Abstract
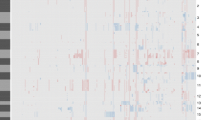
Thirty-nine glial tumours (28 glioblastomas (GB) and 11 low-grade gliomas) were investigated with DNA microarrays to reveal a possible specific gene expression profile. Unsupervised classification through hierarchical cluster analysis identified two groups of tumours, the first composed of low-grade gliomas and the second mainly composed of GB. Nine genes were identified as most informative: seven were over-expressed in low-grade gliomas and under-expressed in GB; on the contrary, two genes, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) and cell division cycle 20 homologue (CDC20), were over-expressed in GB and under-expressed in low-grade tumours. This same genetic profile was confirmed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Immunohistochemistry for IGFBP-2 was positive in 88.8% of the cases of GB and in only one low-grade glioma, whilst CDC20 immunostained 74.1% of the cases of GB and none low-grade glioma. This was confirmed in an additional series of cases studied with immunohistochemistry only. In conclusion, over-expression of mRNA levels of IGFBP-2 and CDC20 is highly related to GB, IGFBP-2 and CDC-20 gene and protein expressions are strongly correlated, and IGFBP-2 and CDC20 immunopositivity can be useful for the identification of GB in small biopsies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) World Health Organization classification of tumours of the central nervous system. IARC, Lyon
Coons SW, Johnson PC, Scheithauer BW et al (1997) Improving diagnostic accuracy and interobserver concordance in the classification and grading of primary gliomas. Cancer 79:1381–1393
Nutt CL, Mani DR, Betensky RA et al (2003) Gene expression-based classification of malignant gliomas correlates better with survival than histological classification. Cancer Res 63:1602–1607
Reifenberger G, Louis DN (2003) Oligodendroglioma: toward molecular definitions in diagnostic neuro-oncology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:111–126
Gajjar A, Hernan R, Kocak M et al (2004) Clinical, histopathologic and molecular markers of prognosis: toward a new disease risk stratification system for medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22:984–993
Pomeroy SL, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M et al (2002) Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature 415:436–442
Lossos IS, Czerwinski DK, Alizadeh AA et al (2004) Prediction of survival in diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma based on the expression of six genes. N Engl J Med 350:1828–1837
van ‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ et al (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415:530–536
Zahrak M, Parmigiani G, Wayne Y (2007) Pre-processing Agilent microarray data. BMC Bioinformatics 8:142
Smyth GK, Speed TP (2003) Normalization of cDNA microarry data. Methods 31:265–273
Tibshirani R, Hastie T, Narasimhan B et al (2002) Diagnosis of multiple cancer types by shrunken centroids of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:6567–6572
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:1–10
Pattyn F, Speleman F, De Paepe A et al (2003) RTPrimerDB: the real-time PCR primer and probe database. Nucleic Acids Res 31:122–123
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F et al (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 18:3–4
Flyvbjerg A, Mogensen O, Mogensen B et al (1997) Elevated serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) and decreased IGFBP-3 in epithelial ovarian cancer: correlation with cancer antigen 125 and tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2308–2313
el Atiq F, Garrouste F, Remacle-Bonnet M et al (1994) Alterations in serum levels of insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth-factor-binding proteins in patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 57:491–497
Ho PJ, Baxter RC (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in patients with prostate carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Endocrinol 46:333–342
Richardsen E, Ukkonen T, Bjørnsen T et al (2003) Overexpression of IGBFB2 is a marker for malignant transformation in prostate epithelium. Virchows Arch 442:329–335
Ranke MB, Maier KP, Schweizer R et al (2003) Pilot study of elevated levels of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 as indicators of hepatocellular carcinoma. Horm Res 60:174–180
Russo VC, Schütt BS, Andaloro E et al (2005) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 binding to extracellular matrix plays a critical role in neuroblastoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Endocrinology 146:4445–4455
Dunlap SM, Celestino J, Wang H et al (2007) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 promotes glioma development and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:11736–11741
Wang H, Wang H, Shen W et al (2003) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 enhances glioblastoma invasion by activating invasion-enhancing genes. Cancer Res 63:4315–4321
Godard S, Getz G, Delorenzi M et al (2003) Classification of human astrocytic gliomas on the basis of gene expression: a correlated group of genes with angiogenic activity emerges as a strong predictor of subtypes. Cancer Res 63:6613–6625
Fang G, Yu H, Kirschner MW (1998) Direct binding of CDC20 protein family members activates the anaphase-promoting complex in mitosis and G1. Mol Cell 2:163–171
Ouellet V, Guyot MC, Le Page C et al (2006) Tissue array analysis of expression microarray candidates identifies markers associated with tumor grade and outcome in serous epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 119:599–607
Kim JM, Sohn HY, Yoon SY et al (2005) Identification of gastric cancer-related genes using a cDNA microarray containing novel expressed sequence tags expressed in gastric cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11:473–482
Mondal G, Sengupta S, Panda CK et al (2007) Overexpression of CDC20 leads to impairment of the spindle assembly checkpoint and aneuploidization in oral cancer. Carcinogenesis 28:81–92
Yuan B, Xu Y, Woo JH et al (2006) Increased expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with chromosomal instability. Clin Cancer Res 12:405–410
Kidokoro T, Tanikawa C, Furukawa Y et al (2008) CDC20, a potential cancer therapeutic target, is negatively regulated by p53. Oncogene 27:1562–71
Zhang L, Huang W, Chen J et al (2007) Expression of IGFBP2 in gastric carcinoma and relationship with clinicopathologic parameters and cell proliferation. Dig Dis Sci. 52:248–253
Elmlinger MW, Deininger MH, Schuett BS et al (2001) In vivo expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in human gliomas increases with the tumor grade. Endocrinology 142:1652–1658
Yokota T, Kouno J, Adachi K et al (2006) Identification of histological markers for malignant glioma by genome-wide expression analysis: dynein, alpha-PIX and sorcin. Acta Neuropathol 111:29–38
Boda B, Mas C, Muller D (2002) Activity-dependent regulation of genes implicated in X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Neuroscience 114:13–17
Acknowledgment
We wish to thank Dr. M. Guizzardi for the encouragement to enter into the world of gene array. This work was presented as Presidential free paper at the 3rd Intercontinental Congress of Pathology, May 2008, Barcelona
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the MIUR /FISR project 1509 (202).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marucci, G., Morandi, L., Magrini, E. et al. Gene expression profiling in glioblastoma and immunohistochemical evaluation of IGFBP-2 and CDC20. Virchows Arch 453, 599–609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-008-0685-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-008-0685-7