocation of Bim to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) mediates ER stress signaling for activation of caspase-12 during ER stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:50375–50381
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND, Hughes PD, Michalak EM, McKimm-Breschkin J, Motoyama N et al (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129:1337–1349
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 30770869, 30871013 and 81170082 to YF Qi) and the State Major Basic Research Development Program of the People’s Republic of China (grant no. 2011CB503904 to YF Qi)
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no competing financial interests to disclose in relation to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, X., Song, J., Zhang, G. et al. Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress by intermedin1–53 protects against myocardial injury through a PI3 kinase–Akt signaling pathway. J Mol Med 89, 1195–1205 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0808-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0808-5