Abstract
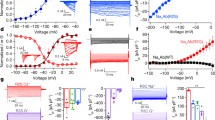
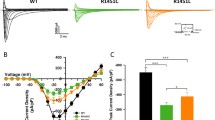
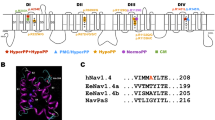
The loop connecting domains II and III of the sodium channel α-subunit is not known to have a major effect on channel gating. Recently mutations in the II-III loop of various sodium channel isoforms have been reported to cause channelopathies suggesting the functional importance of this region. In the II-III loop of the skeletal muscle isoform Nav1.4, we found a Ser-to-Thr substitution at position 906 in 5% of patients with dyskalemic periodic paralysis but also in 4% of healthy human individuals. To investigate whether this position is important for channel gating, we characterized the following amino acids at 906 by whole-cell patch-clamp experiments: Gln, Ser, Thr, Cys, Pro, Val, ordered according to their hydrophobicity. All substitutions mainly affected slow inactivation. For example, Gln caused a +13-mV right-shift of the steady-state slow inactivation curve, and entry into slow inactivation was 6 times slower compared with Ser, leading to a destabilization of the slow inactivated state; in contrast, Val, at the other end of the hydrophobicity spectrum, shifted the steady-state slow inactivation curve by –6 mV and slowed the recovery from the slow inactivated state threefold compared with Ser, resulting in an enhancement of slow inactivation. Recovery from the slow inactivated state was also slowed by Pro, Cys and Thr. Our results suggest that (1) a benign polymorphism affects channel function, (2) the II-III loop is important for slow inactivation, and (3) the effects on slow inactivation may depend on the hydrophobicity of the residue at position 906.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman MJ, Siu BL, Sturner WQ, Tester DJ, Valdivia CR, Makielski JC, Towbin JA (2001) Postmortem molecular analysis of SCN5A defects in sudden infant death syndrome. J Am Med Assoc 286:2264–2269
Alekov AK, Rahman MM, Mitrovic N, Lehmann-Horn F, Lerche H (2001) Enhanced inactivation and acceleration of activation of the sodium channel associated with epilepsy in man. Eur J Neurosci 13:2171–2176
Bendahhou S, Cummins TR, Potts JF, Tong J, Agnew WS (1995) Serine-1321-independent regulation of the μ1 adult skeletal muscle Na+ channel by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:12003–12007
Bennett ES (2001) Channel cytoplasmic loops alter voltage-dependent sodium channel activation in an isoform-specific manner. J Physiol (Lond) 535:371–381
Black SD, Mould DR (1991) Development of hydrophobicity parameters to analyze proteins which bear post- or cotranslational modifications. Anal Biochem 193:72–82
Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (1999) Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J Mol Biol 294:1351–1362
Cannon SC (2002) Sodium channel gating: no margin for error. Neuron 34:853–854
Cantrell AR, Smith RD, Goldin AL, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (1997) Dopaminergic modulation of sodium current in hippocampal neurons via cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of specific sites in the sodium channel alpha subunit. J Neurosci 17:7330–7338
Di Blasi C, He Y, Morandi L, Cornelio F, Guicheney P, Mora M (2001) Mild muscular dystrophy due to a nonsense mutation in the LAMA2 gene resulting in exon skipping. Brain 124:698–704
Escayg A, Heils A, MacDonald BT, Haug K, Sander T, Meisler MH (2001) A novel SCN1A mutation associated with generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus and prevalence of variants in patients with epilepsy. Am J Hum Genet 68:866–873
Fitzgerald EM, Okuse K, Wood JN, Dolphin AC, Moss SJ (1999) cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of the tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-dependent sodium channel SNS. J Physiol (Lond) 516 (Pt 2):433–446
Fujiwara T, Sugawara T, Mazaki-Miyazaki E, Takahashi Y, Fukushima K, Watanabe M, Hara K, Morikawa T, Yagi K, Yamakawa K, Inoue Y (2003) Mutations of sodium channel alpha subunit type 1 (SCN1A) in intractable childhood epilepsies with frequent generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Brain 126:531–546
Green DS, Hayward LJ, George AL Jr., Cannon SC (1997) A proposed mutation, Val781Ile, associated with hyperkalemic periodic paralysis and cardiac dysrhythmia is a benign polymorphism. Ann Neurol 42:253–256
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 391:85–100
