Abstract
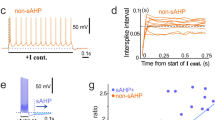
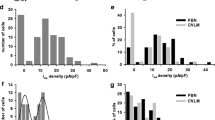
A transient K+ current in cultured olfactory bulb neurons of Xenopus tadpoles was studied using the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. The current, which was resistant to 80 mM tetraethylammoniumchloride (TEA) and 10 nM charybdotoxin but blocked by 5 mM 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), activated between −60 and −4C mV and showed time-and voltage-dependent inactivation. Its peak amplitude was nearly independent of the extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]o) in the range of 0.05 to 10 mM, indicating that its conductance increased upor increasing [K+]o. The transient K+ current showed a slow recovery from inactivation with the time for half-maximum recovery from a conditioning pulse to 80 mV for 1 s varying from 100 ms to 500 ms. Complete recovery required as much as 5–10 s at −80 mV, but could be speed-ed up at hyperpolarized potentials. The current resemble; the RCK4 (Kv1.4) current of rat neurons except that it; recovery from inactivation was independent of [K+]o. High-freqency stimulation (20–67 Hz) of the neurons with short (5 ms) voltage pulses resulted in a frequency-dependent, progressive inactivation of the transient K+ current. This suggests that, during phasic responses of ol-factory bulb neurons, inactivation of the transient K+ current occurs and may lead to lengthening of action potentials and facilitation of synaptic transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischofberger J, Schild D (1995) Different spatial patterns of [Ca2+] increase caused by N-and L-type Ca2+ channel activation in frog olfactory bulb neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 487:305–317
Bischofberger J, Geiling H, Engel J, Schultens HA, Schild D (1995) A cultured network of olfactory bulb neurons of Xeno-pus laevis tadpoles: calcium imaging and spontaneous activity. Adv Biosci 93:133–139
Carmeliet E (1989) K+ channels in cardiac cells: mechanisms of activation, inactivation, rectification and K+e sensitivity. Pflügers Arch 414:S88-S92
Connor JA, Stevens CF (1971) Voltage clamp studies of a transient outward membrane current in gastropod neural somata. J Physiol (Lond) 213:21–30
Dubois JM (1981) Evidence for the existence of three types of potassium channels in the frog Ranvier node membrane. J Physiol (Lond) 318:297–316
Hamil OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hamilton KA, Kauer JS (1985) Intracellular potentials of salamander mitral/tufted neurons in response to odor stimulation. Brain Res 338:181–185
Hille B (1992) Ionic channels of excitable membranes, 2nd edn. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
Kauer JS (1974) Response patterns of amphibian olfactory bulb to odour stimulation. J Physiol (Lond) 243:675–715
Kauer JS, Shepherd GM (1977) Analysis of the onset phase of olfactory bulb unit response to odour pulses in the salamander. J Physiol (Lond) 272:495–516
Kues WA, Wunder F (1992) Heterogeneous expression patterns of mammalian potassium channel genes in developing and adult rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 4:1296–1308
Ludewig U, Lorra C, Pongs O, Heinemann SH (1993) A site accessible to extracellular TEA+ and K+ influences intracellular Mg2+ block of cloned potassium channels. Eur Biophys J 22:237–247
Lynch JW, Barry PH (1989) Action potentials initiated by single channel opening in a small neuron (rat olfactory receptor). Biophys J 55:755–768
Pardo LA, Heinemann SH, Terlau H, Ludewig U, Lorra C, Pongs O, Stühmer W (1992) Extracellular K+ specifically modulates a rat brain K+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:2466–2470
Rizzo MA, Nonner W (1992) Transient K current in the somatic membrane of cultured central neurons of embryonic rat. J Neurophysiol 68:1708–1719
Ruppersberg JP, Stocker M, Pongs O, Heinemann SH, Frank R, Koenen M (1991) Regulation of fast inactivation of cloned mammalian IK(A) channels by cysteine oxidation. Nature 352:711–714
Ruppersberg JP, Ermler M, Knopf M, Kues W, Jonas P, Koenen M (1993) Properties of Shaker-homologous potassium channels expressed in the mammalian brain. Cell Physiol Biochem 3:250–269
Safronov BV, Vogel W (1995) Modulation of delayed rectifier K+ channel activity by external K+ ions in Xenopus axon. Pflügers Arch 430:879–886
Schild D, Lischka FW (1994) Amiloride-insensitive cation conductance in Xenopus laevis olfactory neurons: a combined patch clamp and calcium imaging analysis. Biophys J 66:299–304
Schwarz JR, Vogel W (1971) Potassium inactivation in single myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. Pflügers Arch 330: 61–73
Stuart GJ, Sakmann B (1994) Active propagation of somatic action potentials into neocortical pyramidal cell dendrites. Nature 367:69–72
Stühmer W, Ruppersberg JP, Schröter KH, Sakmann B, Stocker M, Giese KP, Perschke A, Baumann A, Pongs O (1989) Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J 8:3235–3244
Tseng GN, Tseng-Crank J (1992) Differential effects of elevating [K]o on three transient outward potassium channels. Circ Res 71:657–672
Vogel W, Schwarz JR (1995) Voltage-clamp studies in axons: macroscopic and single channel currents. In: Waxman SG, Kocsis JD, Stys PK (ed) The axon. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 257–280
Yao JA, Tseng GN (1994) Modulation of 4-AP block of a mammalian A-type K channel clone by channel gating and membrane voltage. Biophys J 67:130–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engel, J., Rabba, J. & Schild, D. A transient, RCK4-like K+ current in cultured Xenopus olfactory bulb neurons. Pflügers Arch. 432, 845–852 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050207