Abstract.
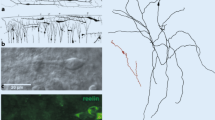
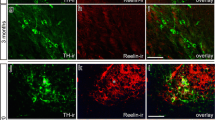
Cajal-Retzius (CR) cells are transient neurons located in the marginal zones of the neocortex and hippocampus. Recent studies have shown that they synthesize and secrete the glycoprotein reelin. This extracellular matrix protein has sequence similarities with cell adhesion molecules and other extracellular matrix proteins, such as tenascin and laminin, suggesting a role in cell migration and process outgrowth. In reeler mutant mice lacking reelin, the orderly inside-out deposition of neocortical cells during development is disturbed, indicating that reelin is essential for normal cortical lamination. In the hippocampus, CR cells and reelin have recently been found to be important for the normal lamina-specific fiber ingrowth of afferents from the entorhinal cortex. These fibers are known to terminate in superficial layers of the hippocampus and dentate gyrus, regions in which CR cells are located. Both selective elimination of CR cells by local lesions and antibody blockade (CR-50 antibody) of an important epitope near the N-terminus of reelin result in severe alterations of the growth of entorhinal axons in co-cultures of the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus. It is hypothesized in this review that reelin functions as a stop signal for both migrating neurons and growing fibers in the developing central nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 April 1997 / Accepted: 22 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frotscher, M. Dual role of Cajal-Retzius cells and reelin in cortical development. Cell Tissue Res 290, 315–322 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050936
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004410050936