Abstract
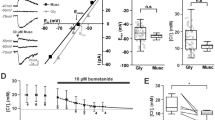
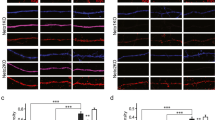
Cajal–Retzius (CR) cells, early generated neurons in the marginal zone of developing neocortex, are reported to be highly vulnerable to excitotoxic damage. Because extracellular glutamate concentration in the central nervous system is mainly controlled by glutamate transporters (EAATs), we studied the effects of EAAT blockade on CR cells. dl-TBOA, a specific EAAT antagonist, induced NMDA receptor-dependent bursting discharges in layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons, indicating that EAATs operate in the uptake mode and their blockade leads to elevation of extracellular glutamate concentration. In CR cells, however, dl-TBOA failed to change either the membrane resistance or holding current, and moreover, it reduced the frequency of spontaneous GABAergic postsynaptic currents. dl-TBOA decreased the mean amplitude and increased paired-pulse ratio of evoked GABAergic postsynaptic currents, indicating the presynaptic locus of its action. Indeed, LY379268, a specific agonist of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR-II), mimicked the dl-TBOA-mediated effects, and LY341495, an unspecific mGluR antagonist, eliminated the dl-TBOA-induced effects. As dihydrokainic acid, a specific EAAT2 blocker, failed to affect evoked GABAergic postsynaptic currents, whereas TFB-TBOA, a selective blocker of EAAT1 and EAAT2, produced effects similar to that of dl-TBOA, extracellular glutamate concentration in the marginal zone is mainly controlled by EAAT1 (GLAST). Thus, even though CR cells are highly vulnerable to excitotoxic damage, a number of mechanisms serve to protect them against excessive extracellular glutamate concentration including a lack of functional glutamatergic synapses, Mg2+ blockade of NMDA receptors, and presynaptic mGluRs that inhibit transmission at GABAergic synapses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilles K, Okabe A, Ikeda M, Shimizu-Okabe C, Yamada J, Fukuda A, Luhmann HJ, Kilb W (2007) Kinetic properties of Cl uptake mediated by Na+-dependent K+-2Cl cotransport in immature rat neocortical neurons. J Neurosci 27:8616–8627
Balslev Y, Saunders NR, Mollgard K (1996) Synaptogenesis in the neocortical anlage and early developing neocortex of rat embryos. Acta Anat (Basel) 156:2–10
Behar TN, Schaffner AE, Scott CA, Greene CL, Barker JL (2000) GABA receptor antagonists modulate postmitotic cell migration in slice cultures of embryonic rat cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:899–909
Behar TN, Scott CA, Greene CL, Wen X, Smith SV, Maric D, Liu QY, Colton CA, Barker JL (1999) Glutamate acting at NMDA receptors stimulates embryonic cortical neuronal migration. J Neurosci 19:4449–4461
Chan CH, Yeh HH (2003) Enhanced GABAA receptor-mediated activity following activation of NMDA receptors in Cajal-Retzius cells in the developing mouse neocortex. J Physiol (Lond) 550:103–111
D’Arcangelo G, Nakajima K, Miyata T, Ogawa M, Mikoshiba K, Curran T (1997) Reelin is a secreted glycoprotein recognized by the CR-50 monoclonal antibody. J Neurosci 17:23–31
Danbolt NC (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog Neurobiol 65:1–105
Demarque M, Villeneuve N, Manent JB, Becq H, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y, Aniksztejn L (2004) Glutamate transporters prevent the generation of seizures in the developing rat neocortex. J Neurosci 24:3289–3294
During MJ, Ryder KM, Spencer DD (1995) Hippocampal GABA transporter function in temporal-lobe epilepsy. Nature 376:174–177
Frotscher M (1998) Cajal–Retzius cells, Reelin, and the formation of layers. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8:570–575
Furuta A, Rothstein JD, Martin LJ (1997) Glutamate transporter protein subtypes are expressed differentially during rat CNS development. J Neurosci 17:8363–8375
Hirai K, Yoshioka H, Kihara M, Hasegawa K, Sakamoto T, Sawada T, Fushiki S (1999) Inhibiting neuronal migration by blocking NMDA receptors in the embryonic rat cerebral cortex: a tissue culture study. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 114:63–67
Hu B, McDonald JW, Johnston MV, Silverstein FS (1991) Excitotoxic brain injury suppresses striatal high-affinity glutamate uptake in perinatal rats. J Neurochem 56:933–937
Ikonomidou C, Price MT, Mosinger JL, Frierdich G, Labruyere J, Salles KS, Olney JW (1989) Hypobaric-ischemic conditions produce glutamate-like cytopathology in infant rat brain. J Neurosci 9:1693–1700
Jakobs KH, Lasch P, Minuth M, Aktories K, Schultz G (1982) Uncoupling of alpha-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of human platelet adenylate cyclase by N-ethylmaleimide. J Biol Chem 257:2829–2833
Kirischuk S, Verkhratsky A (1996) [Ca2+]i recordings from neural cells in acutely isolated cerebellar slices employing differential loading of the membrane- permeant form of the calcium indicator fura-2. Pflugers Arch 431:977–983
Kirmse K, Dvorzhak A, Grantyn R, Kirischuk S (2008) Developmental down-regulation of excitatory GABAergic transmission in neocortical layer I via presynaptic adenosine A1 receptors. Cereb Cortex 18:424–432
Kirmse K, Dvorzhak A, Henneberger C, Grantyn R, Kirischuk S (2007) Cajal-Retzius cells in the mouse neocortex receive two types of pre- and postsynaptically distinct GABAergic inputs. J Physiol 585:881–895
Kirmse K, Kirischuk S (2006) Ambient GABA constrains the strength of GABAergic synapses at Cajal–Retzius cells in the developing visual cortex. J Neurosci 26:4216–4227
