Abstract
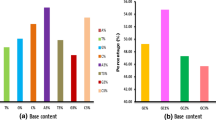
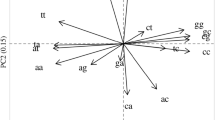
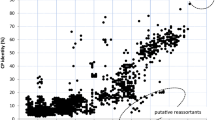
Understanding the extent and causes of biases in codon usage and nucleotide composition is essential to the study of viral evolution, particularly the interplay between viruses and host cells or immune responses. To understand the common features and differences among viruses we analyzed the genomic characteristics of a representative collection of all sequenced vertebrate-infecting DNA viruses. This revealed that patterns of codon usage bias are strongly correlated with overall genomic GC content, suggesting that genome-wide mutational pressure, rather than natural selection for specific coding triplets, is the main determinant of codon usage. Further, we observed a striking difference in CpG content between DNA viruses with large and small genomes. While the majority of large genome viruses show the expected frequency of CpG, most small genome viruses had CpG contents far below expected values. The exceptions to this generalization, the large gammaherpesviruses and iridoviruses and the small dependoviruses, have sufficiently different life-cycle characteristics that they may help reveal some of the factors shaping the evolution of CpG usage in viruses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acken UV, Simon D, Grunert F, Döring H-P, Kröger H (1979) Methylation of viral DNA in vivo and in vitro. Virology 99:152–157
Ambinder RF, Robertson KD, Tao Q (1999) DNA methylation and the Epstein-Barr virus. Semin Cancer Biol 9:369–375
Bernardi G, Bernardi G (1986) Compositional constraints and genome evolution. J Mol Evol 24:1–11
Beutler E, Gelbart T, Han J, Koziol JA, Beutler B (1989) Evolution of the genome and the genetic code: Selection at the dinucleotide level by methylation and polyribonucleotide cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:192–196
Breslauer KJ, Frank R, Blocker H, Marky LA (1986) Predicting DNA duplex stability from the base sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3746–3750
Bronson EC, Anderson JN (1994) Nucleotide composition as a driving force in the evolution of retroviruses. J Mol Evol 38:506–532
Burge C, Campbell AM, Karlin S (1992) Over- and under-representation of short oligonucleotides in DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1358–1362
Chamary J-V, Hurst LD (2004) Similar rates but different modes of sequence evolution in introns and at exonic silent sites in rodents, evidence for selectively driven codon usage. Mol Biol Evol 21:1014–1023
Cole CN, Conzen SD (2001) Polyomaviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Fundamental virology, vol 4. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 985–1018
De Amicis F, Marchetti S (2000) Intercodon dinucleotides affect codon choice in plant genes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:3339–3345
Duan J, Antezana MA (2003) Mammalian mutation pressure, synonymous codon choice, and mRNA degradation. J Mol Evol 57:694–701
El Antri S, Bittoun P, Mauffret O, Monnot M, Lescot E, Convert O, Fermandjian S (1993a) Effect of distortions in the phosphate backbone conformation of six related octanucleotide duplexes on CD and 31P NMR spectra. Biochemistry 32:7079–7088
El Antri S, Mauffret O, Monnot M, Lescot E, Convert O, Fermandjian S (1993b) Structural deviations at CpG provide a plausible explanation for the high frequency of mutation at this site, Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism studies. J Mol Biol 230:373–378
Gentles AJ, Karlin S (2001) Genome-scale compositional comparisons in eukaryotes. Genome Res 11:540–546
Gouy M, Gautier C (1982) Codon usage in bacteria, correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res 10:7055–7047
Grantham R, Gautier C, Guoy M, Mercier R, Pave A (1980) Codon catalogue usage and the genome hypothesis. Nucleic Acids Res 8:49–62
Grantham R, Perrin P, Mouchiroud D (1986) Patterns in codon usage of different kinds of species. Oxford Surv Evol Biol 3:48–81
Grzeskowiak K, Yanagi K, Privé GG, Dickerson RE (1991) The structure of B-helical C-G-A-T-C-G-A-T-C-G and comparison with C-C-A-A-C-G-T-T-G-GJ. Biol Chem 266:8861–8883
Gu W, Zhou T, Ma J, Sun X, Lu Z (2004) Analysis of synonymous codon usage in SARS Coronavirus and other viruses in the Nidovirales. Virus Res 101:155–161
Harte MT, Haga IR, Maloney G, Gray P, Reading PC, Bartlett NW, Smith GL, Bowie A, O’Neill AJ (2003) The poxvirus protein A52R targets toll-like receptor signalling complexes to suppress host defense. J Exp Med 197:343–351
Howley PM, Lowy DR (2001) Papillomaviruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Fundamental virology, vol 4. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 1019–1051
Jenkins GM, Holmes EC (2003) The extent of codon usage bias in human RNA viruses and its evolutionary origin. Virus Res 92:1–7
Jones PA, Rideout WMIII, Shen J-C, Spruck CH, Tsai YC (1992) Methylation, mutation and cancer. Bioessays 14:33–36
Kämmer C, Doerfler W (1995) Genomic sequencing reveals absence of DNA methylation in the major late promoter of adenovirus type 2 DNA in the virion and in productively infected cells. FEBS Lett 362:301–305
Karlin S, Burge C (1995) Dinucleotide relative abundance extremes, a genomic signature. Trends Genet 11:283–290
Karlin S, Mrázek J (1997) Compositional differences within and between eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:1027–10232
