Abstract
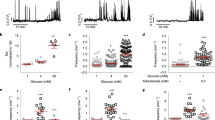
The effect of the novel imidazoline compound 2-[2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-1-(5-methyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-7-yl)-ethyl]-pyridine (NNC77-0020) on stimulus-secretion coupling and hormone secretion was investigated in mouse pancreatic islets and isolated α- and β-cells. In the presence of elevated glucose concentrations NNC77-0020 stimulated insulin secretion concentration dependently (EC50 64 nM) by 200% without affecting the whole-cell K+ current or cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels. Capacitance measurements in single mouse β-cells showed that intracellular application of NNC77-0020 via the recording pipette enhanced Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. This action was dependent on protein kinase C (PKC) and cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) activity and required functional granular ClC-3 Cl− channels. In intact islets NNC77-0020 stimulated glucose-dependent somatostatin secretion, an effect that was also dependent on PKC and cPLA2 activity. NNC77-0020 also inhibited glucagon secretion. In single mouse α-cells this action was not associated with a change in spontaneous electrical activity and resulted from a reduction in the rate of Ca2+-dependent exocytosis. Inhibition of exocytosis by NNC77-0020 was pertussis toxin sensitive and mediated by activation of the protein phosphatase calcineurin. In conclusion, our data suggest that the imidazoline compound NNC77-0020 modulates pancreatic hormone secretion in a complex fashion, comprising glucose-dependent stimulation of insulin and somatostatin secretion and inhibition of glucagon release. These mechanisms of action constitute an ideal basis for the development of novel imidazoline-containing anti-diabetic compounds.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barg S, Renström E, Berggren P-O, Bertorello A, Bokvist K, Braun M, Eliasson L, Holmes WE, Köhler M, Rorsman P, Thévenod F (1999) The stimulatory action of tolbutamide on Ca2+-dependent exocytosis in pancreatic β cells is mediated by a 65-kDa mdr-like P-glucoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5539–5544
Barg S, Galvanovskis J, Göpel SO, Rorsman P, Eliasson L (2000) Tight coupling between electrical activity and exocytosis in mouse glucagon-secreting α-cells. Diabetes 49:1500–1510
Barg S, Huang P, Eliasson L, Nelson DJ, Obermüller S, Rorsman P, Thévenod F, Renström E (2001) Priming of insulin granules for exocytosis by granular Cl− uptake and acidification. J Cell Sci 114:2145–2154
Bokvist K, Olsen HL, Høy M, Gotfredsen CF, Holmes WF, Buschard K, Rorsman P, Gromada J (1999) Characterisation of sulphonylurea and ATP-regulated K+-channels in rat pancreatic A-cells. Pflugers Arch 438:428–436
DeFronzo RA (1992) Pathogenesis of type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus: a balanced overview. Diabetologia 35:389–397
Dunne MJ, Harding EA, Jaggar JH, Squires PE, Liang R, Kane C, James RFL, London NJM (1995) Potassium channels, imidazolines, and insulin-secreting cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 763:242–261
Efanov AM, Zaitsev SV, Mest HJ, Raap A, Appelskog IB, Larsson O, Berggren PO, Efendic S (2001) The novel imidazoline compound BL11282 potentiates glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells in the absence of modulation of KATP channel activity. Diabetes 50:797–802
Efanova IB, Zaitsev SV, Efanov AM, Ostenson C, Raap A, Mest H, Berggren PO, Efendic S (1998) Effects of imidazoline derivative RX871024 on insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin secretion from isolated perfused rat pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 252:162–165
Efendic S, Efanov AM, Breggren PO, Zaitsev SV (2002) Two generations of insulinotropic imidazoline compounds. Diabetes 51 (Suppl):S448–S454
Fuhlendorff J, Rorsman P, Kofod H, Brand CL, Rolin B, MacKay P, Shymko R, Carr RD (1998) Stimulation of insulin release by repaglinide and glibenclamide involves both common and distinct processes. Diabetes 47:345–351
Gerich JE (1977) Somatostatin; its possible role in carbohydrate disposal and absorption in diabetes mellitus. Arch Intern Med 137:659–666