Kirmse K, Kirischuk S (2006) N-ethylmaleimide increases release probability at GABAergic synapses in layer I of the mouse visual cortex. Eur J Neurosci 24:2741–2748
Lu SM, Zecevic N, Yeh HH (2001) Distinct NMDA and AMPA receptor-mediated responses in mouse and human Cajal–Retzius cells. J Neurophysiol 86:2642–2646
Manent JB, Demarque M, Jorquera I, Pellegrino C, Ben Ari Y, Aniksztejn L, Represa A (2005) A noncanonical release of GABA and glutamate modulates neuronal migration. J Neurosci 25:4755–4765
Marin-Padilla M (1998) Cajal–Retzius cells and the development of the neocortex. Trends Neurosci 21:64–71
Martinez-Galan JR, Lopez-Bendito G, Lujan R, Shigemoto R, Fairen A, Valdeolmillos M (2001) Cajal–Retzius cells in early postnatal mouse cortex selectively express functional metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Neurosci 13:1147–1154
Matsugami TR, Tanemura K, Mieda M et al (2006) Indispensability of the glutamate transporters GLAST and GLT1 to brain development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12161–12166
Mienville JM (1998) Persistent depolarizing action of GABA in rat Cajal–Retzius cells. J Physiol 512:809–817
Mienville JM, Barker JL (1997) Potassium current expression during prenatal corticogenesis in the rat. Neuroscience 81:163–172
Mienville JM, Pesold C (1999) Low resting potential and postnatal upregulation of NMDA receptors may cause Cajal–Retzius cell death. J Neurosci 19:1636–1646
Minelli A, Barbaresi P, Conti F (2003) Postnatal development of high-affinity plasma membrane GABA transporters GAT-2 and GAT-3 in the rat cerebral cortex. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 142:7–18
Minelli A, DeBiasi S, Brecha NC, Zuccarello LV, Conti F (1996) GAT-3, a high-affinity GABA plasma membrane transporter, is localized to astrocytic processes, and it is not confined to the vicinity of GABAergic synapses in the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 16:6255–6264
Olsen RW, Sieghart W (2008) International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors: classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacol Rev 60:243–260
Owens DF, Kriegstein AR (2002) Is there more to GABA than synaptic inhibition? Nat Rev Neurosci 3:715–727
Radnikow G, Feldmeyer D, Lubke J (2002) Axonal projection, input and output synapses, and synaptic physiology of Cajal–Retzius cells in the developing rat neocortex. J Neurosci 22:6908–6919
Ramon y Cajal S (1911) Histologie du systeme nerveux de l’homme et des vertebres. Maloine, Paris, France, pp 407–413
Regan MR, Huang YH, Kim YS, Dykes-Hoberg MI, Jin L, Watkins AM, Bergles DE, Rothstein JD (2007) Variations in promoter activity reveal a differential expression and physiology of glutamate transporters by glia in the developing and mature CNS. J Neurosci 27:6607–6619
Reiprich P, Kilb W, Luhmann HJ (2005) Neonatal NMDA receptor blockade disturbs neuronal migration in rat somatosensory cortex in vivo. Cereb Cortex 15:349–358
Represa A, Ben-Ari Y (2005) Trophic actions of GABA on neuronal development. Trends Neurosci 28:278–283
Shibata T, Watanabe M, Tanaka K, Wada K, Inoue Y (1996) Dynamic changes in expression of glutamate transporter mRNAs in developing brain. Neuroreport 7:705–709
Shimamoto K, Sakai R, Takaoka K, Yumoto N, Nakajima T, Amara SG, Shigeri Y (2004) Characterization of novel l-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate derivatives, potent blockers of the glutamate transporters. Mol Pharmacol 65:1008–1015
Soda T, Nakashima R, Watanabe D, Nakajima K, Pastan I, Nakanishi S (2003) Segregation and coactivation of developing neocortical layer 1 neurons. J Neurosci 23:6272–6279
Soriano E, del Rio JA (2005) The cells of Cajal–Retzius: still a mystery one century after. Neuron 46:389–394
Super H, del Rio JA, Martinez A, Perez-Sust P, Soriano E (2000) Disruption of neuronal migration and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex following ablation of Cajal–Retzius cells. Cereb Cortex 10:602–613
Super H, Soriano E, Uylings HBM (1998) The functions of the preplate in development and evolution of the neocortex and hippocampus. Brain Res Rev 27:40–64
Varoqueaux F, Sigler A, Rhee JS, Brose N, Enk C, Reim K, Rosenmund C (2002) Total arrest of spontaneous and evoked synaptic transmission but normal synaptogenesis in the absence of Munc13-mediated vesicle priming. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:9037–9042
Verhage M, Maia AS, Plomp JJ et al (2000) Synaptic assembly of the brain in the absence of neurotransmitter secretion. Science 287:864–869
Voutsinos-Porche B, Knott G, Tanaka K, Quairiaux C, Welker E, Bonvento G (2003) Glial glutamate transporters and maturation of the mouse somatosensory cortex. Cereb Cortex 13:1110–1121
Acknowledgments
The technical assistance of Mrs. Kerstin Rückwardt is highly appreciated. This study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (KI1093/1-2 to SK) and by Stiftung Rheinland-Pfalz für Innovation (961-386261/955 to SK). We thank Dr. Werner Kilb and Prof. Heiko Luhmann for the helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dvorzhak, A., Unichenko, P. & Kirischuk, S. Glutamate transporters and presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors protect neocortical Cajal–Retzius cells against over-excitation. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 464, 217–225 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1109-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1109-8