Abstract
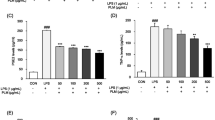
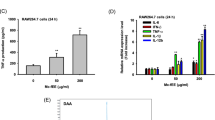
Royal jelly (RJ) fatty acids have recently been shown to possess various pharmacological and biological activities. In this work, we studied the immunomodulatory effects of 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA) and 3,10-dihydroxy-decanoic acid (3,10-DDA), isolated from RJ, using a model of phytohaemagglutinin-activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). We showed that higher concentrations (500 μM) of both fatty acids inhibited the proliferation of PBMCs, and the process was followed by a decrease in the production of interleukin-2 (IL-2). 10-HDA at the concentration of 500 μM inhibited the production of IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α by stimulated PBMCs, whereas the same dose of 3,10-DDA had no effect on the levels of these cytokines. Regarding T helper (Th) cytokine profile, higher concentration of 10-HDA, in contrast to the lower one (50 μM), inhibited both Th1 and Th2 response, whereas Th17 response was not significantly modulated, as judged by the levels of interferon-γ, IL-5 and IL-17A in culture supernatants, respectively. Lower concentration of 3,10-DDA stimulated Th1 and Th17 responses and inhibited IL-10 production, whereas the higher dose augmented the Th2 response. In conclusion, our results showed a significant, dose-dependent, immunomodulatory effect of RJ fatty acids in vitro, which was also associated with their structure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ramadan MF, Al-Ghamdi A (2012) Bioactive compounds and health-promoting properties of royal jelly: a review. J Funct Foods 4:39–52
Viuda-Martos M, Ruiz-Navajas Y, Fernández-López J, Pérez-Álvarez JA (2008) Functional properties of honey, propolis, and royal jelly. J Food Sci 73:R117–R124
Bincoletto C, Eberlin S, Figueiredo CA, Luengo MB, Queiroz ML (2005) Effects produced by Royal Jelly on haematopoiesis: relation with host resistance against Ehrlich ascites tumour challenge. Int Immunopharmacol 5:679–688
Gasic S, Vucevic D, Vasilijic S, Antunovic M, Chinou I, Colic M (2007) Evaluation of the immunomodulatory activities of royal jelly components in vitro. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 29:521–536
Vucevic D, Melliou E, Vasilijic S, Gasic S, Ivanovski P, Chinou I, Colic M (2007) Fatty acids isolated from royal jelly modulate dendritic cell-mediated immune response in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol 7:1211–1220
Dzopalic T, Vucevic D, Tomic S, Djokic J, Chinou I, Colic M (2011) 3,10-Dihydroxy-decanoic acid, isolated from royal jelly, stimulates Th1 polarising capability of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Food Chem 126:1211–1217
Mihajlovic D, Rajkovic I, Chinou I, Colic M (2013) Dose-dependent immunomodulatory effects of 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Funct Foods 5:838–846
Okamoto I, Taniguchi Y, Kunikata T, Kohno K, Iwaki K, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M (2003) Major royal jelly protein 3 modulates immune responses in vitro and in vivo. Life Sci 73:2029–2045
Majtan J, Kovacova E, Bilikova K, Simuth J (2006) The immunostimulatory effect of the recombinant apalbumin 1-major honeybee royal jelly protein-on TNFalpha release. Int Immunopharmacol 6:269–278
Kohno K, Okamoto I, Sano O, Arai N, Iwaki K, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M (2004) Royal jelly inhibits the production of proinflammatory cytokines by activated macrophages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:138–145
Mannoor MK, Shimabukuro I, Tsukamotoa M, Watanabe H, Yamaguchi K, Sato Y (2009) Honeybee royal jelly inhibits autoimmunity in SLE-prone NZB × NZW F1 mice. Lupus 18:44–52
Matsui T, Yukiyoshi A, Doi S, Sugimoto H, Yamada H, Matsumoto K (2002) Gastrointestinal enzyme production of bioactive peptides from royal jelly protein and their antihypertensive ability in SHR. J Nutr Biochem 13:80–86
Fontana R, Mendes MA, de Souza BM, Konno K, Cesar LM, Malaspina O, Palma MS (2004) Jelleines: a family of antimicrobial peptides from the Royal Jelly of honeybees (Apis mellifera). Peptides 25:919–928
Oka H, Emori Y, Kobayashi N, Hayashi Y, Nomoto K (2001) Suppression of allergic reactions by royal jelly in association with the restoration of macrophage function and the improvement of Th1/Th2 cell responses. Int Immunopharmacol 1:521–532
Jamnik P, Goranovic D, Raspor P (2007) Antioxidative action of royal jelly in the yeast cell. Exp Gerontol 42:594–600
Melliou E, Chinou I (2005) Chemistry and bioactivity of royal jelly from Greece. J Agric Food Chem 53:8987–8992
Isidorov VA, Czyżewska U, Jankowska E, Bakier S (2011) Determination of royal jelly acids in honey. Food Chem 124:387–391
Jenny M, Klieber M, Zaknun D, Schroecksnadel S, Kurz K, Ledochowski M, Schennach H, Fuchs D (2011) In vitro testing for anti-inflammatory properties of compounds employing peripheral blood mononuclear cells freshly isolated from healthy donors. Inflamm Res 60:127–135
Zhu J, Yamane H, Paul WE (2010) Differentiation of effector CD4 T cell populations (*). Annu Rev Immunol 28:445–489
Erem C, Deger O, Ovali E, Barlak Y (2006) The effects of royal jelly on autoimmunity in Graves’ disease. Endocrine 30:175–183
