Abstract
Background
Patients with recurrent small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) have dismal outcomes. The failure of salvage therapy is due to the possible development of resistance mechanisms, such as the upregulation of the anti-apoptosis protein, Bcl-2. We conducted a phase II study to evaluate if modulation of Bcl-2 with 13-cis-retinoic acid (13-CRA) and interferon alpha could improve response rates when combined with paclitaxel in patients with recurrent SCLC.
Methods
Patients with recurrent SCLC and measurable disease were treated with interferon alpha at 6 million units/m2 subcutaneously and 13-CRA 1 mg/kg orally on days 1 and 2 and paclitaxel 75 mg/m2 intravenously on day 2 of each week for 6 weeks of an 8-week treatment cycle. Treatment was continued until disease progression, development of unacceptable toxicity, or withdrawal of consent. The primary endpoint was response rate with secondary endpoints of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). Bcl-2 levels were assessed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
Results
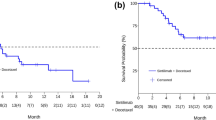
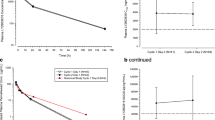
Thirty-seven patients were enrolled; 34 were included in the intention-to-treat analysis as 3 patients were ineligible for the study. There were 3 partial responses (9 %), and 5 patients had stable disease (15 %) as best response. The median PFS was 2 months, and median OS was 6.2 months. Although mean Bcl-2 protein levels decreased with therapy in PBMCs, there was no association between Bcl-2 levels and response rate or survival.
Conclusion
Despite sound pre-clinical evidence, the addition of 13-CRA and interferon alpha to paclitaxel did not improve outcomes for recurrent SCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2013) Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 63(1):11–30
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A et al (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4539–4544
Ettinger DS, Aisner J (2006) Changing face of small-cell lung cancer: real and artifact. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4526–4527
Abrams J, Doyle LA, Aisner J (1988) Staging, prognostic factors, and special considerations in small cell lung cancer. Semin Oncol 15(3):261–277
Aisner J, Alberto P, Bitran J, Comis R, Daniels J, Hansen H et al (1983) Role of chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer: a consensus report of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer workshop. Cancer Treat Rep 67(1):37–43
Sundstrom S, Bremnes RM, Kaasa S, Aasebo U, Hatlevoll R, Dahle R et al (2002) Cisplatin and etoposide regimen is superior to cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and vincristine regimen in small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized phase III trial with 5 years’ follow-up. J Clin Oncol 20(24):4665–4672
Baka S, Califano R, Ferraldeschi R, Aschroft L, Thatcher N, Taylor P et al (2008) Phase III randomised trial of doxorubicin-based chemotherapy compared with platinum-based chemotherapy in small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 99(3):442–447
von Pawel J, Schiller JH, Shepherd FA, Fields SZ, Kleisbauer JP, Chrysson NG et al (1999) Topotecan versus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine for the treatment of recurrent small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 17(2):658–667
Masuda N, Fukuoka M, Kusunoki Y, Matsui K, Takifuji N, Kudoh S et al (1992) CPT-11: a new derivative of camptothecin for the treatment of refractory or relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 10(8):1225–1229
Johnson DH, Greco FA, Strupp J, Hande KR, Hainsworth JD (1990) Prolonged administration of oral etoposide in patients with relapsed or refractory small-cell lung cancer: a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 8(10):1613–1617
Smit EF, Fokkema E, Biesma B, Groen HJ, Snoek W, Postmus PE (1998) A phase II study of paclitaxel in heavily pretreated patients with small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 77(2):347–351
Cheng S, Evans WK, Stys-Norman D, Shepherd FA (2007) Chemotherapy for relapsed small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and practice guideline. J Thorac Oncol. 2(4):348–354
Reed JC (1995) Bcl-2 family proteins: regulators of chemoresistance in cancer. Toxicol Lett 82–83:155–158
McConkey DJ, Greene G, Pettaway CA (1996) Apoptosis resistance increases with metastatic potential in cells of the human LNCaP prostate carcinoma line. Cancer Res 56(24):5594–5599
