Abstract
Rationale and objective
Since brain proteins such as protein kinase C (PKC), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) are involved in the establishment and maintenance of psychostimulant memory, we sought to determine if systemic treatment with rottlerin, a natural compound affecting all these proteins, may modulate stimulant-supported memory.
Materials and methods
Stimulant-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) was used in modeling stimulant-supported memory.
Results
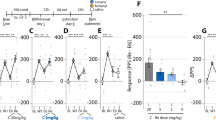
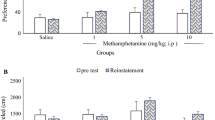
Three cocaine (10 mg/kg; COC) or three methamphetamine (1 mg/kg; MA) conditioning trials reliably established the drug-induced CPP in male C57BL/6 mice. An intra-peritoneal rottlerin injection (5 mg/kg) at least 24 h prior to the first COC or first MA conditioning trial prevented the establishment of CPP. Following the establishment of the COC- or MA-induced CPP, saline conditioning trial was used to extinguish the CPP. Rottlerin (5 mg/kg, intra-peritoneal (i.p.)) administered 20 h prior to the first saline conditioning trial diminished subsequent drug- and stressor-primed reinstatement of the extinguished CPP. Rottlerin (5 mg/kg, i.p.) produced a fast-onset and long-lasting increase in hippocampal BDNF levels. However, treatment with a BDNF tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) receptor antagonist, K252a (5 μg/kg), did not affect rottlerin’s suppressing effect on COC-induced CPP and treatment with 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (10 mg/kg x 6, 7,8-DHF), a selective TrkB agonist, prior to each conditioning trial did not affect COC-induced CPP.
Conclusion
These results suggest that systemic rottlerin treatment may impair the formation of COC- and MA-supported memory. Importantly, such a treatment may advance our understanding of the underlying mechanism through which extinction training resulted in the “forgetting” of the COC- and MA-supported memory.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- COC:
-
Cocaine
- MA:
-
Methamphetamine
- CPP:
-
Conditioned place preference
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- mTORC1:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- BDNF:
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- TrkB:
-
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B
- 7,8-DHF:
-
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
References
Bahi A, Boyer F, Chandrasekar V, Dreyer JL (2008) Role of accumbens BDNF and TrkB in cocaine-induced psychomotor sensitization, conditioned-place preference, and reinstatement in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 199:169–182
Bailey J, Ma D, Szumlinski KK (2012) Rapamycin attenuates the expression of cocaine-induced place preference and behavioral sensitization. Addict Biol 17:248–258
Cherng CG, Lin PS, Chuang JY, Chang WT, Lee YS, Kao GS, Lai YT, Yu L (2010) Presence of conspecifics and their odor-impregnated objects reverse stress-decreased neurogenesis in mouse dentate gyrus. J Neurochem 112:1138–1146
Cherng CF, Chang CP, Su CC, Tzeng WY, Chuang JY, Chen LH, Lin KY, Yu L (2012) Odors from proximal species reverse the stress-decreased neurogenesis via main olfactory processing. Behav Brain Res 229:106–112
Clem RL, Huganir RL (2010) Calcium-permeable AMPA receptor dynamics mediate fear memory erasure. Science 330:1108–1112
Clements RT, Cordeiro B, Feng J, Bianchi C, Sellke FW (2011) Rottlerin increases cardiac contractile performance and coronary perfusion through BKCa++ channel activation after cold cardioplegic arrest in isolated hearts. Circulation 124:S55–S61
Fan HY, Cherng CG, Yang FY, Cheng LY, Tsai CJ, Lin LC, Yu L (2010) Systemic treatment with protein synthesis inhibitors attenuates the expression of cocaine memory. Behav Brain Res 208:522–527
Flavell CR, Lee JL (2013) Reconsolidation and extinction of an appetitive pavlovian memory. Neurobio Learn Mem 104:25–31
Goncalves J, Baptista S, Olesen MV, Fontes-Ribeiro C, Malva JO, Woldbye DP, Silva AP (2012) Methamphetamine-induced changes in the mice hippocampal neuropeptide Y system: implications for memory impairment. J Neurochem 123:1041–1053
Hupbach A, Gomez R, Hardt O, Nadel L (2007) Reconsolidation of episodic memories: a subtle reminder triggers integration of new information. Learn Mem 14:47–53
Kongsuphol P, Mukda S, Nopparat C, Villarroel A, Govitrapong P (2009) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced deactivation of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling to induce autophagy in SK-N-SH cells. J Pineal Res 46:199–206
Kuo YM, Liang KC, Chen HH, Cherng CG, Lee HT, Lin Y, Huang AM, Liao RM, Yu L (2007) Cocaine-but not methamphetamine-associated memory requires de novo protein synthesis. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:93–100
