Abstract
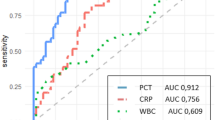
This prospective study, performed in 76 children with a urinary tract infection (UTI), evaluates the diagnostic value of procalcitonin (PCT) and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) in children with acute pyelonephritis documented by dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy (DMSA). Renal parenchymal involvement was assessed by 99m Tc-DMSA scintigraphy within 7 days of admission. The diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis was confirmed only in patients with reversible lesions on scintigraphy. According to DMSA scan results, patients were divided into two groups, lower UTI or acute pyelonephritis. In acute pyelonephritis, serum PCT level was found to be significantly higher than it is in the lower UTI (p <0.001). Also, significantly higher serum proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) levels were detected in those with acute pyelonephritis than those with lower UTI (p <0.001). We conclude that both serum PCT and proinflammatory cytokine levels may be used as accurate markers for diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sirin A, Emre S, Alpay H, Nayir A, Bilge I, Tanman F(1995) Etiology of chronic renal failure in Turkish children. Pediatr Nephrol 9:549–552
Hoberman A, Chao H-P, Keller DM, Hickey R, Davis HW, Ellis DE (1993) Prevalence of urinary tract infection in febrile infants. J Pediatr 123:17–23
Cornu C, Cochat P, Collet J-P, Delair S, Haugh MC, Rolland C, and the GEP (1994) Survey of the attitudes to management of acute pyelonephritis in children. Pediatr Nephrol 8:275–277
Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, Pober JS (1997) Cellular and molecular immunology, 3rd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, USA, pp 250–276
Curfs J, Meis M, Hoogkamp-Korstanje A (1997) A primer on cytokines: Sources, receptors, effects, and inducers. J Clin Microbiol 10:742–780
Assicot M, Gendrel D, Carsin H, Raymond J, Guilbaud J, Bohoun C (1993) High serum procalcitonin concentration in patients with sepsis and infection. Lancet 341:515–518
Karsai W, Oberholffer M, Meier-Hellman A, Reinhart K (1997) Procalcitonin—a new indicator of systemic response to severe infections. Infection 25:329–334
Rushton HG (1997) The evaluation of acute pyelonephritis and renal scarring with technetium 99m-dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy: evolving concepts and future directions. Pediatr Nephrol 11:108–120
Benador D, Benador N, Slosman DO, Nussle D, Mermillod B, Girardin E (1994) Cortical scintigraphy in the evaluation of renal parenchymal changes in children with pyelonephritis. J Pediatr 124:17–20
Stokland E, Hellstorm M, Jacobsson B, Jodat U, Sixt R (1996) Renal damage one year after first urinary tract infection: role of dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy. J Pediatr 129 815–820
Goldraich NP, Ramos OL, Goldraich JH (1995) Urography versus DMSA scan in children with vesicoureteric reflux. Pediatr Nephrol 9:221–226
Goldraich NP, Goldraich JH (1995) Update on dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scanning in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatr Nephrol 9:221–226
Lin KY, Chiu NT, Chen MJ, Lai CH, Huang JJ, Wang YT, Chiou YY (2003) Acute pyelonephritis and sequelae of renal scar in pediatric first febrile urinary tract infection. Pediatr Nephrol 18:362–365
Smolkin V, Koren A, Raz R, Colodner R, Sakran W, Halevy R (2002) Procalcitonin as marker of acute pyelonephritis in infants and children. Pediatr Nephrol 17:409–412
Prat C, Dominguez J, Rodrigo C, Gimenez M, Azuara M, Jimenez O, Gali N, Ausina V (2003) Elevated serum procalcitonin values correlate with renal scarring in children with urinary tract infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22:438–442
Roilides E, Papachristou F, Gioulekas E, Tsaparidou S, Karatzas N, Sotiriou J, Tsiouris J (1999) Increased urine interleukin-6 concentrations correlate with pyelonephritic changes on 99m Tc-Dimercaptosuccinic acid scans in neonates with urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis 180:904–907
Otto G, Braconier JH, Andreason A, Svanborg C (1999) Interleukin-6 and disease severity in patients with bacteremic and nonbacteremic febrile urinary tract infection. J Infect Dis 179:172–179
Benson M, Jodal U, Andreasson A, Karlsson A, Rydberg J, Svanborg C (1994) Interleukin 6 response to urinary tract infection in childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis J 13:612–616
Benson M, Jodal U, Agace W, Hellstrom M, Marild S, Rosberg S, Sjostrom M, Wettergren B, Jonsson S, Svanborg C (1996) Interleukin-6 and IL-8 in children with febrile urinary tract infection and asymptomatic bacteriuria. J Infect Dis 174:1080–1084
Lin SJ, Huang JL (1998) Circulating interleukin (IL)-1 beta, Il-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in children with febrile infection-a comparison with C-reactive protein. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 16:105–109
Tang RB, Lee BH, Chung RL, Chen SJ, Wong TT (2001) Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cerebrospinal fluid of children with bacterial meningitis. Childs Nerv Syst 17:453–456
Prio TK, Bruunsgaard H, Roge B, Pedersen K (2002) Asymptomatic bacteriuria in elderly humans is associated with increased levels of circulating TNF receptors and elevated numbers of neutrophils. Exp Gerontol 37:693–699
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gürgöze, M.K., Akarsu, S., Yilmaz, E. et al. Proinflammatory cytokines and procalcitonin in children with acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 20, 1445–1448 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1941-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-1941-6