Karaca T, Bayiroglu F, Yoruk M, Kaya MS, Uslu S, Comba B, Mis L (2010) Effect of royal jelly on experimental colitis Induced by acetic acid and alteration of mast cell distribution in the colon of rats. Eur J Histochem 54:e35
Sugiyama T, Takahashi K, Mori H (2012) Royal jelly acid, 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid, as a modulator of the innate immune responses. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 12:368–376
Sugiyama T, Takahashi K, Kuzumaki A, Tokoro S, Neri P, Mori H (2013) Inhibitory mechanism of 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid (royal jelly acid) against lipopolysaccharide- and interferon-beta-induced nitric oxide production. Inflammation 36:372–378
Takahashi K, Sugiyama T, Tokoro S, Neri P, Mori H (2012) Inhibition of interferon-gamma-induced nitric oxide production by 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid through inhibition of interferon regulatory factor-8 induction. Cell Immunol 273:73–78
Sugiyama T, Takahashi K, Tokoro S, Gotou T, Neri P, Mori H (2012) Inhibitory effect of 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid on LPS-induced IL-6 production via reducing IkappaB-zeta expression. Innate Immun 18:429–437
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27:693–733
Zubiaga AM, Munoz E, Merrow M, Huber BT (1990) Regulation of interleukin 6 production in T helper cells. Int Immunol 2:1047–1054
Romagnani S, Maggi E, Liotta F, Cosmi L, Annunziato F (2009) Properties and origin of human Th17 cells. Mol Immunol 47:3–7
Banchereau J, Steinman RM (1998) Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245–252
Ouyang W, Rutz S, Crellin NK, Valdez PA, Hymowitz SG (2011) Regulation and functions of the IL-10 family of cytokines in inflammation and disease. Annu Rev Immunol 29:71–109
Petursdottir DH, Hardardottir I (2009) Dietary fish oil decreases secretion of T helper (Th) 1-type cytokines by a direct effect on murine splenic T cells but enhances secretion of a Th2-type cytokine by an effect on accessory cells. Br J Nutr 101:1040–1046
Yang XY, Yang DS, Wei Z, Wang JM, Li CY, Hui Y, Lei KF, Chen XF, Shen NH, Jin LQ, Wang JG (2010) 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic acid from Royal jelly: a potential medicine for RA. J Ethnopharmacol 128:314–321
Georgiadi A, Kersten S (2012) Mechanisms of gene regulation by fatty acids. Adv Nutr 3:127–134
da Rocha Junior LF, Dantas AT, Duarte AL, de Melo Rego MJ, Pitta Ida R, Pitta MG (2013) PPAR gamma agonists in adaptive immunity: what do immune disorders and their models have to tell us? PPAR Res 2013:519724
Malapaka RR, Khoo S, Zhang J, Choi JH, Zhou XE, Xu Y, Gong Y, Li J, Yong EL, Chalmers MJ, Chang L, Resau JH, Griffin PR, Chen YE, Xu HE (2012) Identification and mechanism of 10-carbon fatty acid as modulating ligand of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. J Biol Chem 287:183–195
Jiang C, Ting AT, Seed B (1998) PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines. Nature 391:82–86
Kim DI, Kim KH, Kang JH, Jung EM, Kim SS, Jeung EB, Yang MP (2011) Trans-10, cis-12-conjugated linoleic acid modulates NF-kappaB activation and TNF-alpha production in porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells via a PPARgamma-dependent pathway. Br J Nutr 105:1329–1336
Klotz L, Burgdorf S, Dani I, Saijo K, Flossdorf J, Hucke S, Alferink J, Nowak N, Beyer M, Mayer G, Langhans B, Klockgether T, Waisman A, Eberl G, Schultze J, Famulok M, Kolanus W, Glass C, Kurts C, Knolle PA (2009) The nuclear receptor PPAR gamma selectively inhibits Th17 differentiation in a T cell-intrinsic fashion and suppresses CNS autoimmunity. J Exp Med 206:2079–2089
Liberato MV, Nascimento AS, Ayers SD, Lin JZ, Cvoro A, Silveira RL, Martinez L, Souza PC, Saidemberg D, Deng T, Amato AA, Togashi M, Hsueh WA, Phillips K, Palma MS, Neves FA, Skaf MS, Webb P, Polikarpov I (2012) Medium chain fatty acids are selective peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) gamma activators and pan-PPAR partial agonists. PLoS ONE 7:e36297
Wang J, Wu X, Simonavicius N, Tian H, Ling L (2006) Medium-chain fatty acids as ligands for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR84. J Biol Chem 281:34457–34464
Suzuki M, Takaishi S, Nagasaki M, Onozawa Y, Iino I, Maeda H, Komai T, Oda T (2013) Medium-chain fatty acid-sensing receptor, GPR84, is a proinflammatory receptor. J Biol Chem 288:10684–10691
Acknowledgments
This study has been supported by the following grants: Ministry of Education and Science, R. Serbia (Project No.: 175102); Military Medical Academy, Belgrade, Serbia (Project No: VMA 07-10/B.23); Serbian Academy of Science and Arts; The General Secretariat of Research and Technology of Greece (PENED project). The authors thank S. Vasilijic, S. Gasic, I. Majstorovic and Z. Stojic-Vukanic for their assistance in this work.
Conflict of interest
None.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mihajlovic, D., Vucevic, D., Chinou, I. et al. Royal jelly fatty acids modulate proliferation and cytokine production by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Eur Food Res Technol 238, 881–887 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2154-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2154-7