Abstract
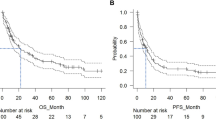
To determine whether peripheral blood absolute lymphocyte/absolute monocyte counts ratio (ALC/AMC ratio) at diagnosis predicts survival of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients treated with standard first-line regimens, we retrospectively analyzed 244 patients with DLBCL who were treated with standard cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone, or rituximab–cyclophosphamide, hydroxydaunorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. Progression-free survival and overall survival (PFS and OS) were estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method and two-tailed log-rank; The Cox proportional hazards model was used to evaluate ALC/AMC ratio as prognostic factors when adjusting for the International Prognostic Index (IPI). On univariate and multivariate analyses performed with factors included in the IPI, the ALC/AMC ratio at diagnosis remained an independent predictor of OS and PFS (OS: P < 0.001; PFS: P < 0.001). Patients with lower ALC/AMC ratio (<3.8) seemed to have lower complete remission rate, 2-year PFS and 3-year OS when compared to patients with ALC/AMC ratio ≥3.8, respectively (26 versus 90 %, P < 0.001; 18 versus 82 %, P < 0.001; 24 versus 86 %; P < 0.001, respectively). Moreover, the ALC/AMC ratio was able to further risk-stratify IPI 0-2 and three–five risk patient groups, respectively. The ALC/AMC ratio at the time of diagnosis may provide additional prognostic information beyond that of the IPI for patients with DLBCL who receive standard first-line regimens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Habermann TM (2012) New developments in the management of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematology Suppl 1:S93–S97
Friedberg JW (2011) Relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell Lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2011:498–505
(1993) A predictive model for aggressive NHL: The International non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. N Engl J Med 329: 987–994.
Rosenwald A, Wright G, Chan WC, Connors JM, Campo E, Fisher RI, Gascoyne RD, Muller-Hermelink HK, Smeland EB, Giltnane JM, Hurt EM, Zhao H, Averett L, Yang L, Wilson WH, Jaffe ES, Simon R, Klausner RD, Powell J, Duffey PL, Longo DL, Greiner TC, Weisenburger DD, Sanger WG, Dave BJ, Lynch JC, Vose J, Armitage JO, Montserrat E, López-Guillermo A, Grogan TM, Miller TP, LeBlanc M, Ott G, Kvaloy S, Delabie J, Holte H, Krajci P, Stokke T, Staudt LM (2002) The use of molecular profiling to predict survival after chemotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346:1937–1947
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E, Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, Pan Z, Farinha P, Smith LM, Falini B, Banham AH, Rosenwald A, Staudt LM, Connors JM, Armitage JO, Chan WC (2004) Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 103:275–282
Nyman H, Adde M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Taskinen M, Berglund M, Amini RM, Blomqvist C, Enblad G, Leppä S (2007) Prognostic impact of immunohistochemically defined germinal center phenotype in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Blood 109:4930–4935
Wilcox RA, Ristow K, Habermann TM, Inwards DJ, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Colgan JP, Nowakowski GS, Ansell SM, Witzig TE, Markovic SN, Porrata L (2011) The absolute monocyte and lymphocyte prognostic score predicts survival and identifies high-risk patients in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 25:1502–1509
Kim DH, Baek JH, Chae YS, Kim YK, Kim HJ, Park YH, Song HS, Chung JS, Hyun MS, Sohn SK (2007) Absolute lymphocyte counts predicts response to chemotherapy and survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 21:2227–2230
Cox MC, Nofroni I, Laverde G, Ferrari A, Amodeo R, Tatarelli C, Saltarelli F, Veggia B, Aloe-Spiriti MA, Ruco L, Monarca B (2008) Absolute lymphocyte count is a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 141:265–268
Oki Y, Yamamoto K, Kato H, Kuwatsuka Y, Taji H, Kagami Y, Morishima Y (2008) Low absolute lymphocyte count is a poor prognostic marker in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and suggests patients' survival benefit from rituximab. Eur J Haematol 81:448–453