Lai YT, Fan HY, Cherng CG, Chiang CY, Kao GS, Yu L (2008) Activation of amygdaloid PKC pathway is necessary for conditioned cues-provoked cocaine memory performance. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:164–170
Li Y, Hu Z, Chen B, Bu Q, Lu W, Deng Y, Zhu R, Shao X, Hou J, Zhao J, Li H, Zhang B, Huang Y, Lv L, Zhao Y, Cen X (2012) Taurine attenuates methamphetamine-induced autophagy and apoptosis in PC12 cells through mTOR signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett 15:1–7
Lin KY, Cherng CG, Yang FR, Lin LC, Lu RB, Yu L (2011) Memantine abolishes the formation of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference possibly via its IL-6-modulating effect in medial prefrontal cortex. Behav Brain Res 220:126–131
Lin J, Liu L, Wen Q, Zheng C, Gao Y, Peng S, Tan Y, Li Y (2014) Rapamycin prevents drug seeking via disrupting reconsolidation of reward memory in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:127–136
Lu W, Lin C, Li Y (2014) Rottlerin induces Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells. Cell Signal 26:1303–1309
Lu QY, Zhang L, Lugea A, Moro A, Edderkaoui M, Eibl G, Pandol SJ, Go VL (2013) Determination of Rottlerin, a Natural Protein Kinases C Inhibitor, in Pancreatic Cancer Cells and Mouse Xenografts by RP-HPLC Method. J Chromatogr Sep Tech 4:100062
Maioli E, Torricelli C, Valacchi G (2012) Rottlerin and cancer: novel evidence and mechanisms. Sci World J 2012:350826
Monfils MH, Cowansage KK, Klann E, LeDoux JE (2009) Extinction-reconsolidation boundaries: key to persistent attenuation of fear memories. Science 324:951–955
Morioka N, Yoshida Y, Nakamura Y, Hidaka N, Hisaoka-Nakashima K, Nakata Y (2013) The regulation of exon-specific brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression by protein kinase C in rat cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res 1509:20–31
Nader K, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2000) The labile nature of consolidation theory. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:216–219
Otis JM, Fitzgerald MK, Mueller D (2014) Infralimbic BDNF/TrkB enhancement of GluN2B currents facilitates extinction of a cocaine-conditioned place preference. J Neurosci 34:6057–6064
Rao-Ruiz P, Rotaru DC, van der Loo RJ, Mansvelder HD, Stiedl O, Smit AB, Spijker S (2011) Retrieval-specific endocytosis of GluA2-AMPARs underlies adaptive reconsolidation of contextual fear. Nat Neurosci 14:1302–1308
Sara SJ (2000) Retrieval and reconsolidation toward a neurobiology of remembering. Learn Mem 7:73–84
Schiller D, Monfils MH, Raio CM, Johnson DC, LeDoux JE, Phelps EA (2010) Preventing the return of fear in humans using reconsolidation update mechanisms. Nature 463:49–53
Shi X, Miller JS, Harper LJ, Poole RL, Gould TJ, Unterwald EM (2014) Reactivation of cocaine reward memory engages the Akt/GSK3/mTOR signaling pathway and can be disrupted by GSK3 inhibition. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231:3109–3118
Soltoff SP (2001) Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cdelta tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276:37986–37992
Sotres-Bayon F, Cain CK, LeDoux JE (2006) Brain mechanisms of fear extinction: historical perspectives on the contribution of prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 60:329–336
Torricelli C, Daveri E, Salvadori S, Valacchi G, Ietta F, Muscettola M, Carlucci F, Maioli E (2015) Phosphorylation-independent mTORC1 inhibition by the autophagy inducer Rottlerin. Cancer Lett 360:17–27
Tzeng WY, Chuang JY, Lin LC, Cherng CG, Lin KY, Chen LH, Su CC, Yu L (2013) Companions reverse stressor-induced decreases in neurogenesis and cocaine conditioning possibly by restoring BDNF and NGF levels in dentate gyrus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:425–437
Xu H, Czerwinski P, Xia N, Förstermann U, Li H (2015) Downregulation of BDNF expression by PKC and by TNF-α in human endothelial cells. Pharmacology 96:1–10
Xue YX, Luo YX, Wu P, Shi HS, Xue LF, Chen C, Zhu WL, Ding ZB, Bao YP, Shi J, Epstein DH, Shaham Y, Lu L (2012) A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse. Science 336:241–245
Yang FY, Lee YS, Cherng CG, Cheng LY, Chang WT, Chuang JY, Kao GS, Yu L (2013) D-cycloserine, sarcosine and D-serine diminish the expression of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference. J Psychopharmacol 27:550–558
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by ROC Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) grant 103-2410-H-006 -028 -MY3 to L.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tien You Liao and Wen-Yu Tzeng contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, T.Y., Tzeng, WY., Wu, HH. et al. Rottlerin impairs the formation and maintenance of psychostimulant-supported memory. Psychopharmacology 233, 1455–1465 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4251-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4251-8