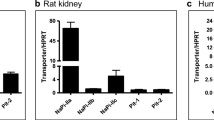
Abstract
Sodium-dependent neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 (SLC6A19) and imino acid (proline) transporter SIT1 (SLC6A20) are expressed at the luminal membrane of small intestine enterocytes and proximal tubule kidney cells where they exert key functions for amino acid (re)absorption as documented by their role in Hartnup disorder and iminoglycinuria, respectively. Expression of B0AT1 was shown in rodent intestine to depend on the presence of the carboxypeptidase angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). This enzyme belongs to the renin-angiotensin system and its expression is induced by treatment with ACE-inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockers (ARBs) in many rodent tissues. We show here in the Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system that human ACE2 also functionally interacts with SIT1. To investigate in human intestine the potential effect of ACEIs or ARBs on ACE2, we analysed intestinal biopsies taken during routine gastroduodenoscopy and ileocolonoscopy from 46 patients of which 9 were under ACEI and 13 ARB treatment. Analysis of transcript expression by real-time PCR and of proteins by immunofluorescence showed a co-localization of SIT1 and B0AT1 with ACE2 in the brush-border membrane of human small intestine enterocytes and a distinct axial expression pattern of the tested gene products along the intestine. Patients treated with ACEIs displayed in comparison with untreated controls increased intestinal mRNA levels of ACE2, peptide transporter PEPT1 (SLC15A1) and AA transporters B0AT1 and PAT1 (SLC36A1). This study unravels in human intestine the localization and distribution of intestinal transporters involved in amino acid absorption and suggests that ACEIs impact on their expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B0AT1:
-
Sodium-dependent broad substrate selectivity neutral amino acid transporter 1
- SIT1:
-
Sytem imino transporter 1
- ACE2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
References
Anderson CM et al (2004) H+/amino acid transporter 1 (PAT1) is the imino acid carrier: an intestinal nutrient/drug transporter in human and rat. Gastroenterology 127:1410–1422
Attia E, Wolk S, Cooper T, Glasofer D, Walsh BT (2005) Plasma tryptophan during weight restoration in patients with anorexia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry 57:674–678. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.045
Blachier F, Boutry C, Bos C, Tome D (2009) Metabolism and functions of l-glutamate in the epithelial cells of the small and large intestines. Am J Clin Nutr 90:814S–821S. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27462S
Brandsch M (2009) Transport of drugs by proton-coupled peptide transporters: pearls and pitfalls. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 5:887–905. doi:10.1517/17425250903042292
Broer S, Palacin M (2011) The role of amino acid transporters in inherited and acquired diseases. Biochem J 436:193–211. doi:10.1042/BJ20101912
Broer A, Wagner CA, Lang F, Broer S (2000) The heterodimeric amino acid transporter 4F2hc/y+LAT2 mediates arginine efflux in exchange with glutamine. Biochem J 349(Pt 3):787–795
Broer S et al (2008) Iminoglycinuria and hyperglycinuria are discrete human phenotypes resulting from complex mutations in proline and glycine transporters. J Clin Invest 118:3881–3892. doi:10.1172/JCI36625
Broer A et al (2011) Impaired nutrient signaling and body weight control in a Na + neutral amino acid cotransporter (Slc6a19)-deficient mouse. J Biol Chem 286:26638–26651. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.241323
Camargo SM et al (2009) Tissue-specific amino acid transporter partners ACE2 and collectrin differentially interact with hartnup mutations. Gastroenterology 136:872–882 (S0016-5085(08)01893-3)
Cartharius K et al (2005) MatInspector and beyond: promoter analysis based on transcription factor binding sites. Bioinformatics 21:2933–2942 (bti473)
Chappel MC, Ferrario CM (2006) ACE and ACE2: their role to balance the expression of angiotensin II and angiotensin-(1-7). Kidney Int 70:8–10. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5000321
