Abstract
Rationale
Previous research on attention bias in nondependent social drinkers has focused on adult samples with limited focus on the presence of attention bias for alcohol cues in adolescent social drinkers.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to examine the presence of alcohol attention bias in adolescents and the relationship of this cognitive bias to alcohol use and alcohol-related expectancies.
Methods
Attention bias in adolescent social drinkers and abstainers was measured using an eye tracker during exposure to alcohol and neutral cues. Questionnaires measured alcohol use and explicit alcohol expectancies.
Results
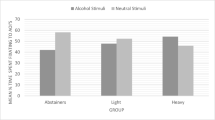
Adolescent social drinkers spent significantly more time fixating to alcohol stimuli compared to controls. Total fixation time to alcohol stimuli varied in accordance with level of alcohol consumption and was significantly associated with more positive alcohol expectancies. No evidence for automatic orienting to alcohol stimuli was found in adolescent social drinkers.
Conclusion
Attention bias in adolescent social drinkers appears to be underpinned by controlled attention suggesting that whilst participants in this study displayed alcohol attention bias comparable to that reported in adult studies, the bias has not developed to the point of automaticity. Initial fixations appeared to be driven by alternative attentional processes which are discussed further.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JP, Litten RZ, Fertig JB, Babor T (1997) A review of research on the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:613–619
Barkovich AJ, Kuzniecky RI, Jackson GD, Guerrini R, Dobyns WB (2005) A developmental and genetic classification for malformations of cortical development. Neurology 65(12):1873–1887
Brown SA, Christiansen BA, Goldman MS (1987a) The alcohol expectancy questionnaire: an instrument for the assessment of adolescent and adult alcohol expectancies. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 48:483–491
Brown SA, Creamer VA, Stetson BA (1987b) Adolescent alcohol expectancies in relation to personal and parental drinking patterns. J Abnorm Psychol 96:117–121
Burgess WP, Simons SJ, Dumontheil I, Gilbert S (2005) Chapter 9: The gateway hypothesis of rostral prefrontal cortex (Area 10) function). In: Duncan J, Phillips L, McLeod P (eds) Measuring the mind: speed, control and age. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 217–248
Burrow-Sanchez JJ (2006) Understanding adolescent substance abuse: prevalence, risk factors, and clinical implications. J Couns Dev 84(3):283–290
Cable N, Sacker A (2008) Typologies of alcohol consumption in adolescence: predictors and adult outcomes. Alcohol Alcohol 43:81–90
Callas PW, Flynn BS, Worden JK (2004) Potentially modifiable psychosocial factors associated with alcohol use during early adolescence. Addict Behav 29:1503–1515
Ceballos NA, Komogortsev OV, Turner GM (2009) Ocular imaging of attentional bias among college students: automatic and controlled processing of alcohol-related scenes. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 70:652–659
Christiansen BA, Goldman MS (1983) Alcohol-related expectancies versus demographic/background variables in the prediction of adolescent drinking. J Consult Clin Psychol 51:249–257
Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety (2011) Adult Drinking Patterns in Northern Ireland. Department of Health, Social Services and Public Safety
Fadardi JS, Cox WM (2006) Alcohol attentional bias: drinking salience or cognitive impairment? Psychopharmacology 185:169–178
Fadardi JS, Cox WM (2008) Alcohol-attentional bias and motivational structure as independent predictors of social drinkers’ alcohol consumption. Drug Alcohol Depend 97:247–256
Fadardi JS, Cox WM (2009) Reversing the sequence: reducing alcohol consumption by overcoming alcohol attentional bias. Drug Alcohol Depend 101:137–145
Field M, Eastwood B (2005) Experimental manipulation of attentional bias increases the motivation to drink alcohol. Psychopharmacology 183(3):350–357
Field M, Mogg K, Zetteler J, Bradley BP (2004) Attentional biases for alcohol cues in heavy and light social drinkers: the roles of initial orienting and maintained attention. Psychopharmacology 176:88–93
Field M, Christiansen P, Cole J, Goudie A (2007a) Delay discounting and the alcohol Stroop in heavy-drinking adolescents. Addiction 102:579–586
Field M, Duka T, Eastwood B, Child R, Santarcangelo M, Gayton M (2007b) Experimental manipulation of attentional biases in heavy drinkers: do the effects generalise? Psychopharmacology 192:593–608
Freeth M, Foulsham T, Chapman P (2011) The influence of visual saliency on fixation patterns in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Neuropsychologia 49:156–160
Fuster JM (2002) Frontal lobe and cognitive development. J Neurocytol 31(3–5):373–385
Guo K, Smith C, Powell K, Nicholls K (2012) Consistent left gaze bias in processing different facial cues. Psychological Research 76:263–269
