Abstract
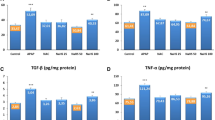
Nitric oxide synthesized from inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) plays role in acetaminophen (APAP)-induced liver damage. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of iNOS inhibitor S-methylisothiourea (SMT) in APAP-induced hepatotoxicity in rats (1 g/kg, i.p.). SMT was (10, 30, and 100 mg/kg; i.p.) given 30 min before and 3 h after APAP administration. At 6 and 24 h, blood was collected to measure alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), and nitrate plus nitrite (NOx) levels in serum. At 48 h, animals were sacrificed, and blood and liver tissues were collected for biochemical estimation. SMT reduced significantly the serum ALT, AST, and NOx levels at 24 and 48 h and liver NOx levels at 48 h as compared with APAP-treated control. The amount of peroxynitrite measured by rhodamine assay was significantly reduced by SMT, as compared with APAP-treated control group. SMT treatment (30 mg/kg) has significantly reduced the lipid peroxidation and protein carbonyl levels, increased SOD and catalase, and reduced glutathione and total thiol levels significantly as compared with APAP-treated control. SMT 30 mg/kg dose has protected animals from APAP-induced hypotension and reduced iNOS gene expression. Hepatocytes were isolated from animals, and effect of SMT on apoptosis, MTP, and ROS generation was studied, and their increased value in APAP intoxicated group was found to be significantly decreased by SMT (30 mg/kg) at 24 and 48 h. In conclusion, nitric oxide produced from iNOS plays important role in toxicity at late hours (24 to 48 h), and SMT inhibits iNOS and reduces oxidative and nitrosative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Zaher AO, Abdel-Rahman MM, Hafez MM, Omran FM (2007) Role of nitric oxide and reduced glutathione in the protective effects of aminoguanidine, gadolinium chloride and oleanolic acid against acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal damage. Toxicol 234:124–134
Ajith TA, Hema U, Aswathy MS (2007) Zingiber officinale Roscoe prevents acetaminophen-induced acute hepatotoxicity by enhancing hepatic antioxidant status. Food Chem Toxicol 45:2267–2272
Aranow JS, Zhuang J, Wang H, Larkin V, Smith M, Fink MP (1996) A selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase prolongs survival in a rat model of bacterial peritonitis: comparison with two nonselective strategies. Shock 5:116–121
Arkovitz MS, Wispe JR, Garcia VF, Szabo C (1996) Selective inhibition of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase prevents pulmonary transvascular flux during acute endotoxemia. J Prd Swg 31:1009–1015
Baggiolini M, Wymann MP (1990) Turning on the respiratory burst. Trends Biochem Sci 15:69–72
Bergemeyer HU (1983) Methods of enzymatic analysis (Berg Meyer, H. U., Ed.) 3rd edn., New York, NY: Academic Press. pp 165-166
Bourdi M, Masubuchi Y, Reilly TP, Amouzadeh HR, Martin JL, George JW, Shah AG (2002) Protection against acetaminophen-induced liver injury and lethality by interleukin 10: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Hepatol 35:289–298
Bus JS, Aust SD, Gibson JE (1976) Paraquat toxicity: proposed mechanism of action involving lipid peroxidation. Environ Health Pers 16:139–146
Castedo M, Ferri K, Roumier T, Me’tivier D, Zamzami N, Kroemer G (2002) Quantitation of mitochondrial alterations associated with apoptosis. J Immunol Meth 265:39–47
Chance B, Stein GD, Roughton RJ (1952) The mechanism of catalase action 1—steady state analysis. Arch Biochem Biophys 37:301–309
Chen C, Krausz KW, Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ (2008) Identification of novel toxicity-associated metabolites by metabolomics and mass isotopomer analysis of acetaminophen metabolism in wild-type and Cyp2e1-null mice. J Biol Chem 283:4543–4559
Chen SJ, Li SY, Shih CC, Liao MH, Wu CC (2010) NO contributes to abnormal vascular calcium regulation and reactivity induced by peritonitis-associated septic shock in rats. Shock 33:473–478
