Abstract
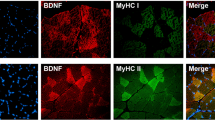
Oestrogen receptor β (ERβ) is expressed in human skeletal muscle tissue. In the present study, we have developed an immunohistochemical method to reveal if ERβ is located within the muscle fibres as well as within capillaries. Skeletal muscle biopsies were obtained from m. quadriceps femoris vastus lateralis in four healthy young subjects. Immunohistochemical triple staining was applied to transverse sections of paraffin-wax-embedded tissue. The basement membrane of muscle fibres and capillaries was identified by using an antibody to collagen IV, endothelial cells using an antibody to CD34 and ERβ using a corresponding antibody. The ERβ-positive (ERβ+) nuclei were located within the muscle fibre defined by the localisation of collagen IV. ERβ+ nuclei were also, for the first time, found in endothelial cells of capillaries in skeletal muscle tissue. Quantification was performed on transverse cryostat sections after performing a double staining (collagen IV and ERβ). It was shown that 24% of the ERβ+ nuclei were located within capillaries, and 76% were located within muscle fibres. In conclusion, ERβ in human skeletal muscle tissue is expressed not only in the muscle fibres themselves, but also within the capillary endothelial cells. This observation might improve understanding of the physiological role of oestrogen and its receptor.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcic N, Zacchigna S, Zentilin L, Ramirez-Correa G, Pattarini L, Salvi A, Sinagra G, Giacca M (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo. Mol Ther 10:844–854
Bergström J (1962) Muscle electrolytes in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 68:1–110
Crithchley HOD, Brenner RM, Henderson TA, Williams K, Nayak NR, Slayden OD, Millar MR, Saunders PTK (2001) Estrogen receptor beta, but not estrogen receptor alfa, is present in the vascular endothelium of the human and nonhuman primate endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1370–1378
Farhat MY, Lavigne MC, Ramwell PW (1996) The vascular protective effects estrogen. FASEB J 10:615–624
Gargett CE, Zaitseva M, Bucak K, Chu S, Fuller P J, Rogers PAW (2002) 17 β-estradiol up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 expression in human myometrial microvascular endothelial cells: Role of estrogen receptor-α and –β. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:4341–4349
Gustafsson T, Kraus WE (2001) Exercise-induced angiogenesis-related growth and transcription factors in skeletal muscle, and their modification in muscle pathology. Front Biosci 1:75–89
Jesmin S, Sakuma I, Hattori Y, Kitabatake A (2002) In vivo estrogen manipulations on coronary capillary network and angiogenic molecule expression in middle-aged female rats. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1591–1597
Kalluri R (2003) Basement membranes: structure, assembly and role in tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 3:422–433
Kim-Schulze S, McGowan KA, Hubchak S et al (1996) Expression of an estrogen receptor by human coronary artery and umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circulation 94:1402–1407
Malm C, Nyberg P, Engström M, Sjödin B, Lenkej R, Ekblom B, Lundberg I (2000) Immunological changes in human skeletal muscle and blood after eccentric exercise and multiple biopsies. J Physiol 529:243–262
Saji S, Jensen EV, Nilsson S, Rylander T, Warner M, Gustafsson JÅ (2000) Estrogen receptors alfa and beta in the rodent mammary gland. Med Sci 97:337–342
Taylor AH, Al-Azzawi F (2000) Immunolocalisation of oestrogen receptor beta in human tissues. J Mol Endocrinol 24:145–155
Wiik A, Glenmark B, Ekman M, Esbjörnsson-Liljedahl M, Johansson O, Bodin K, Enmark E, Jansson E (2003) Oestrogen receptor β is expressed in adult human skeletal muscle both at the mRNA and protein level. Acta Physiol Scand 179:381–387
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Swedish National Centre for Research in Sports, Swedish Research Council (14295), Åke Wibergs Stiftelse, Magnus Bergvalls Stiftelse, Centre of Gender-Related Medicine and The Cancer and Allergy Foundation (Cancer och Allergifonden). The authors wish to acknowledge Associate Professor Margaret Warner for providing the ERβ 503 antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wiik, A., Ekman, M., Morgan, G. et al. Oestrogen receptor β is present in both muscle fibres and endothelial cells within human skeletal muscle tissue. Histochem Cell Biol 124, 161–165 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0030-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0030-z