Batty N, Ghonimi E, Feng L, Fayad L, Younes A, Rodriguez MA, Romaguera JE, McLaughlin P, Samaniego F, Kwak LW, Hagemeister FB Jr (2013) The absolute monocyte and lymphocyte prognostic index for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma who receive R-CHOP. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma 13:15–18
Li ZM, Huang JJ, Xia Y, Sun J, Huang Y, Wang Y, Zhu YJ, Li YJ, Zhao W, Wei WX, Lin TY, Huang HQ, Jiang WQ (2012) Blood lymphocyte-to-mono- cyte ratio identifies high-risk patients in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. PLoS ONE 7:e41658
Porrata LF, Ristow K, Habermann TM, Ozsan N, Dogan A, Macon W, Colgan JP, Witzig TE, Inwards DJ, Ansell SM, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Nowakowski GS, Thompson C, Markovic SN (2012) Absolute monocyte/ lymphocyte count prognostic score is independent of immunohistochemically determined cell of origin in predicting survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 53:2159–2165
Wilcox RA, Ristow K, Habermann TM, Inwards DJ, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Colgan JP, Nowakowski GS, Ansell SM, Witzig TE, Markovic SN, Porrata L (2012) The absolute monocyte count is associated with overall survival in patients newly diagnosed with follicular lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 53:575–580
Koh YW, Kang HJ, Park C, Yoon DH, Kim S, Suh C, Go H, Kim JE, Kim CW, Huh J (2012) The ratio of the absolute lymphocyte count to the absolute monocyte count is associated with prognosis in Hodgkin's lymphoma: correlation with tumor-associated macrophages. Oncologist 17:871–880
Porrata LF, Ristow K, Colgan JP, Habermann TM, Witzig TE, Inwards DJ, Ansell SM, Micallef IN, Johnston PB, Nowakowski GS, Thompson C, Markovic SN (2012) Peripheral blood lymphocyte/monocyte ratio at diagnosis and survival in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma. Haematologica 97:262–269
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Fisher RI, Hagenbeek A, Zucca E, Rosen ST, Stroobants S, Lister TA, Hoppe RT, Dreyling M, Tobinai K, Vose JM, Connors JM, Federico M, Diehl V (2007) Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:579–586
Tzankov A, Zlobec I, Went P, Robl H, Hoeller S, Dirnhofer S (2010) Prognostic immunophenotypic biomarker studies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma with special emphasis on rational determination of cut-off scores. Leuk Lymphoma 51:199–212
Kohave R (1995) A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence(IJCAI): 1137-1145.
Song MK, Chung JS, Seol YM, Kim SG, Shin HJ, Choi YJ, Cho GJ, Shin DH (2010) Influence of low absolute lymphocyte count of patients with nongerminal center type diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with R-CHOP therapy. Ann Oncol 21:140–144
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM (2007) The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109:1857–1861
Cox MC, Nofroni I, Ruco L, Amodeo R, Ferrari A, La Verde G, Cardelli P, Montefusco E, Conte E, Monarca B, Aloe-Spiriti MA (2008) Low absolute lymphocyte count is a poor prognostic factor in diffuse-large-B-cell-lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 49:1745–1751
Lenz G, Wright G, Dave SS, Xiao W, Powell J, Zhao H, Xu W, Tan B, Goldschmidt N, Iqbal J, Vose J, Bast M, Fu K, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC, Armitage JO, Kyle A, May L, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM, Troen G, Holte H, Kvaloy S, Dierickx D, Verhoef G, Delabie J, Smeland EB, Jares P, Martinez A, Lopez-Guillermo A, Montserrat E, Campo E, Braziel RM, Miller TP, Rimsza LM, Cook JR, Pohlman B, Sweetenham J, Tubbs RR, Fisher RI, Hartmann E, Rosenwald A, Ott G, Muller-Hermelink HK, Wrench D, Lister TA, Jaffe ES, Wilson WH, Chan WC, Staudt LM (2008) Stromal gene signatures in large-B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med 359:2313–2323
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 3:162–174
Schmidt H, Bastholt L, Geertsen P, Christensen IJ, Larsen S, Gehl J, von der Maase H (2005) Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts in peripheral blood are associated with poor survival in patients with metastatic melanoma: a prognostic model. Br J Cancer 93:273–278
Donskov F, von der Maase H (2006) Impact of immune parameters on long-term survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24:1997–2005
Mandrekar SJ, Schild SE, Hillman SL, Allen KL, Marks RS, Mailliard JA, Krook JE, Maksymiuk AW, Chansky K, Kelly K, Adjei AA, Jett JR (2006) A prognostic model for advanced stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. Pooled analysis of North Central cancer treatment group trials. Cancer 107:781–792