Cigremis Y, Turel H, Adiguzel K, Akgoz M, Kart A, Karaman M, Ozen H (2009) The effects of acute acetaminophen toxicity on hepatic mRNA expression of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, and levels of peroxynitrite, nitric oxide, reduced glutathione, and malondialdehyde in rabbit. Mol Cell Biochem 323:31–38
Dormandy TL (1980) An APAProach to free radicals in medicine and biology. Acta Physiol Scand 492:153–168
Fiorucci S, Antonelli E, Mencarelli A, Palazzetti B, Alvarez-Miller L, Muscara M, del Soldato P (2002) A NO-releasing derivative of acetaminophen spares the liver by acting at several checkpoints in the Fas pathway. Br J Pharmacol 135:589–599
Futter LE, Al-Swayeh OA, Moore PK (2001) A comparison of the effect of nitroparacetamol and paracetamol on liver injury. Br J Pharmacol 132:10–12
Gardner CR, Heck DE, Yang CS, Thomas PE, Zhang XJ, DeGeorge GL, Laskin JD, Laskin DL (1998) Role of nitric oxide in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat. Hepatol 27:748–754
Gardner CR, Laskin JD, Dambach DM, Sacco M, Durham SK, Bruno MK, Cohen SD, Gordon MK, Gerecke DR, Zhou P, Laskin DL (2002) Reduced hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase: potential role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10. Toxicol APAPl Pharmacol 184:27–36
Graham GG, Scott KF, Day RO (2005) Tolerability of paracetamol. Drug Safety 28:227–240
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Hinson JA, Bucci TJ, Irwin LK, Michael SL, Mayeux PR (2002) Effect of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Nitric Oxide 6:160–167
Hinson JA, Reid AB, McCullough SS, James LP (2004) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: role of metabolic activation, reactive oxygen/nitrogen species, and mitochondrial permeability transition. Drug Metab Rev 36:805–822
Ito Y, Abril ER, Bethea NW, McCuskey RS (2004) Role of nitric oxide in hepatic microvascular injury elicited by acetaminophen in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G60–G67
Jaeschke H, Knight TR, Bajt ML (2003) The role of oxidant stress and reactive nitrogen species in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 144:279–288
James LP, McCullough SS, Lamps LW, Hinson JA (2003) Effect of N-acetylcysteine on acetaminophen toxicity in mice: relationship to reactive nitrogen and cytokine formation. Toxicol Sci 75:458–467
Jensen EV (1959) Sulfhydryl–disulfide interchanges. Science 130:1319–1323
Julou-Schaeffer G, Gray GA, Fleming I, Parratt JR, Stoclet JC (1990) Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves the l-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol 259:H1038–H1043
Kamanaka Y, Kawabatab A, Matsuyaa H, Tagaa C, Sekiguchib F, Kawao N (2003) Effect of a potent iNOS inhibitor (ONO-1714) on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in the rat. Life Sci 74:793–802
Kamiyama T, Sato C, Liu J, Tajiri K, Miyakawa H, Marumo F (1993) Role of lipid peroxidation in acetaminopheninduced hepatotoxicity: comparison with carbon tetrachloride. Toxicol Lett 66:7–12
Kaplowitz N (2000) Mechanism of liver cell injury. J Hepatol 32:39–47
Kaplowitz N (2004) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: what do we know, what don’t we know, and what do we do next? Hepatology 40:23–26
Kim PKM, Billiar TR (2000) Give me iNOS or give me death. Hepatol 34:436–437
Knight TR, Ho YS, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2002) Peroxynitrite is a critical mediator of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in murine livers: protection by glutathione. J Pharmacol Exp Therap 303:468–475
Knight TR, Fariss MW, Farhood A, Jaeschke H (2003) Role of lipid peroxidation as a mechanism of liver injury after acetaminophen overdose in mice. Toxicol Sci 76:229–236
Kon K, Kim JS, Jaeschke H, Lemasters JJ (2004) Mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced necrosis and apoptosis of cultured mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology 40:1170–1179
Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, Davern TJ, Lalani E, Hynan LS, Reisch JS, Schiodt FV, Ostapowicz G, Shakil AO, Lee WM (2005) Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology 42:1364–1372
