Abstract
Background
Rituximab (RTX) is known to be effective for the treatment of refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome (SDNS). However, there are insufficient data on the risk factors for relapse and long-term outcome after RTX treatment.
Methods
We administered a single dose of RTX to patients with refractory SDNS from November 2007 to December 2013 and continued with immunosuppressants. The risk factors for early relapse and long-term outcome were analyzed.
Results
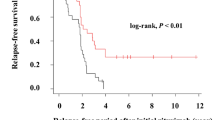
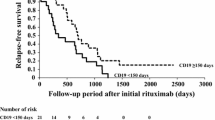
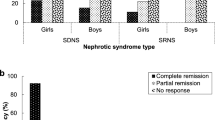
Eighty-one patients were included and the observation period was 13–90 months. Seventy-six patients (94 %) discontinued steroids. Median duration of B-cell depletion was 160 days and 50 % relapse-free survival was 482 days. In multivariate analyses, only a history of steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome (SRNS) was a statistically significant risk factor (hazard ratio, 2.44; p = 0.048). Fifty percent relapse-free survival in patients without a history of SRNS was 615 days, longer than that of patients with one relapse (393 days; p = 0.005). Fifty-one patients (63 %) received additional RTX treatments for relapses. At last observation, patients using calcineurin inhibitors decreased from 89 % to 23 %, and 12 patients (15 %) discontinued immunosuppressants.
Conclusions
Rituximab treatment followed by immunosuppressants is an effective option for patients with SDNS, although a history of SRNS is a risk factor for early relapse.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima K, Hamahira K, Tanaka R, Kobayashi A, Nozu K, Nakamura H, Yoshikawa N (2002) Risk factors for cyclosporine-induced tubulointerstitial lesions in children with minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 61:1801–1805
Latta K, von Schnakenburg C, Ehrich JH (2001) A meta-analysis of cytotoxic treatment for frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 16:271–282
Kamei K, Ito S, Nozu K, Fujinaga S, Nakayama M, Sako M, Saito M, Yoneko M, Iijima K (2009) Single dose of rituximab for refractory steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in children. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1321–1328
Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Nishizaki N, Kamei K, Ito S, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T, Kaneko K (2010) Single infusion of rituximab for persistent steroid-dependent minimal-change nephrotic syndrome after long-term cyclosporine. Pediatr Nephrol 25:539–544
Gulati A, Sinha A, Jordan SC, Hari P, Dinda AK, Sharma S, Srivastava RN, Moudgil A, Bagga A (2010) Efficacy and safety of treatment with rituximab for difficult steroid-resistant and -dependent nephrotic syndrome: multicentric report. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:2207–2212
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Macher MA, Loirat C, Guérin V, Watier H, Peuchmaur M, Baudouin V, Deschênes G (2010) Rituximab efficiency in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25:1109–1115
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Sato M, Fujimaru T, Ishikawa T, Udagawa T, Iijima K (2011) Maintenance therapy with mycophenolate mofetil after rituximab in pediatric patients with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 26:1823–1828
Ravani P, Magnasco A, Edefonti A, Murer L, Rossi R, Ghio L, Benetti E, Scozzola F, Pasini A, Dallera N, Sica F, Belingheri M, Scolari F, Ghiggeri GM (2011) Short-term effects of rituximab in children with steroid- and calcineurin-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:1308–1315
Sinha A, Bagga A, Gulati A, Hari P (2012) Short-term efficacy of rituximab versus tacrolimus in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 27:235–241
Ito S, Kamei K, Ogura M, Udagawa T, Fujinaga S, Saito M, Sako M, Iijima K (2013) Survey of rituximab treatment for childhood-onset refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:257–264
Ruggenenti P, Ruggiero B, Cravedi P, Vivarelli M, Massella L, Marasà M, Chianca A, Rubis N, Ene-Iordache B, Rudnicki M, Pollastro RM, Capasso G, Pisani A, Pennesi M, Emma F, Remuzzi G, Rituximab in Nephrotic Syndrome of Steroid-Dependent or Frequently Relapsing Minimal Change Disease Or Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (NEMO) Study Group (2014) Rituximab in steroid-dependent or frequently relapsing idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 25:850–863
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Takahashi S, Tanaka R, Kaito H, Nakamura H, Ishikura K, Ito S, Ohashi Y, Rituximab for Childhood-onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome (RCRNS) Study Group (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 384:1273–1281
