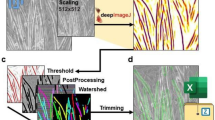
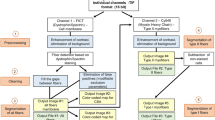
Abstract
An accurate characterisation of muscle fibres is essential for studying muscle plasticity. During some transient events such as ageing, myogenesis, physical activity or conversion of muscle to meat, the morphological parameters and/or the fibre type distribution may change. Nowadays, this information is generally obtained using immunohistology techniques, but these analyses are acknowledged to be laborious and time-consuming. In fact, each myofibre, from thousands, must be measured individually and its expression profile in response to different anti-myosin antibodies must be established step by step. In this paper, we describe a new histological approach using double-labelling (laminin, myosin) serial sections, fluorescence microscopy visualisation and, finally, semi-automatic image analysis. The goal of the study was to propose a tool allowing faster fibre type characterisation, including the identification of hybrid fibres from pure ones. The steps in the image processing prone to subjectivity have been fully automated. On the other hand, the expert retained control of all image analysis procedures requiring visual diagnosis. The tool that we developed with the Visilog software allowed a rapid and objective fibre typing and morphometric characterisation of two different bovine muscles. The results were in agreement with our previous histological and densitometric assays. The method and the tool proved to be potentially more efficient than other techniques used in our institute or described in the literature. A more global evaluation will be considered in other laboratories as well as on other animal species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol 23:369–379
Buche P, Mauron D (1997) Quantitative characterization of muscle fiber by image analysis. Comput Electron Agr 16:189–217
Cerisuelo A, Sala R, Nürnberg G, Baucells M, Rehfeldt C (2007) How many muscle samples are required to obtain reliable estimations of muscle fibre characteristics from pig longissimus muscle? Meat Sci 76:583–587
Duris MP, Picard B, Geay Y (2000) Specificity of different anti-myosin heavy chain antibodies in bovine muscle. Meat Sci 55:67–78
Guth L, Samaha FJ (1969) Qualitative differences between actomyosin ATPase of slow and fast mammalian muscle. Exp Neurol 25:138–152
Hemmings KM, Parr T, Daniel ZCTR, Picard B, Buttery PJ, Brameld JM (2009) Examination of myosin heavy chain isoform expression in ovine skeletal muscles. J Anim Sci 87:3915–3922
Henckel P, Ducro B, Oksbjerg N, Hassing L (1998) Objectivity of two methods of differentiating fibre types and repeatability of measurements by application of the TEMA image analysing system. Eur J Histochem 42:49–62
Jurie C, Picard B, Hocquette JF, Dransfield E, Micol D, Listrat A (2007) Muscle and meat quality characteristics of Holstein and Salers cull cows. Meat Sci 77:459–466
Karen P, Stevanec M, Smerdu V, Cvetko E, Kubínová L, Erzen I (2009) Software for muscle fibre type classification and analysis. Eur J Histochem 53:87–95
Lefaucheur L, Buche P, Ecolan P, Lemoing M (1992) Classification of pig myofibres and assessment of post-mortem glycogen depletion according to fibre type by computerized image analysis. Meat Sci 32:267–278
Listrat A, Picard B, Jailler R, Collignon H, Peccatte JR, Micol D, Geay Y, Dozias D (2001) Grass valorisation and muscular characteristics of blonde d’Aquitaine steers. Anim Res 50:105–118
Luthon F, Liévin M, Faux F (2004) On the use of entropy power for threshold selection. Signal Process 84:1789–1804
Miller GR, Stauber WT (1994) Use of computer-assisted analysis for myofiber size measurements of rat soleus muscles from photographed images. J Histochem Cytochem 42:377–382
Model MA, Burkhardt JK (2001) A standard for calibration and shading correction of a fluorescence microscope. Cytometry 44:309–316
Noesis (2010) Visilog 6 Programming Guide. http://www.noesis.fr/fr/download.html. Accessed 26 April 2010
Peter JB, Barnard RJ, Edgerton UR, Gillespie A, Stempel KE (1972) Metabolic profiles of three fibre types of skeletal muscle in guinea pigs and rabbits. Biochemistry 11:2627–2633
Pette D, Staron RS (1990) Cellular and molecular diversities of mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 116:1–76
Picard B, Cassar-Malek I (2009) Evidence for expression of IIb myosin heavy chain isoform in some skeletal muscles of Blonde d’Aquitaine bulls. Meat Sci 82:30–36
Picard B, Duris MP, Jurie C (1998) Classification of bovine muscle fibres by different histochemical techniques. Histochem J 30:473–479
Raats JMH, Hof D (2005) Recombinant antibody expression vectors enabling double and triple immunostaining of tissue culture cells using monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Cell Biol 84:517–521
Raheem O, Huovinen S, Suominen T, Haapasalo H, Udd B (2010) Novel myosin heavy chain immunohistochemical double staining developed for the routine diagnostic separation of I, IIA and IIX fibers. Acta Neuropathol 119:495–500
Rivero JLL, Talmadge RJ, Edgerton VR (1997) A sensitive electrophoretic method for the quantification of myosin heavy chain isoforms in horse skeletal muscle: Histochemical and immunocytochemical verifications. Electrophoresis 18:1967–1972
Sabri S, Richelme F, Pierres A, Benoliel AM, Bongrand P (1997) Interest of image processing in cell biology and immunology. J Immunol Methods 208:1–27
Schiaffino S, Gorza L, Sartore S, Saggin L, Ausoni S, Vianello M, Gundersen K, Lomo T (1989) Three myosin heavy chain isoforms in type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 10:197–205
Sifre L, Berge P, Engel E, Martin JF, Bonny JM, Listrat A, Taylor R, Culioli J (2005) Influence of the spatial organization of the perimysium on beef tenderness. J Agric Food Chem 53:8390–8399
Tomazevic D, Likar B, Pernus F (2002) Comparative evaluation of retrospective shading correction methods. J Microsc 208:212–223
Verveer PJ, Bastiaens PIH (2008) Quantitative microscopy and systems biology: seeing the whole picture. Histochem Cell Biol 130:833–843
Zitová B, Flusser J (2003) Image registration methods: a survey. Image Vision Comput 21:977–1000
Acknowledgments
The animals were provided by the ProSafeBeef European project. We would like to acknowledge the Experimental Station of the INRA Herbivores Research Unit for the management of the animals and for the slaughtering. We wish to thank David Chadeyron for the implementation of the electrophoretic analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meunier, B., Picard, B., Astruc, T. et al. Development of image analysis tool for the classification of muscle fibre type using immunohistochemical staining. Histochem Cell Biol 134, 307–317 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0733-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-010-0733-7