Abstract
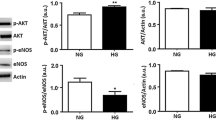
Emerging evidence demonstrates the involvement of endothelin-1 (ET-1) in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disorders associated with diabetes mellitus. The molecular mechanisms accountable for the increased production of ET-1 are not completely defined. The Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway is an essential pathogenic mechanism leading to endothelial cell dysfunction. Our aim has been to investigate the role of JAK/STAT in the regulation of ET-1 synthesis in human endothelial cells (EAhy926 cells line). EAhy926 cells were exposed to normal (5 mM) or high (25 mM) glucose concentrations in the presence/absence of various JAK/STAT inhibitors. Using real-time polymerase chain reaction, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and gene reporter assay, we found that JAK/STAT inhibitors (STAT1 decoy oligodeoxynucleotides, AG490, S3I201, WP1066) significantly diminished the high-glucose-dependent up-regulation of ET-1 mRNA, peptide synthesis, and promoter activity. In silico analysis of the human ET-1 promoter revealed the presence of typical STAT1-gamma-activated sequence (STAT1-GAS) elements. Transient overexpression of STAT1 indicated an up-regulation of ET-1 promoter activity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated the physical interaction of STAT1 proteins with the predicted GAS sites. Regulation of ET-1 synthesis by the JAK/STAT pathway thus represents a novel mechanism by which high glucose induces endothelial cell dysfunction in diabetes. Since the JAK/STAT system is an important regulator of the response of endothelial cells to injury, the modulation of this system and the subsequent decrease in ET-1 level may represent a key pharmacological target in diabetes-associated cardiovascular disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banes AKL, Shaw SM, Tawfik A, Patel BP, Ogbi S, Fulton D, Marrero MB (2005) Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in vascular smooth muscle by serotonin. J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:805–812
Banes-Berceli AKL, Ketsawatsomkron P, Ogbi S, Patel B, Pollock DM, Marrero MB (2007) Angiotensin II and endothelin-1 augment the vascular complications of diabetes via JAK2 activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:1291–1299
Calkin AC, Thomas MC (2008) PPAR agonists and cardiovascular disease in diabetes. PPAR Res 2008:1–12
Darnell JE, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) JAK-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Eckel RH, Wassef M, Chait A, Sobel B, Barrett E, King G, Lopes-Virella M, Reusch J, Ruderman N, Steiner G, Vlassara H (2002) Prevention Conference VI: diabetes and cardiovascular disease: writing group II: pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in diabetes. Circulation 105:138–143
Edgell CJS, McDonald CC, Graham JB (1983) Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3734–3737
Ferrajoli A, Fadrel S, Van Q, Kock P, Harris D, Liu Z, Hazan-Halevy I, Wang Y, Kantarjian HM, Priebe W, Estrov Z (2007) WP1066 disrupts Janus kinase-2 and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res 67:11291–11299
Ferri C, Pittoni V, Piccoli A, Laurenti O, Cassone MR, Bellini C, Properzi G, Valesini G, De Mattia G, Santucci A (1995) Insulin stimulates endothelin-1 secretion from human endothelial cells and modulates its circulating levels in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:829–835
Hargrove GM, Dufresne J, Whiteside C, Muruve DA, Wong NCW (2000) Diabetes mellitus increases endothelin-1 gene transcription in rat kidney. Kidney Int 58:1534–1545
Jinga VV, Bogdan I, Fruchter J (1986) Experimental model for the quantitative estimation of transendothelial transport in vitro; a two-compartment system. Physiologie 23:227–236
Khamaisi M, Dahan R, Hamed S, Abassi Z, Heyman SN, Raz I (2009) Role of protein kinase C in the expression of endothelin converting enzyme-1. Endocrinology 15:1440–1449
Kirkby NS, Hadoke PW, Bagnall AJ, Webb DJ (2008) The endothelin system as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease: great expectations or bleak house? Br J Pharmacol 153:1105–1119
