Abstract
Recent studies have provided evidence for a major role of urothelially released ATP acting on a subpopulation of pelvic afferent nerves in mechano-afferent transduction in the bladder. We investigated whether desensitization of capsaicin-sensitive nerve fibres by systemic resiniferatoxin (RTX)-pretreatment can counteract the detrusor over-activity induced by intravesical capsaicin, acetic acid or ATP.
Cystometric investigations were performed on awake female Sprague-Dawley rats before and 24 h after injection of RTX (0.3 mg/kg s.c.) or vehicle. The effects of intravesically instilled ATP (0.1 or 1.0 mM), capsaicin (30 µM) or acetic acid (pH 4.0) were compared with those of intravesical saline.
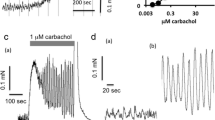
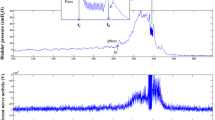
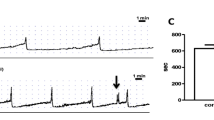
RTX, but not its vehicle, significantly increased threshold pressure, voiding interval, micturition volume and bladder capacity. In the vehicle-pretreated rats, intravesical instillation of capsaicin or acetic acid significantly decreased voiding interval, micturition volume, and bladder capacity. However, in the RTX-pretreated rats, neither capsaicin nor acetic acid affected any parameter. On the other hand, intravesical ATP (0.1 mM) significantly decreased voiding interval and micturition volume in both groups of animals. At 1.0 mM, ATP also increased basal pressure and decreased the pressure threshold for micturition in both groups. The present results support the view that increased extracellular ATP has a role in mechano-afferent transduction in the rat bladder and that ATP-induced facilitation of the micturition reflex is mediated, at least partly, by nerves other than capsaicin-sensitive afferent nerves.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birder LA, Kanai AJ, de Groat WC, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Burke NE, Dineley KE, Watkins S, Reynolds IJ, Caterina MJ (2001) Vanilloid receptor expression suggests a sensory role for urinary bladder epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13396–13401
Birder LA, Nakamura Y, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Barrick S, Kanai AJ, Wang E, Ruiz G, De Groat WC, Apodaca G, Watkins S, Caterina MJ (2002) Altered urinary bladder function in mice lacking the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. Nat Neurosci 5:856–60
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389:816–824
Cockayne DA, Hamilton SG, Zhu QM, Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Novakovic S. Malmberg AB, Cain G, Berson A, Kassotakis L, Hedley L, Lachnit WG, Burnstock G, McMahon SB, Ford APDW (2000) Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behaviour in P2X3-deficient mice. Nature 407:1011–1015
Elneil S, Skepper JN, Kidd EJ, Willamson JG, Ferguson DR (2000) The distribution of P2X1 and P2X3 in the rat and human urinary bladder. Neurol Urodyn 19:462–463
Ferguson DR, Kennedy I, Burton TJ (1997) ATP is released from rabbit urinary bladder epithelial cells by hydrostatic pressure change—a possible sensory mechanism? J Physiol (Lond) 505:503–551
Gamse R, Leeman SE, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1981) Differential effects of capsaicin on the content of somatostatin, substance P, and neurotensin in the nervous system of the rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:140–148
Guo A, Vulchanova L, Wang J, Li X, Elde R (1999) Immunocytochemical localization of the vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1): relationship to neuropeptides, the P2X3 purinoceptor and IB4 binding sites. Eur J Neurosci 11:946–958
Jordt SE, Tominaga M, Julius D (2000) Acid potentiation of the capsaicin receptor determined by a key extracellular site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8134–8139
Malmgren A, Sjogren C, Uvelius B, Mattiasson A, Andersson K-E, Andersson PO (1987) Cystometrical evaluation of bladder instability in rats with infravesical outflow obstruction. J Urol 137:1291
Morrison J, Wen J, Kibble A (1999) Activation of pelvic afferent nerves from the rat bladder during filling. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 201:73–75
Morrison JFB (1998) The activation of bladder wall afferent nerves. Exp Physiol 84:131–136
Pandita RK, Andersson K-E (2002) Intravesical adenosine triphosphate stimulates the micturition reflex in awake, freely moving rats. J Urol 168:1230–1234
Rong W, Spyer KM, Burnstock G (2002) Activation and sensitisation of low and high threshold afferent fibers mediated by P2X receptors in the mouse urinary bladder. J Physiol (Lond) 541:591–600
Vlaskovska M, Kasakov L, Rong W, Bodin P, Bardini M, Cockayne DA, Ford APDW, Burnstock G (2001) P2X3 knockout mice reveal a major sensory role for urothelially released ATP. J Neurosci 21:5670–5677
Vulchanova L, Riedl MS, Shuster SJ, Stone LS, Hargreaves KM, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R (1998) P2X3 is expressed by DRG neurons that terminate in inner laminaII. Eur J Neurosci 10:3470–3478
Waldmann R, Bassilana F, de Weille J, Champigny G, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997a) Molecular cloning of a non-inactivating proton-gated Na+ channel specific for sensory neurons. J Biol Chem 272:20975–20978
Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1997b) A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature 386:173–177
Yiangou Y, Facer P, Ford A, Brady C, Wiseman O, Fowler CJ, Anand P (2001) Capsaicin receptor VR1 and ATP-gated ion channel P2X3 in human urinary bladder. BJU Int 87:774–779
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid 13671641 for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of the Japanese Government and Grant 6837 from the Swedish Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Igawa, Y., Ishizuka, O. et al. Effects of resiniferatoxin desensitization of capsaicin-sensitive afferents on detrusor over-activity induced by intravesical capsaicin, acetic acid or ATP in conscious rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 367, 473–479 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0748-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0748-x