Abstract
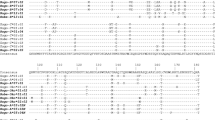
Nonhuman primates express varying responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis: New World monkeys appear to be resistant to tuberculosis (TB) while Old World monkeys seem to be particularly susceptible. The aim of this study was to elucidate the presence of the regulatory guanine–thymine (GT) repeat polymorphisms in intron 2 of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) associated with the development of TB in humans and to determine any variations in these microsatellite polymorphisms in primates. We sequenced the region encompassing the regulatory GT repeat microsatellites in intron 2 of TLR2 in 12 different nonhuman primates using polymerase chain reaction amplification, TA cloning, and automatic sequencing. The nonhuman primates included for this study were as follows: chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), bonobo (Pan paniscus), gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus), Celebes ape (Macaca nigra), rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta), pigtail macaque (Macaca nemestrina), patas monkey (Erythrocebus patas), spider monkey (Ateles geoffroyi), Woolly monkey (Lagothrix lagotricha), tamarin (Saguinus labiatus), and ring-tailed lemur (Lemur catta). Nucleotide sequences encompassing the regulatory GT repeat region are similar across species and are completely conserved in great apes. However, Old World monkeys lack GT repeats altogether, while New World monkeys and ring-tailed lemurs have much more complex structures around the position of the repeats. In conclusion, the genetic structures encompassing the regulatory GT repeats in intron 2 of human TLR2 are similar among nonhuman primates. The sequence is most conserved in New World monkeys and less in Old World monkeys.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd Y, Goodchild M, Morroll S, Bumstead N (2001) Mapping of the chicken and mouse genes for toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) to an evolutionarily conserved chromosomal segment. Immunogenetics 52:294–298
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1993) Tuberculosis in imported nonhuman primates-United States, June 1990-May 1993. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 42:572–576
Chaudhary PM, Ferguson C, Nguyen V, Nguyen O, Massa HF, Eby M, Jasmin A, Trask BJ, Hood L, Nelson PS (1998) Cloning and characterization of two Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor-like genes TIL3 and TIL4: evidence for a multi-gene receptor family in humans. Blood 91:4020–4027
Drennan MB, Nicolle D, Quesniaux VJ, Jacobs M, Allie N, Mpagi J, Fremond C, Wagner H, Kirschning C, Ryffel B (2004) Toll-like receptor 2-deficient mice succumb to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Am J Pathol 164:49–57
Ellegren H (2000) Heterogeneous mutation processes in human microsatellite DNA sequences. Nat Genet 24:400–402
Good RC (1968) Biology of the mycobacterioses. Simian tuberculosis: immunologic aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 154:200–213
Goodman M, Porter CA, Czelusniak J, Page SL, Schneider H, Shoshani J, Gunnell G, Groves CP (1998) Toward a phylogenetic classification of primates based on DNA evidence complemented by fossil evidence. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9:585–598
Hajishengallis G, Tapping RI, Martin MH, Nawar H, Lyle EA, Russell MW, Connell TD (2005) Toll-like receptor 2 mediates cellular activation by the B subunits of type II heat-labile enterotoxins. Infect Immun 73:1343–1349
Hirono I, Takami M, Miyata M, Miyazaki T, Han HJ, Takano T, Endo M, Aoki T (2004) Characterization of gene structure and expression of two toll-like receptors from Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Immunogenetics 56:38–46
Hoffmann JA, Kafatos FC, Janeway CA, Ezekowitz RA (1999) Phylogenetic perspectives in innate immunity. Science 284:1313–1318
Jault C, Pichon L, Chluba J (2004) Toll-like receptor gene family and TIR-domain adapters in Danio rerio. Mol Immunol 40:759–771
Jones BW, Means TK, Heldwein KA, Keen MA, Hill PJ, Belisle JT, Fenton MJ (2001) Different Toll-like receptor agonists induce distinct macrophage responses. J Leukoc Biol 69:1036–1044
Kopp EB, Medzhitov R (1999) The Toll-receptor family and control of innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 11:13–18
