Abstract
Summary
The efficacy and safety of denosumab were evaluated in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Total hip and distal 1/3 radius bone mineral densities (BMDs) were increased, and lumbar spine BMD was increased in magnitude with increasing dose. Bone turnover markers significantly decreased compared with placebo. Denosumab was well tolerated in Japanese subjects.
Introduction
The efficacy and safety of three doses of denosumab were compared with a placebo over 12 months in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
Methods
In this phase 2 multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study, 226 subjects were randomized and 212 subjects received at least 1 dose of investigational product, subcutaneously. All subjects also received daily supplements of at least 600 mg elemental calcium and 400 IU vitamin D from the beginning of screening through 12 months of treatment.
Results
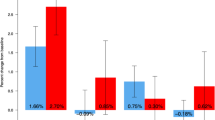
Compared with placebo, denosumab (14, 60, and 100 mg) showed significant increases in percent BMD values of lumbar spine (5.25, 6.27, and 7.00) and total hip (3.90, 3.69, and 4.35) from baseline in 12 months. Distal 1/3 radius BMD was also significantly increased except at the 100-mg dose (1.82, 1.35, and 1.15). Denosumab significantly decreased the serum C-terminal crosslinking telopeptide of type 1 collagen and urinary N-terminal crosslinking telopeptide of type I collagen/urinary creatinine levels in 8 days, and bone alkaline phosphatase in 3 months. No new vertebral fracture was observed on spinal radiographs in either group. The overall incidences of adverse events were similar in the denosumab groups and the placebo group. No subject developed antibodies to denosumab. These results were similar to those obtained in the US phase 2 study.
Conclusions
Denosumab 60 mg could be an effective dose for Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis as was shown in the Caucasian population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy (2001) Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA 285:785–795
Reginster JY, Burlet N (2006) Osteoporosis: a still increasing prevalence. Bone 38(2 suppl 1):S4–S9
Sone T, Fukunaga M (2004) Prevalence of osteoporosis in Japan and the international comparison. Nippon Rinsho 62(Suppl 2):197–200
Rodan GA, Martin TJ (2000) Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science 289:1508–1514
McClung MR, Lewiecki EM, Cohen SB, Bolognese MA, Woodson GC, Moffett AH, Peacock M, Miller PD, Lederman SN, Chesnut CH, Lain D, Kivitz AJ, Holloway DL, Zhang C, Peterson MC, Bekker PJ, AMG 162 Bone Loss Study Group (2006) Denosumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med 354:821–831
Lewiecki EM, Miller PD, McClung MR, Cohen SB, Bolognese MA, Liu Y, Wang A, Siddhanti S, Fitzpatrick LA, AMG 162 Bone Loss Study Group (2007) Two-year treatment with denosumab (AMG 162) in a randomized phase 2 study of postmenopausal women with low BMD. J Bone Miner Res 22:1832–1841
Miller PD, Bolognese MA, Lewiecki EM, McClung MR, Ding B, Austin M, Liu Y, San Martin J, AMG 162 Bone Loss Study Group (2008) Effect of denosumab on bone density and turnover in postmenopausal women with low bone mass after long-term continued, discontinued, and restarting of therapy: a randomized blinded phase 2 clinical trial. Bone 43:222–229
Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, Siris ES, Eastell R, Reid IR, Delmas P, Zoog HB, Austin M, Wang A, Kutilek S, Adami S, Zanchetta J, Libanati C, Siddhanti S, Christiansen C, FREEDOM Trial (2009) Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 361:756–765
Orimo H, Sugioka Y, Fukunaga M, Muto Y, Hotokebuchi T, Gorai I, Nakamura T, Kushida K, Tanaka H, Ikai T, Oh-hashi Y, The Committee of the Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research for Development of Diagnostic Criteria of Osteoporosis (1998) Diagnostic criteria of primary osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab 16:139–150
Orimo H, Hayashi Y, Fukunaga M, Sone T, Fujiwara S, Shiraki M, Kushida K, Miyamoto S, Soen S, Nishimura J, Oh-hashi Y, Hosoi T, Gorai I, Tanaka H, Igai T, Kishimoto H, The Osteoporosis Diagnostic Criteria Review Committee: Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research (2001) Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: year 2000 revision. J Bone Miner Metab 19:331–337
Genant HK, Wu CY, Van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Seeman E, Delmas PD, Hanley DA, Sellmeyer D, Cheung AM, Shane E, Kearns A, Thomas T, Boyd SK, Boutroy S, Bogado C, Majumdar S, Fan M, Libanati C, Zanchetta J (2010) Microarchitectural deterioration of cortical and trabecular bone: differing effects of denosumab and alendronate. J Bone Miner Res 25(8):1886–1894
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by funding from Amgen Inc.
Conflicts of interest
Drs. Nakamura, Matsumoto, Sugimoto, and Shiraki have received consultant/honorarium fees from Amgen Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, T., Matsumoto, T., Sugimoto, T. et al. Dose–response study of denosumab on bone mineral density and bone turnover markers in Japanese postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 23, 1131–1140 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1786-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1786-8