Laskin JD, Heck DE, Gardner CR, Laskin D (2001) Prooxidant and antioxidant functions of nitric oxide in liver toxicity. Antioxid Redox Signal 3:261–271
Leung TM, George LT, Emily CL, Thomas YH, Lau ML, Amin AN (2008) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase is a critical factor in experimental liver fibrosis. Int J Exp Path 89:241–250
Li C, Liu J, Saavedra JE, Keefer LK, Waalkes MP (2003) The nitric oxide donor, V-PYRRO/NO, protects against acetaminophen-induced nephrototoxicity in mice. Toxicol 189:173–180
Lin CC, Shieh DE, Yen MH (1997) Hepatoprotective effect of the fractions of Ban-zhi-lian on experiment liver injuries in rat. J Ethnopharmacol 56:193–200
Liu J, Li C, Waalkes MP, Clark J, Myers P, Saavedra JE, Keefer LK (2003) The nitric oxide donor, V-PYRRO/NO, protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Hepatology 37:324–333
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔct methods. Methods 25:402–408
Madesh M, Balasubramanium KA (1998) Microtitre plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MMT reduction by superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys 35:184–188
Masubuchi Y, Suda C, Horie T (2005) Involvement of mitochondrial permeability transition in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J Hepatol 42:110–116
Mc Crod JM, Keele BB, Fridovich I (1976) An enzyme based theory of obligate anaerobiosis, the physiological functions of superoxide dismutase. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 68:1024–1032
Michael SL, Mayeux PR, Bucci TJ, Warbritton AR, Irwin LK, Pumford NR, Hinson JA (2001) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase activity. Nitric Oxide 5:432–441
Mitchell JR, Corcoran GB, Smith CV, Hughes H, Lauterburg BH (1981) Alkylation and peroxidation injury from chemically reactive metabolites. Adv Exp Med Biol 136:199–223
Mladenovic D, Radosavljevic T, Ninkovic M, Vucevic D, Jesic-Vukicevic R, Todorovic V (2009) Liver antioxidant capacity in the early phase of acute paracetamol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 47:866–870
Myhre O, Andersen JM, Aarnes H, Fonnum F (2003) Evaluation of the probes 2, 7-dichlorofluorescin diacetate, luminol and lucigenin as indicators of reactive species formation. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1575–1582
Neil W, Kooy JA, Royall HS, Joseph SB (1994) Peroxynitrite mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine123. Free Radical Biol Med 16:149–156
Nicotera P, Rundgren M, Porubek DJ, Cotgreave I, Moldeus P, Orrenius S, Nelson SD (1989) On the role of Ca2+ in the toxicity of alkylating and oxidizing quinone imines in isolated hepatocytes. Chem Res Toxicol 2:46–50
Nieminen AL, Gores GJ, Bond JM, Imberti R, Herman B, Lemasters JJ (1992) A novel cytotoxicity screening assay using a multiwell fluorescence scanner. Toxicol APAPl Pharmacol 115:147–155
Numata M, Shunsuke S, Naoki M, Akira M, Yoji N, Satoshi I, Takeshi K, Takao O (1998) Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury in dogs. J Immunol 160:3031–3037
Raghuramulu N, Nair KM, Kalyanasundaram S (2003) A manual of laboratory techniques, National Institutes of Nutrition, Hyderabad, India
Recknagel RO, Glende EA, Dolak JA, Waller RL (1989) Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol Ther 43:139–154
Reid AB, Kurten RC, McCullough SS, Brock RW, Hinson JA (2005) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity: role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial permeability transition in freshly isolated mouse hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:509–516
Saito C, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H (2010) C-jun N-terminal kinase modulates oxidant stress and peroxynitrite formation independent of inducible nitric oxide synthase in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol APAPl Pharmacol 246:8–17
Saran M, Michel C, Bors W (1990) Implications for the action of endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF). Free Radic Res Commun 10:221–226