Hayward LJ, Sandoval GM, Cannon SC (1999) Defective slow inactivation of sodium channels contributes to familial periodic paralysis. Neurology 52:1447–1453
Janin J (1979) Surface and inside volumes in globular proteins. Nature 277:491–492
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Lossin C, Wang DW, Rhodes TH, Vanoye CG, George AL Jr (2002) Molecular basis of an inherited epilepsy. Neuron 34:877–884
Makita N, Horie M, Nakamura T, Ai T, Sasaki K, Yokoi H, Sakurai M, Sakuma I, Otani H, Sawa H, Kitabatake A (2002) Drug-induced long-QT syndrome associated with a subclinical SCN5A mutation. Circulation 106:1269–1274
Murphy BJ, Rossie S, De Jongh KS, Catterall WA (1993) Identification of the sites of selective phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatases. J Biol Chem 268:27355–27362
Murphy BJ, Rogers J, Perdichizzi AP, Colvin AA, Catterall WA (1996) cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of two sites in the alpha subunit of the cardiac sodium channel. J Biol Chem 271:28837–28843
Noda M, Shimizu S, Tanabe T, Takai T, Kayano T, Ikeda T, Takahashi H, Nakayama H, Kanaoka Y, Minamino N, et al (1984) Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature 312:121–127
Noda M, Ikeda T, Kayano T, Suzuki H, Takeshima H, Kurasaki M, Takahashi H, Numa S (1986) Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature 320:188–192
Rieger R, Michailis A, Green MM (1991) Glossary of genetics, fifth edition. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Rose GD, Geselowitz AR, Lesser GJ, Lee RH, Zehfus MH (1985) Hydrophobicity of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Science 229:834–838
Rossie S, Catterall WA (1987) Cyclic-AMP-dependent phosphorylation of voltage-sensitive sodium channels in primary cultures of rat brain neurons. J Biol Chem 262:12735–12744
Rossie S, Catterall WA (1989) Phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of rat brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent protein kinase at a new site containing Ser686 and Ser687. J Biol Chem 264:14220–14224
Schreibmayer W, Frohnwieser B, Dascal N, Platzer D, Spreitzer B, Zechner R, Kallen RG, Lester HA (1994) Beta-adrenergic modulation of currents produced by rat cardiac Na+ channels expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Receptors Channels 2:339–350
Schwartz PJ, Priori SG, Dumaine R, Napolitano C, Antzelevitch C, Stramba-Badiale M, Richard TA, Berti MR, Bloise R (2000) A molecular link between the sudden infant death syndrome and the long-QT syndrome. N Engl J Med 343:262–267
Smith RD, Goldin AL (1996) Phosphorylation of brain sodium channels in the I--II linker modulates channel function in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci 16:1965–1974
Smith RD, Goldin AL (1997) Phosphorylation at a single site in the rat brain sodium channel is necessary and sufficient for current reduction by protein kinase A. J Neurosci 17:6086–6093
Smith RD, Goldin AL (2000) Potentiation of rat brain sodium channel currents by PKA in Xenopus oocytes involves the I-II linker. Am J Physiol 278:C638–C645
Splawski I, Shen J, Timothy KW, Lehmann MH, Priori S, Robinson JL, Moss AJ, Schwartz PJ, Towbin JA, Vincent GM, Keating MT (2000) Spectrum of mutations in long-QT syndrome genes. KVLQT1, HERG, SCN5A, KCNE1, and KCNE2. Circulation 102:1178–1185
Struyk AF, Scoggan KA, Bulman DE, Cannon SC (2000) The human skeletal muscle Na channel mutation R669H associated with hypokalemic periodic paralysis enhances slow inactivation. J Neurosci 20:8610–8617
Stühmer W, Conti F, Suzuki H, Wang XD, Noda M, Yahagi N, Kubo H, Numa S (1989) Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature 339:597–603
West JW, Numann R, Murphy BJ, Scheuer T, Catterall WA (1991) A phosphorylation site in the Na+ channel required for modulation by protein kinase C. Science 254:866–868
Wolfenden R, Andersson L, Cullis PM, Southgate CC (1981) Affinities of amino acid side chains for solvent water. Biochemistry 20:849–855
Acknowledgements
We thank Vanesa Muncan for mutagenesis. This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG) (Mi 472/5–1 and JU 470/1) and the IHP Program of the European Community (HPRN-CT-2002–00331).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzmenkin, A., Jurkat-Rott, K., Lehmann-Horn, F. et al. Impaired slow inactivation due to a polymorphism and substitutions of Ser-906 in the II-III loop of the human Nav1.4 channel. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 447, 71–77 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1137-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1137-5