Abstract
Introduction
Identification of lymph nodes and pathological analysis is crucial for the correct staging of colon cancer. Lymph nodes that drain directly from the tumor area are called “sentinel nodes” and are believed to be the first place for metastasis. The purpose of this study was to perform sentinel node mapping in vivo with indocyanine green and ex vivo with methylene blue in order to evaluate if the sentinel lymph nodes can be identified by both techniques.
Methods
Patients with colon cancer UICC stage I–III were included from two institutions in Denmark from February 2015 to January 2016. In vivo sentinel node mapping with indocyanine green during laparoscopy and ex vivo sentinel node mapping with methylene blue were performed in all patients.
Results
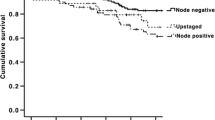
Twenty-nine patients were included. The in vivo sentinel node mapping was successful in 19 cases, and ex vivo sentinel node mapping was successful in 13 cases. In seven cases, no sentinel nodes were identified. A total of 51 sentinel nodes were identified, only one of these where identified by both techniques (2.0%). In vivo sentinel node mapping identified 32 sentinel nodes, while 20 sentinel nodes were identified by ex vivo sentinel node mapping. Lymph node metastases were found in 10 patients, and only two had metastases in a sentinel node.
Conclusion
Placing a deposit in relation to the tumor by indocyanine green in vivo or of methylene blue ex vivo could only identify sentinel lymph nodes in a small group of patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2015) Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 65(1):5–29
Danish colorectal cancer group (DCCG); annual report; 2014. http://www.dccg.dk/pdf/Aarsrapport_2014.pdf
Kobayashi H, Mochizuki H, Sugihara K et al (2007) Characteristics of recurrence and surveillance tools after curative resection for colorectal cancer: a multicenter study. Surgery 141(1):67–75
Pedrazzani C, Lauka L, Sforza S et al (2015) Management of nodal disease from colon cancer in the laparoscopic era. Int J Color Dis 30(3):303–314
Joosten JJA, Strobbe LJA, Wauters CAP, Pruszczynski M, Wobbes T, Ruers TJM (1999) Intraoperative lymphatic mapping and the sentinel node concept in colorectal carcinoma. Br J Surg 86:482–486
Sfeclan MC, Vilcea ID, Barisic G et al (2015) The sentinel lymph node significance in colorectal cancer, methods and results, general report. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 56(3):943–947
Niebling MG, Pleijhuis RG, Bastiaannet E, Brouwers AH, van Dam GM, Hoekstra HJ (2016) A systematic review and meta-analyses of sentinel lymph node identification in breast cancer and melanoma, a plea for tracer mapping. Eur J Surg Oncol 42:466–473
Ankersmit M, van der Pas MH, van Dam DA, Meijerink WJ (2011) Near infrared fluorescence lymphatic laparoscopy of the colon and mesocolon. Color Dis 13(Suppl 7):70–73
Hirche C, Mohr Z, Kneif S et al (2012) Ultrastaging of colon cancer by sentinel node biopsy using fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green. Int J Color Dis 27(3):319–324
Ceranic MS, Kecmanovic DM, Pavlov MJ et al (2010) Validation and feasibility of ex vivo sentinel lymph node “mapping” by methylene blue in colorectal cancer. Hepato-Gastroenterology 57(102–103):1113–1118
Vilcea ID, Vasile I, Mirea CS et al (2011) Sentinel lymph node study in CRC using serial sectioning and HE staining, importance and limitations. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 52(1 suppl):379–383
Park JS, Chang IT, Park SJ et al (2009) Comparison of ex vivo and in vivo injection of blue dye in sentinel lymph node mapping for colorectal cancer. World J Surg 33(3):539–546
Tuech JJ, Pessaux P, Di Fiore F et al (2006) Sentinel node mapping in colon carcinoma: in-vivo versus ex-vivo approach. Eur J Surg Oncol 32(2):158–161
Danish colorectal cancer group (DCCG); Guidelines; 2014. http://www.dccg.dk/retningslinjer/august2014/2014_colonanatomi.pdf
Kusano M, Tajima Y, Yamazaki K, Kato M, Watanabe M, Miwa M (2008) Sentinel node mapping guided by indocyanine green fluorescence imaging: a new method for sentinel node navigation surgery in gastrointestinal cancer. Dig Surg 25(2):103–108
Bembenek AE, Rosenberg R, Wagler E et al (2007) Sentinel lymph node biopsy in colon cancer: a prospective multicenter trial. Ann Surg 245(6):858–863
Liang JT, Lai HS, Huang J, Sun CT (2015) Long-term oncologic results of laparoscopic D3 lymphadenectomy with complete mesocolic excision for right-sided colon cancer with clinically positive lymph nodes. Surg Endosc 29(8):2394–2401
Saha S, Johnston G, Korant A et al (2013) Aberrant drainage of sentinel lymph nodes in colon cancer and its impact on staging and extent of operation. Am J Surg 205(3):302–306
Acknowledgements
The project was financed by internal resources and by a grant from the Beckett-Foundation. Equipment was provided by Karl Storz (Karl Storz GmbH and Co. KG, Tüttlingen, Germany) for the surgeries performed in Zealand University Hospital. We are grateful to Henrik Loft Jakobsen, MD, who led the surgical contribution to the study from Herlev Hospital.
Authors’ contribution
Helene S Andersen, Astrid L B Bennedsen, Stefan K Burgdorf, Jens R Eriksen, Anders Toxværd, Lene B Riis, Jacob Rosenberg, and Ismail Gögenur contributed for the study conception and design; Helene S Andersen, Astrid L B Bennedsen, Jens R Eriksen, Susanne Eiholm, Anders Toxværd, Lene B Riis, and Ismail Gögenur for the acquisition of data; Helene S Andersen, Astrid L B Bennedsen, and Ismail Gögenur for the analysis and interpretation of data; Helene S Andersen, Astrid L B Bennedsen, and Ismail Gögenur for the drafting of the manuscript; and Helene S Andersen, Astrid L B Bennedsen, Stefan K Burgdorf, Jens R Eriksen, Susanne Eiholm, Anders Toxværd, Lene B Riis, Jacob Rosenberg, and Ismail Gögenur for the critical revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the regional research ethics committee and the Danish Data Protection Agency. The study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT02167087) before inclusion of the first patient.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Helene Schou Andersen and Astrid Louise Bjørn Bennedsen shared the first authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersen, H.S., Bennedsen, A.L.B., Burgdorf, S.K. et al. In vivo and ex vivo sentinel node mapping does not identify the same lymph nodes in colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 32, 983–990 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2777-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-017-2777-9