Sastry KVH, Moudgal RP, Mohan J, Tyagi JS, Rao GS (2002) Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper–cadmium alloy. Analyt Biochem 306:79–82
Searle AJ, Wilson RJ (1980) Glutathione peroxidase: effect of superoxide, hydroxyl and bromine free radicals on enzymic activity. Int J Radi Biol 37:213–219
Sedlak J, Lindsay S (1986) Estimation of total, protein-bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. J Biochem Biophys Methods 93:259–267
Shafiq-ur-rehman S (1984) Lead-induced lipid peroxidation in brain. Toxicol Lett 21:333–337
Stoclet JC, Martnez MC, Ohlmann P, Chasserot S, Schott C, Kleschyov AL, Schneider F, Andriantsitohaina R (1999) Induction of nitric oxide synthase and dual effects of nitric oxide and cycloxygenase products in regulation of arterial contraction in human septic shock. Circulation 100:107–112
Szabo C, Southan GJ, Thiemerrnann C (1994) Beneficial effects and improved survival in rodent models of septic shock with S-methylisothiourea sulfate, a potent and selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:12472–12476
Szabo C, Salzman AL, Ischiropoulos H (1995) Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123 occurs in early stages of endotoxic and hemorrhagic shock and ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB Lett 372:229–232
Terneus MV, Kiningham KK, Carpenter AB, Suilivan SB, Valentovic MA (2007) Comparison of S-adenosyl-l-methionine and N-acetylcystine protective effects on acetaminophen hepatic toxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 320:99–107
Terneus MV, Brown JM, Carpenter AB, Valentovic MA (2008) Comparison of S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAMe) and N-acetylcystine protective effects on hepatic damage when administered after acetaminophen overdose. Toxicology 244:25–34
Tirmenstein MA, Nelson SD (1989) Subcellular binding and effects on calcium homeostasis produced by acetaminophen and a nonhepatotoxic regioisomer, 3-hydroxyacetanilide, in mouse liver. J Biol Chem 264:9814–9819
Tsokos KJ (1989) Evidence in vivo for elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ in the liver after diquat, acetaminophen, and CCl4. Biochem Pharmacol 38:3061–3065
Vos TA, Gouw AS, Klok PA, Havinga R, Van GH, Huitema S, Roelofsen H, Kuipers F, Jansen PL, Moshage H (1997) Differential effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on endotoxin-induced liver damage in rats. Gastroenterology 113:1323–1333
Wang JF, Jerrels TR, Spitzer JJ (1996) Decreased production of reactive oxygen intermediates is an early event during in vitro apoptosis of rat thymocytes. Free Rad Biol Med 20:533–542
Winterbourn CC, Buss IH, Chan TP, Plank LD, Clark MA, Windsor JA (2000) Protein carbonyl measurements show evidence of early oxidative stress in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 28:143–149
Wohaieb SA, Godin DV (1987) Alterations in free radical tissue-defense mechanisms in streptozotocin diabetes in rats: effect of insulin treatment. Diabetes 36:1014–1022
Yamamoto T, Tomizawa K, Fujikawa M, Sato Y, Yamada H, Horii I (2007) Evaluation of human hepatocyte chimeric mice as a model for toxicological investigation using panomic APAProaches—effect of acetaminophen on the expression profiles of proteins and endogenous metabolites in liver, plasma and urine. J Toxicol Sci 32:205–215
Yaroshenko T, Corda M (2006) Role of nitric oxide in chemically-induced hepatotoxicity. Annales Universitis Marie Curie-Sklodowska, Lubin-Polonia 19:1–28
Zingarelli B, Hake PW, Yang Z, O’Connor M, Denenberg A, Wong HR (2002) Absence of inducible nitric oxide synthase modulates early reperfusion-induced NF-kB and AP-1 activation and enhances myocardial damage. FASEB J 16:327–342
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
More, A.S., Kumari, R.R., Gupta, G. et al. Effect of S-methylisothiourea in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 385, 1127–1139 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0789-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0789-0