Kemper MJ, Gellermann J, Habbig S, Krmar RT, Dittrich K, Jungraithmayr T, Pape L, Patzer L, Billing H, Weber L, Pohl M, Rosenthal K, Rosahl A, Mueller-Wiefel DE, Dötsch J (2012) Long-term follow-up after rituximab for steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1910–1915
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Baudouin V, Kwon T, Macher MA, Guérin V, Lapillonne H, Deschênes G, Ulinski T (2012) Rituximab in steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in childhood—follow-up after CD19 recovery. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1083–1089
Ravani P, Ponticelli A, Siciliano C, Fornoni A, Magnasco A, Sica F, Bodria M, Caridi G, Wei C, Belingheri M, Ghio L, Merscher-Gomez S, Edefonti A, Pasini A, Montini G, Murtas C, Wang X, Muruve D, Vaglio A, Martorana D, Pani A, Scolari F, Reiser J, Ghiggeri GM (2013) Rituximab is a safe and effective long-term treatment for children with steroid and calcineurin inhibitor-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int 84:1025–1033
Tellier S, Brochard K, Garnier A, Bandin F, Llanas B, Guigonis V, Cailliez M, Pietrement C, Dunand O, Nathanson S, Bertholet-Thomas A, Ichay L, Decramer S (2013) Long-term outcome of children treated with rituximab for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:911–918
Carson KR, Evens AM, Richey EA, Habermann TM, Focosi D, Seymour JF, Laubach J, Bawn SD, Gordon LI, Winter JN, Furman RR, Vose JM, Zelenetz AD, Mamtani R, Raisch DW, Dorshimer GW, Rosen ST, Muro K, Gottardi-Littell NR, Talley RL, Sartor O, Green D, Major EO, Bennett CL (2009) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after rituximab therapy in HIV-negative patients: a report of 57 cases from the Research on Adverse Drug Events and Reports project. Blood 113:4834–4840
Bitzan M, Anselmo M, Carpineta L (2009) Rituximab (B-cell depleting antibody) associated lung injury (RALI): a pediatric case and systematic review of the literature. Pediatr Pulmonol 44:922–934
Chaumais MC, Garnier A, Chalard F, Peuchmaur M, Dauger S, Jacqz-Agrain E, Deschênes G (2009) Fatal pulmonary fibrosis after rituximab administration. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1753–1755
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Belli E, Guérin V, Dorfmüller P, Deschênes G (2013) Fulminant viral myocarditis after rituximab therapy in pediatric nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:1875–1879
Kamei K, Takahashi M, Fuyama M, Saida K, Machida H, Sato M, Ogura M, S (2015) Rituximab-associated agranulocytosis in children with refractory idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: case series and review of literature. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:91–96
Sato M, Ito S, Ogura M, Kamei K, Miyairi I, Miyata I, Higuchi M, Matsuoka K (2013) Atypical Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia with multiple nodular granulomas after rituximab for refractory nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 28:145–149
Fujinaga S, Sakuraya K, Yamada A, Urushihara Y, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T (2015) Positive role of rituximab in switching from cyclosporine to mycophenolate mofetil for children with high-dose steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 30:687–691
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs K. Tanaka (Aomori), K. Tsuruga (Aomori), T. Echizenya (Iwate), D. Ogino (Yamagata), T. Watanabe (Gumma), Y. Owada (Tochigi), R. Hiramoto (Chiba), H. Eguchi (Chiba), M. Hisano (Chiba), Z. Kiuchi (Tokyo), K. Saida (Tokyo), H. Hataya (Tokyo), K Ishikura (Tokyo), E. Tanaka (Tokyo), M. Takahashi (Tokyo), E. Kikuchi (Tokyo), T. Udagawa (Tokyo), M. Okada (Tokyo), T. Fujimaru (Tokyo), M. Fuyama (Kanagawa), K. Honda (Kanagawa), H. Machida (Kanagawa), A. Inaba (Kanagawa), A. Ueda (Kanagawa), S. Noda (Nagano), T. Ishikawa (Nara), H. Kaito (Hyogo), M. Mizutani (Yamaguchi), M. Fujieda (Kochi), M. Ishihara (Kochi), H. Nakazato (Kumamoto), H. Nagasako (Kagoshima), A. Miyazono (Kagoshima), M. Yoshishige (Kagoshima), H. Yoshimura (Okinawa) for their contributions to this study. They would also like to thank Dr J. Tang from the Department of Education for Clinical Research, National Center for Child Health and Development, for proofreading and editing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Ethical disclosure
The study protocol was based on the Declaration of Helsinki and approval of the off-label use of RTX was obtained from the ethics committee of our center (#645). All patients’ parents gave written informed consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamei, K., Ogura, M., Sato, M. et al. Risk factors for relapse and long-term outcome in steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome treated with rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 31, 89–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3197-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-015-3197-0