Levinson G, Gutman GA (1987) Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol 4:203–221
Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr (1997a) Innate immunity: impact on the adaptive immune response. Curr Opin Immunol 9:4–9
Medzhitov R, Janeway CA Jr (1997b) Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell 91:295–298
Medzhitov R, Janeway C Jr (2000) Innate immune recognition: mechanisms and pathways. Immunol Rev 173:89–97
Reiling N, Holscher C, Fehrenbach A, Kroger S, Kirschning CJ, Goyert S, Ehlers S (2002) Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor (TLR)2- and TLR4-mediated pathogen recognition in resistance to airborne infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol 169:3480–3484
Ribi E, Anacker RL, Barclay WR, Brehmer W, Harris SC, Leif WR, Simmons J (1971) Efficacy of mycobacterial cell walls as a vaccine against airborne tuberculosis in the Rheusus monkey. J Infect Dis 123:527–538
Rock FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF (1998) A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:588–593
Rothschild BM, Martin LD, Lev G, Bercovier H, Bar-Gal GK, Greenblatt C, Donoghue H, Spigelman M, Brittain D (2001) Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex DNA from an extinct bison dated 17,000 years before the present. Clin Infect Dis 33:305–311
Schnare M, Barton GM, Holt AC, Takeda K, Akira S, Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors control activation of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 2:947–950
Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning CJ (1999) Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem 274:17406–17409
Scott GBD (1992) Comparative primate pathology. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, Takeda K, Akira S (1999) Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity 11:443–451
Tautz D, Schlotterer C (1994) Simple sequences. Curr Opin Genet Dev 4:832–837
Thompson J, Higgins D, Gibson T (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Underhill DM, Ozinsky A, Smith KD, Aderem A (1999) Toll-like receptor-2 mediates mycobacteria-induced proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:14459–14463
Webster MT, Smith NG, Ellegren H (2002) Microsatellite evolution inferred from human-chimpanzee genomic sequence alignments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8748–8753
Werts C, Tapping RI, Mathison JC, Chuang TH, Kravchenko V, Saint Girons I, Haake DA, Godowski PJ, Hayashi F, Ozinsky A, Underhill DM, Kirschning CJ, Wagner H, Aderem A, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ (2001) Leptospiral lipopolysaccharide activates cells through a TLR2-dependent mechanism. Nat Immunol 2:346–352
West CS, Vainisi SJ, Vygantas CM, Beluhan FZ (1981) Intraocular granulomas associated with tuberculosis in primates. J Am Vet Med Assoc 179:1240–1244
Wieland CW, Knapp S, Florquin S, de Vos AF, Takeda K, Akira S, Golenbock DT, Verbon A, van der Poll T (2004) Non-mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan induces lung inflammation via toll-like receptor 2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170:1367–1374
Yim JJ, Ding L, Schaffer AA, Park GY, Shim YS, Holland SM (2004) A microsatellite polymorphism in intron 2 of human Toll-like receptor 2 gene: functional implications and racial differences. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 40:163–169
Yim JJ, Lee HW, Lee HS, Kim YW, Han SK, Shim YS, Holland SM (2006) The association between microsatellite polymorphisms in intron II of the human Toll-like receptor 2 gene and tuberculosis among Koreans. Genes Immun 7:150–155
Yoshimura A, Lien E, Ingalls RR, Tuomanen E, Dziarski R, Golenbock D (1999) Cutting edge: recognition of Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via Toll-like receptor 2. J Immunol 163:1–5
Zhu Y, Queller DC, Strassmann JE (2000) A phylogenetic perspective on sequence evolution in microsatellite loci. J Mol Evol 50:324–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yim, JJ., Adams, A.A., Kim, J.H. et al. Evolution of an intronic microsatellite polymorphism in Toll-like receptor 2 among primates. Immunogenetics 58, 740–745 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0141-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0141-2