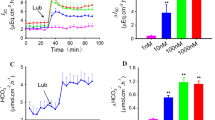
Abstract
The colonic epithelium absorbs and secretes electrolytes and water. Ion and water absorption occurs primarily in surface cells, whereas crypt cells perform secretion. Ion transport in distal colon is regulated by aldosterone, which stimulates both Na+ absorption and K+ secretion. The electrogenic Na+ absorption is mediated by epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) in surface cells. Previously, we identified the large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel, KCa1.1 or big potassium (BK) channel, as the only relevant K+ secretory pathway in mouse distal colon. The exact localisation of KCa1.1 channels along the crypt axis is, however, still controversial. The aim of this project was to further define the localisation of the KCa1.1 channel in mouse distal colonic epithelium. Through quantification of mRNA extracted from micro-dissected surface and crypt cells, we confirmed that Na+/K+/2Cl− (NKCC1) is expressed primarily in the crypts and γ-ENaC primarily in the surface cells. The KCa1.1 α-subunit mRNA was like NKCC1, mainly expressed in the crypts. The crypt to surface expression pattern of the channels and transporters was not altered when plasma aldosterone was elevated. The mRNA levels for NKCC1, γ-ENaC and KCa1.1 α-subunit were, however, under these circumstances substantially augmented (KCa1.1 α-subunit, twofold; NKCC1, twofold and ENaC, tenfold). Functionally, we show that ENaC-mediated Na+ absorption and BK channel-mediated K+ secretion are two independent processes. These findings show that KCa1.1-mediated K+ secretion mainly occurs in the crypts of the murine distal colon. This is in agreement with the general model of ion secretion being preferentially located to the crypt and not surface enterocytes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder HJ, Sandle GI (1994) Electrolyte transport in the mammalian colon. N Y 3:2133–2171
Butterfield I, Warhurst G, Jones MN, Sandle GI (1997) Characterization of apical potassium channels induced in rat distal colon during potassium adaptation. J Physiol 501:537–547
Duc C, Farman N, Canessa CM, Bonvalet JP, Rossier BC (1994) Cell-specific expression of epithelial sodium channel alpha, beta, and gamma subunits in aldosterone-responsive epithelia from the rat: localization by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. J Cell Biol 127:1907–1921
Garty H, Palmer LG (1997) Epithelial sodium channels: function, structure, and regulation. Physiol Rev 77:359–451
Greger R, Bleich M, Leipziger J, Ecke D, Mall M, Kunzelmann K (1997) Regulation of ion transport in colonic crypts. NIPS 12:62–66
Grotjohann I, Gitter AH, Kockerling A, Bertog M, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (1998) Localization of cAMP- and aldosterone-induced K+ secretion in rat distal colon by conductance scanning. J Physiol 507:561–570
Grunnet M, Knaus HG, Solander C, Klaerke DA (1999) Quantification and distribution of Ca2+- activated maxi K+ channels in rabbit distal colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 277:G22–G30
Halm DR, Halm ST (1994) Aldosterone stimulates K secretion prior to onset of Na absorption in guinea pig distal colon. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 266:C552–C558
Hay-Schmidt A, Grunnet M, Abrahamse SL, Knaus HG, Klaerke DA (2003) Localization of Ca2+-activated big-conductance K+ channels in rabbit distal colon. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol 446:61–68
Kunzelmann K, Mall M (2002) Electrolyte transport in the mammalian colon: mechanisms and implications for disease. Physiol Rev 82:245–289
Moreto M, Planas JM, Naftalin RJ (1981) Effects of secretagogues on the K+ permeability of mucosal and serosal borders of rabbit colonic mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta 648:215–224
Pena-Munzenmayer G, Catalan M, Cornejo I, Figueroa CD, Melvin JE, Niemeyer MI, Cid LP, Sepulveda FV (2005) Basolateral localization of native ClC-2 chloride channels in absorptive intestinal epithelial cells and basolateral sorting encoded by a CBS-2 domain di-leucine motif. J Cell Sci 118:4243–4252
Perry MD, Sandle GI (2009) Regulation of colonic apical potassium (BK) channels by cAMP and somatostatin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G159–G167
Puntheeranurak S, Schreiber R, Spitzner M, Ousingsawat J, Krishnamra N, Kunzelmann K (2007) Control of ion transport in mouse proximal and distal colon by prolactin. Cell Physiol Biochem 19:77–88
Rechkemmer G, Halm DR (1989) Aldosterone stimulates K+ secretion across mammalian colon independent of Na+ absorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:397–401
Reynolds A, Parris A, Evans LA, Lindqvist S, Sharp P, Lewis M, Tighe R, Williams MR (2007) Dynamic and differential regulation of NKCC1 by calcium and cAMP in the native human colonic epithelium. J Physiol 582:507–524
Sandle GI, Perry MD, Mathialahan T, Linley JE, Robinson P, Hunter M, MacLennan KA (2007) Altered cryptal expression of luminal potassium (BK) channels in ulcerative colitis. J Pathol 212:66–73
Sausbier M, Matos JE, Sausbier U, Beranek G, Arntz C, Neuhuber W, Ruth P, Leipziger J (2006) Distal colonic K+ secretion occurs via BK channels. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1275–1282
Sorensen MV, Matos JE, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2010) Colonic potassium handling. Pflugers Arch 459:645–656
Sorensen MV, Matos JE, Sausbier M, Sausbier U, Ruth P, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2008) Aldosterone increases KCa1.1 (BK)-channel-mediated colonic K+ secretion. J Physiol 586:4251–4264
Sorensen MV, Sausbier M, Ruth P, Seidler U, Riederer B, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2010) Adrenaline-induced colonic K+ secretion is mediated by KCa1.1 (BK) channels. J Physiol 588:1763–1777
Sweiry JH, Binder HJ (1989) Characterization of aldosterone-induced potassium secretion in rat distal colon. J Clin Invest 83:844–851
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sørensen, M.V., Strandsby, A.B., Larsen, C.K. et al. The secretory KCa1.1 channel localises to crypts of distal mouse colon: functional and molecular evidence. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 462, 745–752 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-1000-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-1000-z