Abstract
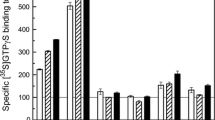
Receptor-mediated guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein (G protein) activation or functional coupling between receptors and G proteins has been investigated by means of agonist-induced [35S]guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate ([35S]GTPγS) binding, especially for the receptor subtypes negatively coupled to adenylyl cyclase through Gi type G proteins. In the present study, 5-HT-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to rat stritatal membranes was pharmacologically characterized in detail with the help of an extensive series of 5-HT receptor ligands. The optimum experimental conditions for the concentrations of GDP, MgCl2 and NaCl in the assay buffer were initially determined, and the standard assay was performed with 20 μM GDP, 5 mM MgCl2 and 100 mM NaCl. The specific [35S]GTPγS binding was stimulated by several compounds that had been shown to be agonists at 5-HT1B/1D receptors. The negative logarithmic values of the concentration eliciting half-maximal effect (pEC50) for these agonists were significantly correlated with their pK i’s reported in the previous study of 5-HT1B receptor binding in rat frontal cortical membranes. The increase in specific [35S]GTPγS binding in response to 1 μM 5-HT was potently inhibited by several 5-HT1B/1D receptor antagonists as well as β-adrenoceptor antagonists such as S(−)-cyanopindolol. On the other hand, 3-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,1-diphenyl-2-propanol HCl (BRL15572), a selective antagonist against human 5-HT1D receptors, was inactive as an antagonist at least up to 1 μM. Additionally, the concentration-response curve for 2-[5-[3-(4-methylsulphonylamino)benzyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]-1H-indol-3-yl]ethanamine (L694247) was shifted rightward in parallel by the addition of S(−)-cyanopindolol at concentrations of 10 and 100 nM, indicative of the competitive inhibitory manner. The specific [35S]GTPγS binding was reduced by 1′-methyl-5-([2′-methyl-4′-(5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]carbonyl)-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrospirospiro(furo[2,3-f]indole-3,4′-piperidine) (SB224289) and methiothepin in a concentration-dependent manner. The inhibitory curve by either compound was shifted to the right by 10 and 100 nM S(−)-cyanopindolol, suggesting that these two drugs behaved as inverse agonists at 5-HT1B receptors in the present functional assay system. 5-HT-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding to rat striatal membranes serves as a simple but useful method of investigating the functional interaction between the native 5-HT1B receptors and their coupled G proteins in this brain region.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Anpirtoline:
-
6-chloro-2[piperidinyl-4-thio]pyridine HCl
- BMY7378:
-
8-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane-7,9-dione 2HCl
- BRL15572:
-
3-[4-(4-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]-1,1-diphenyl-2-propanol HCl
- BRL54443:
-
3-(1-methylpiperidine-4-yl)-1H-indol-5-ol maleate salt
- CGS12066A:
-
7-trifluroromethyl-4(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-pyrrolo-[1,2-a] quinoxaline maleate salt
- CHO:
-
Chinese hamster ovary
- CP93129:
-
1,4-dihydro-3-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-pyridinyl)-5H-pyrrol[3,2-b]pyridin-5-one 2HCl
- CP94253:
-
5-propoxy-3-(1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-4-pyridinyl)-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridine HCl
- 5-CT:
-
5-carboxamidotryptamine maleate
- (±)-DOI:
-
(±)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine HCl
- EC50 :
-
the concentration eliciting half-maximal effect
- G protein:
-
guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein
- GR46611:
-
3-[3-(2-dimethylaminoethyl)-1H-indol-5-yl]-N-(4-methoxybenzyl)acrylamide
- GR55562:
-
3-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]-4-hydroxy-N-[4-(4-pyridinyl)phenyl]benzamide 2HCl
- GR125743:
-
N-[4-methoxy-3-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]-3-methyl-4-(4-pyridyl)-benzamide
- GR127935:
-
N-[4-methoxy-3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)phenyl]-2′-methyl-4′-(5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-1,1′-biphenyl-4-carboxamide HCl
- GTPγS:
-
guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate
- IC50 :
-
the concentration eliciting half-maximal inhibition
- L694247:
-
2-[5-[3-(4-methylsulphonylamino)benzyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]-1H-indol-3-yl]ethanamine
- LSD:
-
lysergic acid diethylamide
- LY278584:
-
1-methyl-N-(8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]-oct-3-yl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide maleate
- mCPP:
-
1-(3-chlorophenyl)piperazine HCl
- 5-MeO-N,N-DMT:
-
5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine
- 5-MeOT:
-
5-methoxytryptamine HCl
- N-methylquipazine:
-
2-[1-(4-methyl)piperazinyl]quinoline dimaleate salt
- N,N-DP-5CT:
-
N,N-dipropyl-5-carboxamidotryptamine maleate
- 8-OH-DPAT:
-
8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin hydrobromide
- PAPP:
-
p-aminophenyl-m-trifluoromethylphenyl piperazine
- pEC50 :
-
the negative logarithmic value of the EC50
- RU24969:
-
5-methoxy-3-(1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-4-pyridinyl)-1H-indole hemisuccinate
- SB224289:
-
1′-methyl-5-([2′-methyl-4′-(5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]carbonyl)-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrospirospiro(furo[2,3-f]indole-3,4(-piperidine)
- TFMPP:
-
N-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazine HCl
- WAY100635:
-
N-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-N-2-pyridinylcyclohexanecarboxamide maleate salt
- WB4101:
-
2-(2,6-dimethoxyphenoxyethyl)aminomethyl-1,4-benzodioxane HCl
References
Audinot V, Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D, Millan MJ (2001) Inverse agonist properties of antipsychotic agents at cloned, human (h) serotonin (5-HT)1B and h5-HT1D receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:410–422
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152
Beer MS, Stanton JA, Bevan Y, Heald A, Reeve AJ, Street LJ, Matassa VG, Hargreaves RJ, Middlemiss DN (1993) L-694,247: a potent 5-HT1D receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol 110:1196–1200
Bonaventure P, Schotte A, Cras P, Leysen JE (1997) Autoradiographic mapping of 5-HT1B- and 5-HT1D receptors in human brain using [3H]alniditan, a new radioligand. Recept Channels 5:225–230
Bouhelal R, Smounya L, Bockaert J (1988) 5-HT1B receptors are negatively coupled with adenylate cyclase in rat substantia nigra. Eur J Pharmacol 151:189–196
Boulenguez P, Peters SL, Mitchell SN, Chauveau J, Gray JA, Joseph MH (1998) Dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens and latent inhibition in the rat following microinjections of a 5-HT1B agonist into the dorsal subiculum: implications for schizophrenia. J Psychopharmacol 12:258–267
Bruinvels AT, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1993) Autoradiographic characterisation and localisation of 5-HT1D compared to 5-HT1B binding sites in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 347:569–582
Clitherow JW, Scopes DIC, Skingle M, Jordan CC, Feniuk W, Campbell IB, Carter MC, Collington EW, Connor HE, Higgins GA, Beattie D, Kelly HA, Mitchell WL, Oxford AW, Wadsworth AH, Tyers MB (1994) Evolution of a novel series of [(N,N-dimethylamino)propyl]- and piperazinylbenzanilides as the first selective 5-HT1D antagonists. J Med Chem 37:2253–2257
Dulawa SC, Gross C, Stark KL, Hen R, Geyer MA (2000) Knockout mice reveal opposite roles for serotonin 1A and 1B receptors in prepulse inhibition. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:650–659
Dupuis DS, Palmier C, Colpaert FC, Pauwels PJ (1998) Autoradiography of serotonin 5-HT1A receptor-activated G proteins in guinea pig brain sections by agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding. J Neurochem 70:1258–1268
Gaster LM, Blaney FE, Davies S, Duckworth DM, Ham P, Jenkins S, Jennings AJ, Joiner GF, King FD, Mulholland KR, Wyman PA, Hagan JJ, Hatcher J, Jones BJ, Middlemiss DN, Price GW, Riley G, Roberts C, Routledge C, Selkirk J, Slade PD (1998) The selective 5-HT1B receptor inverse agonist 1′-methyl-5-[[2′-methyl-4′-(5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)biphenyl-4-yl]carbonyl]-2,3,6,7-tetrahydrospiro[furo[2,3-f]indole-3,4′-piperidine] (SB-224289) potently blocks terminal 5-HT autoreceptor function both in vitro and in vivo. J Med Chem 41:1218–1235
Gerhardt CC, van Heerikhuizen H (1997) Functional characteristics of heterologously expressed 5-HT receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 334:1–23