Manea A, Manea SA, Gafencu AV, Raicu M (2007) Regulation of NADPH oxidase subunit p22 (phox) by NF-kB in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Arch Physiol Biochem 113:163–172
Manea A, Manea SA, Gafencu AV, Raicu M, Simionescu M (2008) AP-1-dependent transcriptional regulation of NADPH oxidase in human aortic smooth muscle cells: role of p22phox subunit. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:878–885
Marrero MB, Banes-Berceli AK, Stern DM, Eaton DC (2006) Role of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:762–768
Matsumoto T, Kobayashi T, Kamata K (2008) Relationships among ET-1, PPARγ, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in diabetic animals. J Smooth Muscle Res 44:41–55
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2002–2007
Quehenberger P, Bierhaus A, Fasching P, Muellner C, Klevesath M, Hong M, Stier G, Sattler M, Schleicher E, Speiser W, Nawroth PP (2000) Endothelin 1 transcription is controlled by nuclear factor-kappaB in AGE-stimulated cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes 49:1561–1570
Rabiet MJ, Plantier JL, Rival Y, Genoux Y, Lampugnani MG, Dejana E (1996) Thrombin-induced increase in endothelial permeability is associated with changes in cell-to-cell junction organization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:488–496
Saijonmaa O, Nyman T, Hohenthal U, Fyhrquist F (1991) Endothelin-1 is expressed and released by a human endothelial hybrid cell line (EA.hy 926). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:529–536
Schiffrin EL, Touyz RM (1998) Vascular biology of endothelin. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 32:2–13
Schindler C, Levy DE, Decker T (2007) JAK-STAT signaling: from interferons to cytokines. J Biol Chem 282:20059–20063
Sud N, Black SM (2009) Endothelin-1 impairs nitric oxide signaling in endothelial cells through a protein kinase Cdelta-dependent activation of STAT3 and decreased endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression. DNA Cell Biol 28:543–553
Tawfik A, Jin L, Banes-Berceli AK, Caldwell RB, Ogbi S, Shirley A, Barber D, Catravas JD, Stern DM, Fulton D, Caldwell RW, Marrero MB (2005) Hyperglycemia and reactive oxygen species mediate apoptosis in aortic endothelial cells through Janus kinase 2. Vascul Pharmacol 43:320–326
Toma L, Stancu CS, Botez GM, Sima AV, Simionescu M (2009) Irreversibly glycated LDL induce oxidative and inflammatory state in human endothelial cells; added effect of high glucose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 390:877–882
Verstovsek S, Manshouri T, Quintás-Cardama A, Harris D, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Kantarjian H, Priebe W, Estrov Z (2008) WP1066, a novel JAK2 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in erythroid human cells carrying the JAK2 V617F mutation. Clin Cancer Res 14:788–796
Wagner AH, Gebauer M, Pollok-Kopp B, Hecker M (2002) Cytokine-inducible CD40 expression in human endothelial cells is mediated by interferon regulatory factor-1. Blood 99:520–525
Wesoly J, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z, Bluyssen HA (2007) STAT activation and differential complex formation dictate selectivity of interferon responses. Acta Biochim Pol 54:27–38
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Goto K, Masaki T (1988) A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 332:411–415
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Dr. Angelika Bierhaus from the University of Heidelberg, Germany for the plasmid containing the human endothelin-1 gene promoter and acknowledge the skilful assistance of Floarea Georgescu, Ioana Manolescu, and Constanta Stan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the Romanian Academy (65/2007) and Romanian Ministry of Education, Research, and Innovation (100/2007).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manea, SA., Manea, A. & Heltianu, C. Inhibition of JAK/STAT signaling pathway prevents high-glucose-induced increase in endothelin-1 synthesis in human endothelial cells. Cell Tissue Res 340, 71–79 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-0936-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-010-0936-1