Tu SM, McConnell K, Marin MC, Campbell ML, Fernandez A, von Eschenbach AC et al (1995) Combination adriamycin and suramin induces apoptosis in bcl-2 expressing prostate carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 93(2):147–155
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LW, Hsieh JT et al (1992) Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 52(24):6940–6944
Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen MW, Day ML, Streitman JS, Buttyan R (1995) Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res 55(19):4438–4445
Kaiser U, Schilli M, Haag U, Neumann K, Kreipe H, Kogan E et al (1996) Expression of bcl-2—protein in small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 15(1):31–40
Ben-Ezra JM, Kornstein MJ, Grimes MM, Krystal G (1994) Small cell carcinomas of the lung express the Bcl-2 protein. Am J Pathol 145(5):1036–1040
Sartorius UA, Krammer PH (2002) Upregulation of Bcl-2 is involved in the mediation of chemotherapy resistance in human small cell lung cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer 97(5):584–592
Smith MA, Parkinson DR, Cheson BD, Friedman MA (1992) Retinoids in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol 10(5):839–864
Dahiya R, Boyle B, Park HD, Kurhanewicz J, Macdonald JM, Narayan P (1994) 13-cis-retinoic acid-mediated growth inhibition of DU-145 human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Mol Biol Int 32(1):1–12
Hu ZB, Minden MD, McCulloch EA (1996) Regulation of the synthesis of bcl-2 protein by growth factors. Leukemia 10(12):1925–1929
Lippman SM, Parkinson DR, Itri LM, Weber RS, Schantz SP, Ota DM et al (1992) 13-cis-retinoic acid and interferon alpha-2a: effective combination therapy for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. J Natl Cancer Inst 84(4):235–241
Lippman SM, Kavanagh JJ, Paredes-Espinoza M, Delgadillo-Madrueno F, Paredes-Casillas P, Hong WK et al (1992) 13-cis-retinoic acid plus interferon alpha-2a: highly active systemic therapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix. J Natl Cancer Inst 84(4):241–245
DiPaola RS, Weiss RE, Cummings KB, Kong FM, Jirtle RL, Anscher M et al (1997) Effect of 13-cis-retinoic acid and alpha-interferon on transforming growth factor beta1 in patients with rising prostate-specific antigen. Clin Cancer Res 3(11):1999–2004
DiPaola RS, Aisner J (1999) Overcoming bcl-2- and p53-mediated resistance in prostate cancer. Semin Oncol 26(1 Suppl 2):112–116
DiPaola RS, Rafi MM, Vyas V, Toppmeyer D, Rubin E, Patel J et al (1999) Phase I clinical and pharmacologic study of 13-cis-retinoic acid, interferon alfa, and paclitaxel in patients with prostate cancer and other advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol 17(7):2213–2218
Rudin CM, Salgia R, Wang X, Hodgson LD, Masters GA, Green M et al (2008) Randomized phase II study of carboplatin and etoposide with or without the bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide oblimersen for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: CALGB 30103. J Clin Oncol 26(6):870–876
Baggstrom MQ, Qi Y, Koczywas M, Argiris A, Johnson EA, Millward MJ et al (2011) A phase II study of AT-101 (gossypol) in chemotherapy-sensitive recurrent extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 6(10):1757–1760
Paik PK, Rudin CM, Pietanza MC, Brown A, Rizvi NA, Takebe N et al (2011) A phase II study of obatoclax mesylate, a Bcl-2 antagonist, plus topotecan in relapsed small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 74(3):481–485
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Garon EB, Ribeiro de Oliveira M, Bonomi PD, Camidge DR et al (2012) Phase II study of single-agent navitoclax (ABT-263) and biomarker correlates in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 18(11):3163–3169
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (Robert L. Comis, M.D., Chair) and supported in part by Public Health Service Grants CA23318, CA66636, CA21115, CA21076 and from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health and the Department of Health and Human Services. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pillai, R.N., Aisner, J., Dahlberg, S.E. et al. Interferon alpha plus 13-cis-retinoic acid modulation of BCL-2 plus paclitaxel for recurrent small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E6501). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 74, 177–183 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2427-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2427-7