Hanania R, Smith LB (2010) Selective attention and attention switching: towards a unified developmental approach. Dev Sci 13:622–635
Hannaford S (2005) Drinking, smoking, drugs and sexual intercourse—education and influences for young people in Northern Ireland. ARK Research update. Ark, Belfast, http://www.ark.ac.uk/publications/updates/update37
Heath R, Rouhana A, Abi Ghanem D (2005) Asymmetric bias in perception of facial affect among Roman and Arabic script readers. Laterality: Asymmetries Body Brain Cogn 10(1):51–64
Huttenlocher PR (1990) Morphometric study of human cerebral cortex development. Neuropsychologia 28(6):517–527
Kann L, Kinchen S, Shanklin SL, Flint KH, Kawkins J, Harris WA, Chyen D (2014) Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2013. MMWR Surveill Summ 63(Suppl 4):1–168
Killen JD, Hayward C, Wilson DM, Haydel KF, Robinson TN, Taylor CB et al (1996) Predicting onset of drinking in a community sample of adolescents: the role of expectancy and temperament. Addict Behav 21:473–480
Laidlaw KE, Risko EF, Kingstone A (2012) A new look at social attention: orienting to the eyes is not (entirely) under volitional control. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 38:1132–1142
Leonards U, Scott-Samuel NE (2005) Idiosyncratic initiation of saccadic face exploration in humans. Vis Res 45(20):2677–2684
Loeber S, Vollstädt-Klein S, Von Der Goltz C, Flor H, Mann K, Kiefer F (2009) Clinical study: attentional bias in alcohol‐dependent patients: the role of chronicity and executive functioning. Addict Biol 14:194–203
Lusher J, Chandler C, Ball D (2004) Alcohol dependence and the alcohol Stroop paradigm: evidence and issues. Drug Alcohol Depend 75:225–231
Mann LM, Chassin L, Sher KJ (1987) Alcohol expectancies and the risk for alcoholism. J Consult Clin Psychol 55:411
McCusker C (2006) Towards understanding loss of control: an automatic network theory of addictive behaviours. In: Munafó M, Alberry I (eds) Cognition and Addiction, 1st edn. Oxford University Press, pp 117–146
McKay MT, Sumnall H, Goudie AJ, Field M, Cole JC (2011) What differentiates adolescent problematic drinkers from their peers? Results from a cross-sectional study in northern Irish school children. Drugs: Educ Prev Polic 18:187–199
Miller MA, Fillmore MT (2010) The effect of image complexity on attentional bias towards alcohol‐related images in adult drinkers. Addiction 105:883–890
Miller MA, Fillmore MT (2011) Persistence of attentional bias toward alcohol-related stimuli in intoxicated social drinkers. Drug Alcohol Depend 117:184–189
Noël X, Colmant M, Van Der Linden M, Bechara A, Bullens Q, Hanak C, Verbanck P (2006) Time course of attention for alcohol cues in abstinent alcoholic patients: the role of initial orienting. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:871–1877
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Sacrey LR, Bryson SE, Zwaigenbaum L (2013) Prospective examination of visual attention during play in infants at high-risk for autism spectrum disorder: a longitudinal study from 6 to 36 months of age. Behav Brain Res 256:441–450
Schoenmakers T, Wiers R (2010) Craving and attentional bias respond differently to alcohol priming: a field study in the pub. Eur Addict Res 16:9–16
Schoenmakers T, Wiers RW, Jones BT, Bruce G, Jansen A (2007) Attentional re‐training decreases attentional bias in heavy drinkers without generalization. Addiction 102:399–405
Schoenmakers T, Wiers RW, Field M (2008) Effects of a low dose of alcohol on cognitive biases and craving in heavy drinkers. Psychopharmacology 197:169–178
Stormark KM, Laberg JC, Nordby H, Hugdahl K (2000) Alcoholics’ selective attention to alcohol stimuli: automated processing? J Stud Alcohol Drugs 61(1):18
Teffer K, Semendeferi K (2012) Human prefrontal cortex: evolution, development, and pathology. Prog Brain Res 195:191
Tiffany ST (1990) A cognitive model of drug urges and drug-use behaviour: role of automatic and non-automatic processes. Psychol Rev 97:147–168
Townshend J, Duka T (2001) Attentional bias associated with alcohol cues: differences between heavy and occasional social drinkers. Psychopharmacology 157:67–74
Vollstädt-Klein S, Loeber S, Von Der Goltz C, Mann K, Kiefer F (2009) Avoidance of alcohol-related stimuli increases during the early stage of abstinence in alcohol-dependent patients. Alcohol Alcohol 44:458–463
Zetteler JI, Stollery BT, Weinstein AM, Lingford-Hughes AR (2006) Attentional bias for alcohol-related information in adolescents with alcohol-dependent parents. Alcohol Alcohol 41:426–430
Conflict of interest
Authors confirm there is no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melaugh McAteer, A., Curran, D. & Hanna, D. Alcohol attention bias in adolescent social drinkers: an eye tracking study. Psychopharmacology 232, 3183–3191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3969-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3969-z