Abstract.
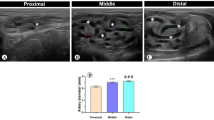
Human spermatic cords were investigated by means of cast preparations, light-microscopic examination and computer-aided 3-dimensional reconstructions from serial sections of paraffin-embedded material. After leaving the testis, the testicular veins formed two principal groups co-existing side by side. Numerous veno-venous anastomoses could be observed within each individual group, whereas only a few mutual intergroup anastomoses were found. The testicular artery ran within one group but showed no close topographical relationship to the other group. Light microscopy of the serial sections revealed that the group of veins with no close topographical relationship to the testicular artery ran at a distance of several centimeters embedded within fatty tissue. With the help of computer-aided 3-dimensional reconstructions, a spatial picture of the vascular organization was obtained. These results allowed the following classification of the veins of the pampiniform plexus. Group-I veins formed a tight plexus around the testicular artery by means of veno-venous anastomoses. Group-II veins formed veno-venous anastomoses between each other and ran over at a sizeable distance embedded in fatty tissue but showed no close topographical relationship to the testicular artery. Group-III vessels formed veno-venous anastomoses between group-I and group-II. Group IV veins formed arterio-venous anastomoses with the testicular artery. Based on the differences in wall structure and diameter, a subclassification in group-I and group-II was undertaken. This organization of the veins of the human pampiniform plexus should further the understanding of physiological processes, such as the transfer of hormones and other substances from the veins to the testicular artery and vice versa. It should also facilitate the tracing of the veins during antegrade sclerosing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 September 1996 / Accepted: 26 November 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ergün, S., Bruns, T., Soyka, A. et al. Angioarchitecture of the human spermatic cord. Cell Tissue Res 288, 391–398 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050825
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050825