Geyer MA (1996) Serotonergic functions in arousal and motor activity. Behav Brain Res 73:31–35
Hamblin MW, McGuffin RW, Metcalf MA, Dorsa DM, Merchant KM (1992) Distinct 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D serotonin receptors in rat: structural and pharmacological comparison of the two cloned receptors. Mol Cell Neurosci 3:578–587
Harrison C, Traynor JR (2003) The [35S]GTPγS binding assay: approaches and applications in pharmacology. Life Sci 74:489–508
Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, Hartig PR, Martin GR, Mylecharane EJ, Saxena FR, Humphrey PA (1994) International union of pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Pharamcol Rev 46:157–203
Kennett GA, Bright F, Trail B, Baxter GS, Blackburn TP (1996) Effects of the 5-HT2B receptor agonist, BW723C86, on three rat models of anxiety. Br J Pharmacol 117:1443–1448
Kennett GA, Ainsworth K, Trail B, Blackburn TP (1997) BW723C86, a 5-HT2B receptor agonist, causes hyperphagia and reduced grooming in rats. Neuropharmacology 36:233–239
Koe BK, Nielsen JA, Macor JE, Heym J (1992) Biochemical and behavioral studies of the 5-HT1B receptor agonist, CP-94,253. Drug Develop Res 26:241–250
Lazareno S, Birdsall NJM (1993) Estimation of antagonist K b from inhibition curves in functional experiments: alternatives to the Cheng-Prusoff equation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:237–239
MacLean MR, Clayton RA, Templeton AGB, Morecroft I (1996) Evidence for 5-HT1-like receptor-mediated vasoconstriction in human pulmonary artery. Br J Pharmacol 119:277–282
Massot O, Rousselle J-C, Fillion M-P, Januel D, Plantefol M, Fillion G (1999) 5-HT1B receptors: a novel target for lithium. Possible involvement in mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:530–541
Meneses A (1999) 5-HT system and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:1111–1125
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Audinot V, Dekeyne A, Newman-Tancredi A (1999) Inverse agonists and serotonergic transmission: from recombinant, human serotonin (5-HT)1B receptors to G-protein coupling and function in corticolimbic structures in vivo. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:61S–67S
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Lochon S, Touzard M, Aubry S, Audinot AV (2002) Specific labelling of serotonin 5-HT1B receptors in rat frontal cortex with the novel, phenylpiperazine derivative, [3H]GR125,743. A pharmacological characterization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:589–598
Mize AL, Alper RH (1999) Serotonin 5-HT1B/1D agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in rat and guinea pig striatal membranes. Brain Res 836:229–236
Moret C, Briley M (2000) The possible role of 5-HT1B/D receptors in psychiatric disorders and their potential as a target for therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 404:1–12
Neumaier JF, Szot P, Peskind ER, Dorsa DM, Hamblin MW (1996) Serotonergic lesioning differentially affects presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1B receptor mRNA levels in rat brain. Brain Res 722:50–58
Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Moreira C, Verrièle L, Millan MJ (2000) Inverse agonism and constitutive activity as functional correlates of serotonin h5-HT1B receptor/G-protein stoichiometry. Mol Pharmacol 58:1042–1049
Odagaki Y, Fuxe K (1995) 5-HT1A receptor-mediated activation of high-affinity GTPase in rat hippocampal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 288:385–388
Odagaki Y, Fuxe K (1997) Agonist-induced high-affinity GTP hydrolysis as an index of receptor-mediated G protein activation in mammalian brain membranes. In: Challis RAJ (ed) Receptor Signal Transduction Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 83. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 133–141
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R (2005a) Detailed pharmacological characterization of 5-HT1A-receptor-mediated [35S]GTPγS binding in rat hippocampal membranes. J Pharmacol Sci 98:66–76 (Erratum; J Pharmacol Sci 99: 190, 2005)
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R (2005b) 5-HT1A receptor-mediated G protein activation assessed by [35S]GTPγS binding in rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 521:49–58