Göpel SO, Kanno T, Barg S, Rorsman P (2000) Patch-clamp characterization of somatostatin-secreting δ-cells in intact mouse pancreatic islets. J Physiol (Lond) 528:497–507
Grynkiewicz B, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Henquin JC (2000) Triggering and amplifying pathways of regulation of insulin secretion by glucose. Diabetes 49:1751–1760
Høy M, Bokvist K, Weng XG, Hansen J, Juhl K, Berggren PO, Buschard K, Gromada J (2001) Phentolamine inhibits exocytosis of glucagon by Gi2 protein-dependent activation of calcineurin in rat pancreatic α-cells. J Biol Chem 276:924–930
Høy M, Olsen HL, Andersen HS, Bokvist K, Buschard K, Hansen J, Jacobsen P, Petersen JS, Rorsman P, Gromada J (2003) Imidazoline NNC77-0074 stimulates insulin secretion and inhibits glucagon release by control of Ca2+-dependent exocytosis in pancreatic α- and β-cells. Eur J Pharmacol 466:213–221
Jakobsen P, Madsen P, Andersen HS (2003) Imidazolines as efficacious glucose-dependent stimulators of insulin secretion. Eur J Med Chem 38:357–362
Jonas JC, Plant TD, Henquin JC (1992) Imidazoline antagonists of α2-adrenoceptors increase insulin release in vitro by inhibiting ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic β-cells. Br J Pharmacol 107:8–14
Juhl K, Høy M, Olsen HL, Bokvist K, Efanov AM, Hoffmann EK, Gromada J (2003) cPLA2α-evoked formation of arachidonic acid and lysophospholipids is required for exocytosis in mouse pancreatic β-cells. Am J Physiol 285: E73–E81
Kameda KY, Ono SE, Koyama I, Abiko Y (1982) Insulin releasing action of 2-[2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imadazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethyl] puridine dihydrochloride sesquihydrate (DG-5128), a new, orally effective hypoglycaemic agent. Acta Endocrinol 99:410–415
Kawazu S, Suzuki M, Watanabe T, Ishii J (1987a) Studies of midaglizole (DG-5128). A new type of oral hypoglycemic drug in healthy subjects. Diabetes 36:216–220
Kawazu S, Suzuki M, Negishi K, Ishii J, Sando H, Katagiri H, Kanazawa Y, Yamanouchi S, Akanuma Y, Kajinumma H, Suzuki K, Watanabe K, Itoh T, Kobayashi T, Kosaka K (1987b) Initial phase II clinical studies on midaglizole (DG-5128). A new hypoglycemic agent. Diabetes 36:221–226
Martell AE, Smith RM (1971) Critical stability constants, Vol. 1 Amino acids; Vol. 2 Amines. Plenum Press, New York
Oh J, Rhee HJ, Kim S-W, Kim SB, You H-J, Kim JH, Na DS (2000) Annexin-I inhibits PMA-induced c-fos SRE activation by suppressing cytosolic phospholipase A2 signal. FEBS Lett 477:244–248
Olsen HL, Nørby PL, Høy M, Spee P, Thams P, Capito K, Petersen JS, Gromada J (2003) Imidazoline NNC77-0074 stimulates Ca2+-evoked exocytosis in INS-1E cells by a phospholipase A2-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:1148–1151
Proks P, Ashcroft FM (1997) Phentolamine block of KATP channels is mediated by Kir 6.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:11716–11720
Unger RH (1985) Glucagon physiology and pathophysiology in the light of new advances. Diabetologia 28:574–578
Wahren J, Efendic S, Luft R, Hagenfeldt L, Björkman O, Felig P (1977) Influence of somatostatin on splanchnic glucose metabolism in postabsorptive and 60-hour fasted humans. J Clin Invest 59:299–307
Wang L, Chen L, Jacob TJC (2000) The role of ClC-3 in volume-activated chloride currents and volume regulation in bovine epithelial cells demonstrated by antisense inhibition. J Physiol (Lond) 524:63–75
Zaitsev SV, Efanov AM, Efanova IB, Larsson O, Ostenson CG, Gold G, Berggren PO, Efendic S (1996) Imidazoline compounds stimulate insulin release by inhibition of KATP channels and interaction with the exocytotic machinery. Diabetes 45:1610–1618
Acknowledgements
We thank Tina Olsen and Berit Gerlach for technical assistance. MH holds a scholarship from the Academy of Technical Sciences and Novo Nordisk, Denmark. HLO holds a scholarship from the Medicon Valley Academy and Novo Nordisk, Denmark
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Høy, M., Olsen, H.L., Bokvist, K. et al. The imidazoline NNC77-0020 affects glucose-dependent insulin, glucagon and somatostatin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 368, 284–293 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0797-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0797-1