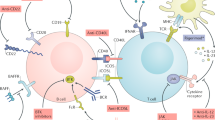
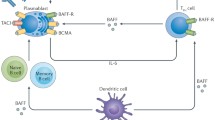
Abstract
Anti-tumor necrosis factor‑α (TNF-α)-induced lupus (ATIL) represents a diagnostic and treatment challenge. Most cases are caused by infliximab and in some cases by etanercept and adalimumab. Symptoms can range from cutaneous manifestations to more rare and serious conditions. Diagnosis requires a temporal relationship between symptoms and positive autoantibody determination. Arthritis and cutaneous symptoms are the most common manifestations accompanied by positive antinuclear antibody (ANA) and anti-double strand DNA (dsDNA) determinations. The etiology of ATILS remains to be definitively established. Several mechanisms have been proposed for anti-TNF-α-induced lupus, including apoptosis, immunosuppression and humoral autoimmunity. Treatment includes discontinuation of anti-TNF‑α agents and in some cases corticosteroids and immunosuppressors. Questions to be answered: (1) Are soluble TNF receptor fusion proteins such as etanercept and anti-TNF chimeric antibodies equally likely to cause ATIL? (2) Can patients with ATIL switch from one anti-TNF‑α antagonist to another? (3) Can the concurrent use of a conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD) like methotrexate or hydroxychloroquine reduce the probability of ATIL?
Zusammenfassung
Durch Antitumornekrosefaktor α-Antagonisten (Anti-TNF-α) induzierter Lupus (ATIL) stellt eine diagnostische und therapeutische Herausforderung dar. Die meisten Fälle werden durch Infliximab verursacht, und in einigen Fällen durch Etanercept und Adalimumab. Die Symptome reichen von kutanen Manifestationen bis hin zu selteneren und schweren Veränderungen. Für die Diagnose ist ein zeitlicher Zusammenhang zwischen den Symptomen und einer positiven Testung auf Autoantikörper erforderlich. Arthritis und kutane Symptome sind die häufigsten Manifestationen, die von positiven Untersuchungen auf antinukleäre Antikörper (ANA) und Antidoppelstrang-DNA(dsDNA)-Antikörper begleitet werden. Die Ätiologie des ATIL-Syndroms (ATILS) muss noch abschließend geklärt werden. Bisher wurden verschiedene Mechanismen für ATIL unterbreitet, einschließlich Apoptose, Immunsuppression und humoraler Autoimmunität. Zur Behandlung gehören das Absetzen von Anti-TNF-α-Antagonisten und in einigen Fällen Kortikosteroide und Immunsuppressiva. Noch zu beantwortende Fragen sind: (1) Sind lösliche TNF-Rezeptor-Fusionsproteine wie Etanercept und chimäre Anti-TNF-Antikörper gleichermaßen wahrscheinliche Auslöser für ATIL? (2) Können Patienten mit ATIL von einem Anti-TNF-α-Antagonisten zu einem anderen wechseln? (3) Kann die gleichzeitige Anwendung von einem csDMARD („conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug“) wie Methotrexat oder Hydroxychloroquin die Wahrscheinlichkeit für ATIL vermindern?