Lin Y, Gustafson MP, Bulur PA, Gastineau DA, Witzig TE, Dietz AB (2011) Immunosuppressive CD14+ HLA-DR (low)/-monocytes in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 117:872–881
Vuk-Pavlović S, Bulur PA, Lin Y, Qin R, Szumlanski CL, Zhao X, Dietz AB (2010) Immunosuppressive CD14+ HLA-DR low/-monocytes in prostate cancer. Prostate 70:443–455
Gustafson MP, Lin Y, New KC, Bulur PA, O'Neill BP, Gastineau DA, Dietz AB (2010) Systemic immune suppression in glioblastoma: the interplay between CD14 + HLA-DRlo/neg monocytes, tumor factors, and dexamethasone. Neuro Oncol 12:631–644
Gustafson MP, Abraham RS, Lin Y, Wu W, Gastineau DA, Zent CS, Dietz AB (2012) Association of an increased frequency of CD14+ HLA-DR lo/neg monocytes with decreased time to progression in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL). Br J Haematol 156:674–676
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang J, Campion LR, Kaiser EA, Snyder LA, Pollard JW (2011) CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature 475:222–225
Wolf MJ, Hoos A, Bauer J, Boettcher S, Knust M, Weber A, Simonavicius N, Schneider C, Lang M, Stürzl M, Croner RS, Konrad A, Manz MG, Moch H, Aguzzi A, van Loo G, Pasparakis M, Prinz M, Borsig L, Heikenwalder M (2012) Endothelial CCR2 signaling induced by colon carcinoma cells enables extravasation via the JAK2-Stat5 and p38MAPK pathway. Cancer Cell 22:91–105
Nakasone ES, Askautrud HA, Kees T, Park JH, Plaks V, Ewald AJ, Fein M, Rasch MG, Tan YX, Qiu J, Park J, Sinha P, Bissell MJ, Frengen E, Werb Z, Egeblad M (2012) Imaging tumor-stroma interactions during chemotherapy reveals contributions of the microenvironment to resistance. Cancer Cell 21:488–503
Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Ancuta P, Crowe S, Dalod M, Grau V, Hart DN, Leenen PJ, Liu YJ, MacPherson G, Randolph GJ, Scherberich J, Schmitz J, Shortman K, Sozzani S, Strobl H, Zembala M, Austyn JM, Lutz MB (2010) Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 116:e74–e80
Subimerb C, Pinlaor S, Lulitanond V, Khuntikeo N, Okada S, McGrath MS, Wongkham S (2010) Circulating CD14(+) CD16(+) monocyte levels predict tissue invasive character of cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Exp Immunol 16:471–479
Schauer D, Starlinger P, Reiter C, Jahn N, Zajc P, Buchberger E, Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Bergmann M, Stift A, Gruenberger T, Brostjan C (2012) Intermediate monocytes but not TIE2-expressing monocytes are a sensitive diagnostic indicator for colorectal cancer. PLoS One 7:e44450
Feng AL, Zhu JK, Sun JT, Yang MX, Neckenig MR, Wang XW, Shao QQ, Song BF, Yang QF, Kong BH, Qu X (2011) CD16+ monocytes in breast cancer patients: expanded by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and may be useful for early diagnosis. Clin Exp Immunol 164:57–65
Maffei R, Bulgarelli J, Fiorcari S, Bertoncelli L, Martinelli S, Guarnotta C, Castelli I, Deaglio S, Debbia G, De Biasi S, Bonacorsi G, Zucchini P, Narni F, Tripodo C, Luppi M, Cossarizza A, Marasca R (2013) Monocytic population in chronic lymphocytic leukemia shows altered composition and deregulation of genes involved in phagocytosis and inflammation. Haematologica 98(7):1115–1123
Randolph GJ (2011) No need to coax monocytes. Science 332:1268–1269
Hasselblom S, Hansson U, Sigurdardottir M, Nilsson-Ehle H, Ridell B, Andersson PO (2008) Expression of CD68+ tumor-associated macrophages in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its relation to prognosis. Pathol Int 58:529–532
Wada N, Zaki MA, Hori Y, Hashimoto K, Tsukaguchi M, Tatsumi Y, Ishikawa J, Tominaga N, Sakoda H, Take H, Tsudo M, Kuwayama M, Morii E, Aozasa K (2012) Tumor-associated macrophages in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study of the Osaka lymphoma study group. Histopathology 60:313–319
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the key technology projects of Anhui Province of China (no. 11010402168) and the project of Chinese National Natural Science Fund (no. 81141104).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, YL., Pan, YY., Jiao, Y. et al. Peripheral blood lymphocyte/monocyte ratio predicts outcome for patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma after standard first-line regimens. Ann Hematol 93, 617–626 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1916-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-013-1916-9