Abstract
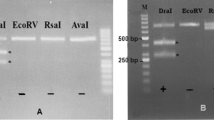
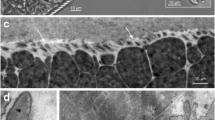
Sarcocystis cameli was first described in one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius), and it is the only species which have so far reported in camels. Although more than 150 species of Sarcocystis were described in various animals, only a few data on camel Sarcocystis ultrastructure were published, and this report is the first for molecular information (DNA sequence and RLFP digestion pattern). The main objective of the present work is to characterize Sarcocystis isolated from camels by electron microscopy and PCR-RFLP methods. Muscle samples were taken from the fresh esophagus, diaphragm, skeletal muscles, and heart of one-humped camels (C. dromedarius) slaughtered in abattoirs of Tehran and Ghazvin provinces, Iran. The dissection and trypsin digestion techniques were applied for the detection of the cysts. The infected samples were fixed in glutaraldehyde and/or frozen at −20°C until use for ultrastructural and molecular studies, respectively. The ultrastructural and molecular studies were carried out contemporaneously. The 18S rRNA gene of the parasites was amplified by PCR. The PCR products were cloned into a pTZ57R/T and sequenced. In addition, the PCR products were digested separately with each of the four restriction enzymes for RFLP. Our results indicated that only microcysts were observed in muscle samples. The microcysts were white, elongated, spindled, and a few spiral-shaped, with mean size 260 × 75 μm which are identical with S. cameli. The ultrastructure of microcyst wall had many non-branched finger-like protrusions irregularly folded. There was a 600-bp specific band amplified after PCR with specific primers. The molecular data for camel Sarcocystis is reported for the first time in Iran and the world.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghaffar F, Mehlhorn H, Bashtar AR, Al-Rasheid K, Sakran T, El-Fayoumi H (2009) Life cycle of Sarcocystis camelicanis infecting the camel (Camelus dromedarius) and the dog (Canis familiaris), light and electron microscopic study. Parasitol Res 106:189–195
Al-Goraishi SAR, Bashtar AR, Al-Rasheid KAS, Abdel-Ghaffar FA (2004) Prevalence and ultrastructure of Sarcocystis species infecting camels (Camelus dromedarius) slaughtered in Riyadh city Saudi Arabia. Saudi J Biol Sci 11(2):135–141
Barham M, Stutzer H, Karanis P, Latif BM, Neiss WF (2005) Seasonal variation in Sarcocystis species infections in goats in northern Iraq. Parasitology 130(2):151–156
Butkauskas D, Sruoga A, Kutkiene L, Prakas P (2007) Investication of the phylogenic relationships of Sarcocystis spp. from Greylag (Anser anser) and white-fronted (Anser aalbifrons) geese to other cyst forming coccidian using 18S rRNA gene sequences. Acta zool 17(2):124–128
Costa da Silva R, Chunlei Su, Langoni H (2009) First identification of Sarcocystis tenella (Railliet, 1886), Moule 1886 (Protozoa: Apicomplexa) by PCR in naturally infected sheep from Brazil. Vet Parasitol 165:332–336
Dalimi A, Khodashenas M, Nouri A, Morovati M (1999) Ultrastructural study of Sarcocystis isolated from water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) in Khozestan province in Iran. Pajouhesh Sazandegi 43:47–49 (In Persian)
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Charleston WAG (1989a) Ultrastructural differentiation between Sarcocystis of Sarcocystis hirsute and S. hominis. Vet Parasitol 34:153–157
Dubey JP, Speer CA, Shah HL (1989b) Ultrastructural of Sarcocystis from water buffalo in India. Vet Parasitol 34:149–152
Dubey JP, Saville WJA, Lindsay DS, Stich RW, Stanek JF, Speer CA, Rosenthal BM, Njoku CJ, Kwok OCH, Shen SK, Reed SM (2000) Completion of life cycle of Sarcocystis neurona. J Parasitol 86:1276–1280
Fayer R (2004) Sarcocystis spp in human infection. Clin Microbiol 17(4):894–902
Fischer S, Odening K (1998) Characterization of bovine Sarcocystis species by analysis of their 18S ribosomal DNA sequences. J Parasitol 84(1):50–54
Ghaffar FA, Heydorn AO, Mehlhorn H (1989) The fine structure of cysts of Sarcocystis moulei from goats. Parasitol Res 75:416–418
Holmdahl OJM, Morrison DA, Ellis JT, Huong LTT (1999) Evolution of ruminant Sarcocystis (Sporozoa) parasites based on small subunit rDNA sequences. Mol Phylo Evol 11:27–37