Odagaki Y, Toyoshima R, Yamauchi (2005) Trazodone and its active metabolite m-chlorophenylpiperazine as partial agonists at 5-HT1A receptors assessed by [35S]GTPγS binding. J Psychopharmacol 19:235–241
Pauwels PJ, Palmier C (1994) Differential functional activity of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor ligands and beta adrenergic receptor antagonists at 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor sites in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts and opossum renal epithelial cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:938–945
Pauwels PJ, Tardif S, Palmier C, Wurch T, Colpaert FC (1997a) How efficacious are 5-HT1B/D receptor ligands: an answer from GTPγS binding studied with stably transfected C6-glioma cell lines. Neuropharmacology 36:499–512
Pauwels PJ, Tardif S, Wurch T, Colpaert C (1997b) Stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding by 5-HT1A receptor agonists in recombinant cell lines. Modulation of apparent efficacy by G-protein activation state. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 356:551–561
Price GW, Burton MJ, Collin LJ, Duckworth M, Gaster L, Göthert M, Jones BJ, Roberts C, Watson JM, Middlemiss DN (1997) SB-216641 and BRL-15572 — compounds to pharmacologically discriminate h5-HT1B and h5-HT1D receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 356:312–320
Sari Y, Miquel M-C, Brisorgueil M-J, Ruiz G, Doucet E, Hamon M, VergéVerrièle D (1999) Cellular and subcellular localization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors in the rat central nervous system: immunocytochemical, autoradiographic and lesion studies. Neuroscience 88:899–915
Saudou F, Amara DA, Dierich A, LeMeur M, Ramboz S, Segu L, Buhot M-C, Hen R (1994) Enhanced aggressive behavior in mice lacking 5-HT1B receptor. Science 265:1875–1878
Schlicker E, Werner U, Hamon M, Gozlan H, Nickel B, Szelenyi I, Göthert M (1992) Anpirtoline, a novel, highly potent 5-HT1B receptor agonist with antinocicetive/antidepressant-like actions in rodents. Br J Pharmacol 105:732–738
Schoeffter P, Waeber C, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1988) The 5-hydroxytryptamine 5-HT1D receptor subtype is negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase in calf substantia nigra. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 337:602–608
Seifert R, Wenzel-Seifert K (2002) Constitutive activity of G-protein-coupled receptors: cause of disease and common property of wild-type receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 366:381–416
Shepherd SL, Williamson DJ, Beer MS, Hill RG, Hargreaves RJ (1997) Differential effects of 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonists on neurogenic dural plasma extravasation and vasodilation in anaesthetized rats. Neuropharmacology 36:525–533
Skingle M, Higgins GA, Feniuk W (1994) Stimulation of central 5-HT1D receptors causes hypothermia in the guinea-pig. J Psychopharmacol 8:14–21
Skingle M, Beattie DT, Scopes DIC, Starkey SJ, Conner HE, Feniuk W, Tyers MB (1996) GR127935: a potent and selective 5-HT1D receptor antagonist. Behav Brain Res 73:157–161
Sóvágó J, Dupuis DS, Gulyás B, Hall H (2001) An overview on functional receptor autoradiography using [35S]GTPγS. Brain Res Rev 38:149–164
Waeber C, Moskowitz HA (1997) 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A and 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptors stimulate [35S]guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate binding to rodent brain sections as visualized by in vitro autoradiography. Mol Pharmacol 52:623–631
Walsh DM, Beattie DT, Connor HE (1995) The activity of 5-HT1D receptor ligands at cloned human \({\text{5 - HT}}_{{{\text{1D}}\alpha }}\) and \({\text{5 - HT}}_{{{\text{1D $\beta $ }}}}\) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 287:79–84
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Masakazu Kinoshita for his technical assistance. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (No. 13671030) (to Y.O.) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odagaki, Y., Toyoshima, R. 5-HT-stimulated [35S]guanosine-5′-O-(3-thio)triphosphate binding as an assay for functional activation of G proteins coupled with 5-HT1B receptors in rat striatal membranes. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 335–345 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0041-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-006-0041-x