Karlin S, Doerfler W, Cardon LR (1994) Why is CpG suppressed in the genomes of virtually all small eukaryotic viruses but not in those of large eukaryotic viruses? J Virol 68: 2889–2897
Kress C, Thomassin H, Grange T (2001) Local DNA methylation in vertebrates, how could it be performed and targeted? FEBS Lett 494:135–140
Krieg AM (2003) CpG DNA, Trigger of sepsis, mediator of protection, or both? Scand J Infect Dis 35:653–659
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921
Lund J, Sato A, Medzhitov R, Iwasaki A (2003) Toll-like receptor 9-mediated recognition of Herpes simplex virus-2 by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Exp Med 198:513–520
Lundberg P, Welander P, Han X, Cantin E (2003) Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA is immunostimulatory in vitro and in vivo. J Virol 77:11158–11169
Moss B (2001) Poxviridae: The viruses and their replication. In: Knipe D, Howley P (eds) Fundamental virology, vol 4. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 1249–1283
Moyer JD, Henderson JF (1985) Compartmentation of intracellular nucleotides in mammalian cells. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 19:45–61
Muzyczka N, Berns KI (2001) Parvoviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Fundamental virology, vol 4. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA, pp 1089–1121
Novembre JA (2002) Accounting for background nucleotide composition when measuring codon usage bias. Mol Biol Evol 19:1390–1394
Oresic M, Shalloway D (1998) Specific correlations between relative synonymous codon usage and protein secondary structure. J Mol Biol 281:31–48
Powell JR, Moriyama EN (1997) Evolution of codon usage bias in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7784–7790
Pride DT (2000) SWAAP Version 1.0.0—Sliding windows alignment analysis program: a tool for analyzing patterns of substitutions and similarity in multiple alignments. Distributed by the author
Rassa J, Ross SR (2003) Viruses and toll-like receptors. Microbes Infect 5:961–968
Rojo G, García-Beato R, Viñuela E, Sala MA, Salas J (1999) Replication of African swine fever virus DNA in infected cells. Virology 257:542–536
Schachtel GA, Bucher P, Mocarski ES, Blaisdell BE, Karlin S (1991) Evidence for selective evolution in codon usage in conserved amino acid segments of human alphaherpesvirus proteins. J Mol Evol 33:483–494
Shackelton LA, Holmes EC (2004) The evolution of large DNA viruses, combining genomic information of viruses and their hosts. Trends Microbiol 12:458–465
Shackelton LA, Parrish CR, Truye U, Holmes EC (2005) High rate of viral evolution associated with the emergence of carnivore parvovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:379–384
Sharp PM, Matassi G (1994) Codon usage and genome evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev 4:851–860
Sharp PM, Tuohy TM, Mosurski KR (1986) Codon usage in yeast, cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res 14:1525–5143
Sharp PM, Stenico M, Peden JF, Lloyd AT (1993) Codon usage, mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem Soc Trans 21:835–841
Smith NGC, Eyre-Walker A (2001) Synonymous codon bias is not caused by mutation bias in G + C-rich genes in humans. Mol Biol Evol 18:982–986
Stenico M, Lloyd AT, Sharp PM (1994) Codon usage in Caenorhabditis elegans, delineation of translational selection and mutational biases. Nucleic Acids Res 22:2437–2446
Strauss EG, Strauss JH, Levine AJ (1996) Virus evolution. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Virology. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, PA, pp 153–171
Sueoka N (1961) Compositional correlation between deoxyribonucleic acid and protein. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 26:35–43
Tao Q, Robertson KD (2003) Stealth technology, how Epstein–Barr virus utilizes DNA methylation to cloak itself from immune detection. Clin Immunol 109:53–63
Truyen U, Gruenberg A, Chang SW, Obermaier B, Veijalainen P, Parrish CR (1995) Evolution of the feline-subgroup parvoviruses and the control of canine host range in vivo. J Virol 69:4702–4710
Wagner H (2004) The immunobiology of the TLR9 subfamily. Trends Immunol 25:381–386
Wagner H, Simon D, Werner E, Gelderblom H, Darai C, Flügel RM (1985) Methylation pattern of fish lymphocystis disease virus DNA. J Virol 53:1005–1007
Williams T (1996) The iridoviruses. Adv Virus Res 46:345–412
Willis DB, Granoff A (1980) Frog virus 3 DNA is heavily methylated at CpG sequences. Virology 107:250–257
Wright F (1990) The “effective number of codons” used in a gene. Gene 87:23–29
Wyatt GR (1952) The nucleic acids of some insect viruses. J Gen Physiol 36:201–205
Xia X (1996) Maximizing transcription efficiency causes codon usage bias. Genetics 144:1309–1320
Zama M (1990) Codon usage and secondary structure of mRNA. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 22:93–94
Zhao K-N, Liu WJ, Frazer IH (2003) Codon usage bias and A + T content variation in human papillomavirus geomes. Virus Res 98:95–104
Acknowledgments
This work was completed under a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Fellowship to L.A.S. and NIH Grant R01AI028385 to C.R.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Nicolas Galtier]
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shackelton, L.A., Parrish, C.R. & Holmes, E.C. Evolutionary Basis of Codon Usage and Nucleotide Composition Bias in Vertebrate DNA Viruses. J Mol Evol 62, 551–563 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0221-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0221-1