Abstract
Rationale
Tolerance and dependence can develop during chronic benzodiazepine treatment; however, cross tolerance and cross dependence to positive modulators acting at other sites on GABAA receptors might not occur.
Objectives
The current study evaluated changes in sensitivity to positive GABAA modulators during chronic treatment with the benzodiazepine flunitrazepam to determine whether cross tolerance and cross dependence varied as a function of site of action.
Methods
Eight rats responded under a fixed ratio 20 schedule of food presentation. Dose–effect curves were determined before, during and after chronic treatment with one or two daily injections of 1 mg/kg of flunitrazepam.
Results
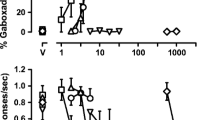
Prior to chronic treatment, benzodiazepines (flunitrazepam, midazolam), a barbiturate (pentobarbital), a neuroactive steroid (pregnanolone), and drugs with primary mechanisms of action at receptors other than GABAA receptors (morphine, ketamine) dose-dependently decreased responding. Twice daily treatment with flunitrazepam produced 9.5- and 23-fold shifts to the right in the flunitrazepam and midazolam dose–effect curves, respectively. In contrast, dose–effect curves for other drugs either were not changed or were shifted less than or equal to fourfold to the right.
Conclusions
Decreased sensitivity to benzodiazepines and not to a barbiturate or a neuroactive steroid during chronic flunitrazepam treatment indicates that tolerance and cross tolerance developed only to benzodiazepines. Despite similar acute behavioral effects among positive GABAA modulators, the differential development of cross tolerance suggests that adaptations at GABAA receptors produced by chronic benzodiazepine treatment differentially affect positive modulators depending on their site of action; such differences might be exploited to benefit patients treated daily with positive GABAA modulators.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan AM, Harris RA (1986) Anesthetic and convulsant barbiturates alter gamma-aminobutyric acid-stimulated chloride flux across brain membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:763–768
Ator NA, Weerts EM, Kaminski BJ, Kautz MA, Griffiths RR (2000) Zaleplon and triazolam physical dependence assessed across increasing doses under a once-daily dosing regimen in baboons. Drug Alcohol Depend 61:69–84
Bonavita CD, Bisagno V, Bonelli CG, Acosta GB, Rubio MC, Wikinski SI (2002) Tolerance to the sedative effect of lorazepam correlates with a diminution in cortical release and affinity for glutamate. Neuropharmacology 42:619–625
Bonavita C, Ferrero A, Cereseto M, Velardez M, Rubio M, Wikinski S (2003) Adaptive changes in the rat hippocampal glutamatergic neurotransmission are observed during long-term treatment with lorazepam. Psychopharmacology 166:163–167
Cesare DA, McKearney JW (1980) Tolerance to suppressive effects of chlordiazepoxide on operant behavior: lack of cross tolerance to pentobarbital. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:545–548
Engel SR, Purdy RH, Grant KA (2001) Characterization of discriminative stimulus effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:489–495
Friedman LK, Gibbs TT, Farb DH (1996) γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor regulation: heterologous uncoupling of modulatory site interactions induced by chronic steroid, barbiturate, benzodiazepine, or GABA treatment in culture. Brain Res 707:100–109
Gasior M, Ungard JT, Beekman M, Carter RB, Witkin JM (2000) Acute and chronic effects of the synthetic neuroactive steroid, ganaxolone, against the convulsive and lethal effects of pentylenetetrazol in seizure-kindled mice: comparison with diazepam and valproate. Neuropharmacology 39:1184–1196
Gerak LR, France CP (1997a) Changes in sensitivity to the rate-decreasing effects of opioids in pigeons treated acutely or chronically with l-alpha-acetylmethadol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:799–809
Gerak LR, France CP (1997b) Repeated administration of flumazenil does not alter its potency in modifying schedule-controlled behavior in chlordiazepoxide-treated rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 131:64–70
Holt RA, Bateson AN, Martin IL (1996) Chronic treatment with diazepam or abecarnil differently affects the expression of GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat cortex. Neuropharmacology 35:1457–1463
