Abstract
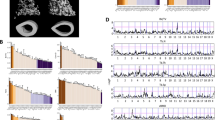
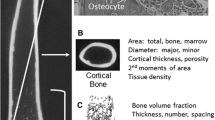
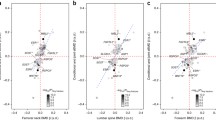
In humans, peak bone mineral density (BMD) is the primary determinant of osteoporotic fracture risk among older individuals, with high peak BMD levels providing protection against osteoporosis in the almost certain event of bone loss later in life. A genome screen to identify quantitative trait loci (QTLs) contributing to areal BMD (aBMD) and volumetric BMD (vBMD) measurements at the lumbar spine and femoral neck was completed in 595 female F2 rats produced from reciprocal crosses of inbred Fischer 344 and Lewis rats. Significant evidence of linkage was detected to rat Chromosomes 1, 2, 8, and 10, with LOD scores above 8.0. The region on rat Chromosome 8 is syntenic to human Chromosome 15, where linkage to spine and femur BMD has been previously reported and confirmed in a sample of premenopausal women.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2000) Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. NIH Consensus Statement 17(2), 1–36
Beamer WG, Shultz KL, Churchill GA, Frankel WN, Baylink DJ, et al. (1999) Quantitative trait loci for bone density in C57BL/6J and CAST/EiJ inbred mice. Mamm Genome 10, 1043–1049
Devoto M, Shimoya K, Caminis J, Ott J, Tenenhouse A, et al. (1998) First-stage autosomal genome screen in extended pedigrees suggests genes predisposing to low bone mineral density on chromosomes 1p, 2p and 4q. Eur J Hum Genet 6, 151–157
Doerge RW, Churchill GA (1996) Permutation tests for multiple loci affecting a quantitative character. Genetics 142, 285–294
Grant SF, Reid DM, Blake G, Herd R, Fogelman I, et al. (1996) Reduced bone density and osteoporosis associated with a polymorphic Sp1 binding site in the collagen type I alpha 1 gene. Nat Genet 14, 203–205
Karasik D, Myers RH, Cupples LA, Hannan MT, Gagnon DR, et al. (2002) Genome screen for quantitative trait loci contributing to normal variation in bone mineral density: the Framingham Study. J Bone Miner Res 17, 1718–1727
Klein RF, Mitchell SR, Phillips TJ, Belknap JK, Orwoll ES (1998) Quantitative trait loci affecting peak bone mineral density in mice. J Bone Miner Res 13, 1648–1656
Koller DL, Econs MJ, Morin PA, Christian JC, Hui SL, et al. (2000) Genome screen for QTLs contributing to normal variation in bone mineral density and osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85, 3116–3120
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, et al. (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1, 174–181
Marshall D, Johnell O, Wedel H (1996) Meta–analysis of how well measures of bone mineral density predict occurrence of osteoporotic fractures. BMJ 312, 1254–1259
Mesches MH, Gemma C, Veng LM, Allgeier C, Young DA, et al. (2004) Sulindac improves memory and increases NMDA receptor subunits in aged Fischer 344 rats. Neurobiol Aging 25: 315–324
Mullins LJ, Mullins JJ (2004) Insights from the rat genome sequence. Genome Biol 5, 221
Peacock M, Hustmyer FG, Hui S, Johnston CC, Christian J (1995) Vitamin D receptor genotype and bone mineral density: evidence conflicts on link. BMJ 311, 874–875
Peacock M, Turner CH, Econs MJ, Foroud T (2002) Genetics of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev 23, 303–326
Peacock M, Koller DL, Hui S, Johnston CC, Foroud T, et al. (2004) Peak bone mineral density at the hip is linked to chromosomes 14q and 15q. Osteoporos Int 15, 489–496
Sano M, Inoue S, Hosoi T, Ouchi Y, Emi M, et al. (1995) Association of estrogen receptor dinucleotide repeat polymorphism with osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217, 378–383
Sato M, Kim J, Short LL, Slemenda CW, Bryant HU (1995) Longitudinal and cross–sectional analysis of reloxifene effects on tibiae from ovariectomized aged rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272, 1252–1259
Turner CH, Roeder RK, Wieczorek A, Foroud T, Liu G, et al. (2001) Variability in skeletal mass, structure, and biomechanical properties among inbred strains of rats. J Bone Miner Res 16, 1532–1539
Turner CH, Sun Q, Schriefer J, Pitner N, Price R, et al. (2003) Congenic mice reveal sex–specific genetic regulation of femoral structure and strength. Calcif Tissue Int 73, 297–303
Wilson SG, Reed PW, Bansal A, Chiano M, Lindersson M, et al. (2003) Comparison of genome screens for two independent cohorts provides replication of suggestive linkage of bone mineral density to 3p21 and 1p36. Am J Hum Genet 72, 144–155
Zeng ZB, Kao CH, Basten CJ (1999) Estimating the genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Genet Res 74, 279–289
Zhang Y, Chong E, Herman B (2002) Age–associated increases in the activity of multiple caspases in Fisher 344 rat organs. Exp Gerontol 37, 777–789
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health through the following grants: R01AR046530 (CHT), P01AG018397 (CHT, DLK, TF, MJE), RO1 AR47866, and RO1 AR42228 (MJE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koller, D.L., Alam, I., Sun, Q. et al. Genome screen for bone mineral density phenotypes in Fisher 344 and Lewis rat strains. Mamm Genome 16, 578–586 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-004-2459-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-004-2459-0