Li QQ, Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Attwood SW, Chen XW, Zhang YP (2002) A PCR-based RLFP analysis of Sarcocystis cruzi (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) in Yunnan Province, PR China, reveals the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) as a natural intermediate host. J Parasitol 88(6):1259–1261
Mason FP (1910) Sarcocystis in the camel in Egypt. J Comp Pathol Therap 23:168–176
Melhorn H (2008) Encyclopedia of parasitology, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin
Mehlhorn H, Heydorn AO (1978) The Sarcosporidia (Protozoa, Sporozoa): life cycle and fine structure. Adv Parasitol 16:43–93
Mehlhorn H, Heydorn AO (1979) Electron microscopical study on gamogony of Sarcocystis suihominis in human tissue cultures. Z Parasitenkd (Parasitol Res) 58:97–113
Mehlhorn H, Hartley WJ, Heydorn AO (1976) A comparative study of the cyst wall of 13 Sarcocystis species. Protistologica 12:451–467
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Heckeroth AR, Johnson AM, Tenter AM (1999) Phylogenetic analysis based on full-length large subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequence comparison reveals that Neospora caninum is more closely related to Hammondia hedorni than to Toxoplasma gondii. Inter J Parasitol 29:1545–1556
Mugridge NB, Morrison DA, Jekel T, Heckeroth AR, Tenter AM, Johnson AM (2000) Effect of sequence alignment for the Protozoa family Sarcocystidae. Soci Mol Biol Evol 17:1842–1853
Odening K, Stolte M, Bockhardt I (1996) On the diagnostics of Sarcocystis in cattle: sarcocysts of a species unusual for Bos taurus in a dwarf zebu. Vet Parasitol 66:19–24
Rahbari S, Bazargani TT, Rak H (1981) Sarcocystosis in the camel in Iran. J Fac Vet Med Univ Tehran 37:1–10
Shekarforoush SS, Shakerian A, Hassanpoor MM (2006) Prevalence of Sarcocystis in slaughtered one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Iran. Trop Anim Health Prod 38:301–303
Singh KP, Agrawal MC, Shah HL (1990) Prevalence of Sarcocysts of Sarcocystis capracanis in oesophagus and tail muscles of naturally infected goats. J Vet Parasitol 36:153–155
Valinezhad A, Oryan A, Ahmadi N (2008) Sarcocystis and its complications in camels (Camelus dromedarius) of Eastern provinces of Iran. Korean J Parasitol 46(4):229–234
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX (2000) The new views of the researchers on cyst forming coccidia species including Sarcocystis by using the molecular biological techniques. Chines J Parasitol Parasit Dis 18:120–126
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Ding B, Chen XW, Luo J, Zhang YP (2000) 18S rRNAgene of Sarcocystis hominis cyst from water buffalo and cattle. Zool Res 21:133–138
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Ding B, Chen XW, Luo J, Zhang YP (2001a) Identification of Sarcocystis hominis-like (Protozoa: Sarcocystidae) cyst in water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) based on 18S rRNA gene sequences. J Parasitol 87:934–937
Yang ZQ, Zuo YX, Yao YG, Chen XW, Yang GC, Zhang YP (2001b) Analysis of the 18S rRNA genes of Sarcocystis species suggests that the morphologically similar organ from cattle and water buffalo should be considered the same species. Mol Biochem Parasitol 115:283–288
Yang ZQ, Li QQ, Zuo YX, Chen XW, Chen YJ, Nie L, Wei CG, Zen JS, Attwood SW, Zhang XZ, Zhang YP (2002) Characterization of Sarcocystis species in domestic animal using a PCR-RLFP analysis of variation in the 18S rRNA gene: a cost effective and simple technique for routine species identification. Exp Parasitol 102:212–217
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported financially by Razi Vaccine and Serum Institute and Tarbiat Modares University. The authors would like to thank the staff of Parasitology, Electron Microscopy and Biotechnology Departments of Razi Institute for their kind cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motamedi, G.R., Dalimi, A., Nouri, A. et al. Ultrastructural and molecular characterization of Sarcocystis isolated from camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Iran. Parasitol Res 108, 949–954 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2137-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2137-y