Hu XJ, Ticku MK (1994a) Chronic benzodiazepine agonist treatment produces functional uncoupling of the γ-aminobutyric acid-benzodiazepine receptor ionophore complex in cortical neurons. Mol Pharmacol 45:618–625
Hu XJ, Ticku MK (1994b) Chronic flurazepam treatment produces decreased efficacy of the benzodiazepine ligands and pentobarbital with γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors in cortical neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:485–490
Izzo E, Auta J, Impagnatiello F, Pesold C, Guidotti A, Costa E (2001) Glutamic acid decarboxylase and glutamate receptor changes during tolerance and dependence to benzodiazepines. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:3483–3488
Kaminski BJ, Sannerud CA, Weerts EM, Lamb RJ, Griffiths RR (2003) Physical dependence in baboons chronically treated with low and high doses of diazepam. Behav Pharmacol 14:331–342
Majewska MD, Harrison NL, Schwartz RD, Barker JL, Paul SM (1986) Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232:1004–1007
McMahon LR, France CP (2002) Daily treatment with diazepam differentially modifies sensitivity to the effects of γ-aminobutyric acidA modulators on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:1017–1025
McMahon LR, Javors MA, France CP (2007) Changes in relative potency among positive GABAA receptor modulators upon discontinuation of chronic benzodiazepine treatment in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 192:135–145
McMillan DE (1992) Effects of drugs on behavior before and during chronic diazepam administration. Eur J Pharmacol 215:145–152
McMillan DE, Leander JD (1978) Chronic chlordiazepoxide and pentobarbital interactions on punished and unpunished behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:515–520
Obata T, Morelli M, Concas A, Serra M, Yamamura HI (1988) Modulation of GABA-stimulated chloride influx into membrane vesicles from rat cerebral cortex by benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) Chloride channels and their modulation by neurotransmitters and drugs. Raven, New York, pp 175–187
Perez MF, Salmiron R, Ramirez OA (2003) NMDA-NR1 and -NR2B subunits mRNA expression in the hippocampus of rats tolerant to diazepam. Behav Brain Res 144:119–124
Sannerud CA, Marley RJ, Serdikoff SL, Alastra AJ, Cohen C, Goldberg SR (1993) Tolerance to the behavioral effects of chlordiazepoxide: pharmacological and biochemical selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:1311–1320
Van Sickle BJ, Cox AS, Schak K, Greenfield LJ Jr, Tietz EI (2002) Chronic benzodiazepine administration alters hippocampal CA1 neuron excitability: NMDA receptor function and expression. Neuropharmacology 43:595–606
Vanover KE, Suruki M, Robledo S, Huber M, Wieland S, Lan NC, Gee KW, Wood PL, Carter RB (1999) Positive allosteric modulators of the GABA(A) receptor: differential interaction of benzodiazepines and neuroactive steroids with ethanol. Psychopharmacology 141:77–82
Wieland S, Belluzzi J, Hawkinson JE, Hogenkamp D, Upasani R, Stein L, Wood PL, Gee KW, Lan NC (1997) Anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity of a synthetic neuroactive steroid Co 3–0593. Psychopharmacology 134:46–54
Acknowledgments
The author thanks R. Lopez, O. Dominguez, J. Kite, and D. Mojica for their excellent technical assistance.
Animals used in these studies were maintained in accordance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, and guidelines of the Committee on Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council [Department of Health, Education and Welfare, publication No. (NIH) 85-23, revised 1996].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These studies were supported by United States Public Health Service Grant DA017240. The content is solely the responsibility of the author and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute on Drug Abuse or the National Institutes of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerak, L.R. Selective changes in sensitivity to benzodiazepines, and not other positive GABAA modulators, in rats receiving flunitrazepam chronically. Psychopharmacology 204, 667–677 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1497-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1497-4