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams EL, Gadola S, Edwards CJ (2009) Anti-TNF-induced lupus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48(7):716–720
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Muñoz S, Soria N, Galiana D, Bertolaccini L, Cuadrado MJ, Khamashta MA (2007) Autoimmune diseases induced by TNF-targeted therapies: analysis of 233 cases. Medicine 86(4):242–251
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277
Perez-Alvarez R, Pérez-de-Lis M, Ramos-Casals M (2013) BIOGEAS study group. Biologics-induced autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 25(1):56–64
Katz U, Zandman-Goddard G (2010) Drug-induced lupus: an update. Autoimmun Rev 10(1):46–50
Ding T, Ledingham J, Luqmani R, Westlake S, Hyrich K, Lunt M, Kiely P, Bukhari M, Abernethy R, Bosworth A, Ostor A, Gadsby K, McKenna F, Finney D, Dixey J, Deighton C (2010) Standards, audit and guidelines working group of BSR clinical affairs committee; BHPR. BSR and BHPR rheumatoid arthritis guidelines on safety of anti-TNF therapies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49(11):2217–2219
Williams VL, Cohen PR (2011) TNF alpha antagonist-induced lupus-like syndrome: report and review of the literature with implications for treatment with alternative TNF alpha antagonists. Int J Dermatol 50(5):619–625
Mudduluru BM, Shah S, Shamah S, Swaminath A (2017) TNF-alpha antagonist induced lupus on three different agents. Postgrad Med 129(2):304–306
Costa MF, Said NR, Zimmermann B (2008) Drug induced lupus due to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha agents. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37(6):381–387
Schneider SW, Staender S, Schlutter B, Lugger TA, Bonsmann G (2006) Infliximab-induced lupus erythematosus tumidus in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Dermatol 142:115–116
Wetter DA, Davis MD (2009) Lupus-like syndrome attributable to antitumor necrosis factor alpha therapy in 14 patients during an 8‑year period at Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clin Proc 84(11):979–984
Eriksson C, Engstrand S, Sundqvist KG et al (2005) Autoantibody formation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF alpha. Ann Rheum Dis 64:403–407
Williams EL, Gadola S, Edwards CJ (2009) Anti-TNF-induced lupus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:716–720
Cambien B, Bergmeier W, Saffaripour S, Mitchell HA, Wagner DD (2003) Antithrombotic activity of TNF-alpha. J Clin Invest 112(10):1589–1596
Almoallim H, Almasari A, Khadawardi H (2011) Lupus myositis with normal creatinine kinase levels following adalimumab use in a rheumatoid arthritis patient. Turk J Rheumatol 26(4):328
Gonnet-Gracia C, Barnetche T, Richez C, Blanco P, Dehais J, Schaeverbeke T (2008) Antinuclear antibodies, anti-DNA and C4 complement evolution in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis treated with TNF-alpha blockers. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26(3):401–407
Charles PJ, Smeenk RJ, De Jong J, Feldmann M, Maini RN (2000) Assessment of antibodies to double-stranded DNA induced in rheumatoid arthritis patients following treatment with infliximab, a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor alpha: findings in open-label and randomized placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 43(11):2383–2390
de Rycke L, Baeten D, Kruithof E, Van den Bosch F, Veys E, de Keyser F (2005) Infliximab, but not etanercept, induces IgM anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibodies as main antinuclear reactivity—biologic and clinical implications in autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 52(7):2192–2201
Picardo S, So K, Venugopal K (2020) Anti-TNF-induced lupus in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. JGH Open 4:507–510
Kerbleski JF, Gottieb AB (2009) Dermatological complications and safety of anti-TNF treatments. Gut 58:1033–1039
Boehm IB, Boehm GA, Bauer R (1998) Management of cutaneous lupus erythematosus with low-dose methotrexate: indication for modulation of inflammatory mechanisms. Rheumatol Int 18(2):59–62
Bolton C, Chen Y, Hawthorne R, Schepel IRM, Harriss E, Hofmann SC, Ellis S, Clarke A, Wace H, Martin B, Smith J (2020) Systematic review: monoclonal antibody-induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Drugs R D 20(4):319–330
Ledingham J, Deighton C (2005) British society for rheumatology standards, guidelines and audit working group. Update on the British society for rheumatology guidelines for prescribing TNFalpha blockers in adults with rheumatoid arthritis (update of previous guidelines of april 2001). Rheumatology (Oxford) 44(2):157–163
Kocharla L, Mongey AB (2009) Is the development of drug-related lupus a contraindication for switching from one TNF alpha inhibitor to another? Lupus 18(2):169–171
Loebenstein M, Schulberg JD (2020) Anti-TNF Rechallenge after infliximab induced lupus in Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 158(8):2069–2071
Sifuentes Giraldo WA, Ahijón Lana M, Vázquez Díaz M (2013) Cutaneous lupus erythematosus induced by the treatment with tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Reumatol Clin 9(4):255–256
De Brandt M, Sibilia J, Le Loet X (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus induced by antitumour necrosis factor alpha therapy: a French national survey. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R445–R451
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the assistance of study participants, radiographers, study nurses and laboratory staff who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
C. Sieiro Santos, C. Álvarez Castro, C. Moriano Morales and E. Diez Alvarez declare that they have no competing interests.
This study was approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of Complejo Asistencial Universitario de León.
Additional information
Redaktion
U. Müller-Ladner, Bad Nauheim
U. Lange, Bad Nauheim
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sieiro Santos, C., Álvarez Castro, C., Moriano Morales, C. et al. Anti-TNF-α-induced lupus syndrome. Z Rheumatol 80, 481–486 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-021-00983-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-021-00983-8