Chillaron J, Font-Llitjos M, Fort J, Zorzano A, Goldfarb DS, Nunes V, Palacin M (2010) Pathophysiology and treatment of cystinuria. Nat Rev Nephrol 6:424–434. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2010.69
Daniel H (2004) Molecular and integrative physiology of intestinal peptide transport. Annu Rev Physiol 66:361–384. doi:10.1146/annurev.physiol.66.032102.144149
Daniel H, Kottra G (2004) The proton oligopeptide cotransporter family SLC15 in physiology and pharmacology. Pflugers Arch 447:610–618. doi:10.1007/s00424-003-1101-4
Danilczyk U et al (2006) Essential role for collectrin in renal amino acid transport. Nature 444:1088–1091. doi:10.1038/nature05475
Dave MH, Schulz N, Zecevic M, Wagner CA, Verrey F (2004) Expression of heteromeric amino acid transporters along the murine intestine. J Physiol 558:597–610
Douard V, Cui XL, Soteropoulos P, Ferraris RP (2008) Dexamethasone sensitizes the neonatal intestine to fructose induction of intestinal fructose transporter (Slc2A5) function. Endocrinology 149:409–423. doi:10.1210/en.2007-0906
Dyer J, Hosie KB, Shirazi-Beechey SP (1997) Nutrient regulation of human intestinal sugar transporter (SGLT1) expression. Gut 41:56–59
Fairweather SJ, Broer A, O’Mara ML, Broer S (2012) Intestinal Peptidases Form Functional Complexes with Neutral Amino Acid Transporter B0AT1. Biochem J. doi:10.1042/BJ20120307
Feliubadalo L et al (1999) Non-type I cystinuria caused by mutations in SLC7A9, encoding a subunit (bo,+AT) of rBAT. Nat Genet 23:52–57. doi:10.1038/12652
Fernandez E, Carrascal M, Rousaud F, Abian J, Zorzano A, Palacin M, Chillaron J (2002) rBAT-b(0, +)AT heterodimer is the main apical reabsorption system for cystine in the kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F540–F548. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00071.2002
Ferrario CM, Varagic J (2010) The ANG-(1-7)/ACE2/mas axis in the regulation of nephron function. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298:F1297–F1305. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00110.2010
Ferrario CM, Trask AJ, Jessup JA (2005) Advances in biochemical and functional roles of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin-(1-7) in regulation of cardiovascular function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H2281–H2290. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00618.2005
Font-Llitjos M et al (2007) Slc7a9 knockout mouse is a good cystinuria model for antilithiasic pharmacological studies. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F732–F740. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00121.2007
Frech K, Danescu-Mayer J, Werner T (1997) A novel method to develop highly specific models for regulatory units detects a new LTR in GenBank which contains a functional promoter. J Mol Biol 270:674–687. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1140
Hashimoto T et al (2012) ACE2 links amino acid malnutrition to microbial ecology and intestinal inflammation. Nature 487:477–481. doi:10.1038/nature11228
Igase M, Strawn WB, Gallagher PE, Geary RL, Ferrario CM (2005) Angiotensin II AT1 receptors regulate ACE2 and angiotensin-(1-7) expression in the aorta of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289:H1013–H1019. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00068.2005
Kim DK et al (2002) The human T-type amino acid transporter-1: characterization, gene organization, and chromosomal location. Genomics 79:95–103. doi:10.1006/geno.2001.6678
Kleta R et al (2004) Mutations in SLC6A19, encoding B0AT1, cause Hartnup disorder. Nat Genet 36:999–1002
Kowalczuk S, Bröer A, Munzinger M, Tietze N, Klingel K, Bröer S (2005) Molecular cloning of the mouse IMINO system: an Na+ and Cl− dependent proline transporter. Biochem J 386:417–422. doi:10.1042/BJ20050100
Kowalczuk S, Bröer A, Tietze N, Vanslambrouck JM, Rasko JE, Bröer S (2008) A protein complex in the brush-border membrane explains a Hartnup disorder allele. FASEB J 22:2880–2887. doi:10.1096/fj.08-107300
Kuba K, Imai Y, Ohto-Nakanishi T, Penninger JM (2010) Trilogy of ACE2: a peptidase in the renin-angiotensin system, a SARS receptor, and a partner for amino acid transporters. Pharmacol Ther 128:119–128. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.06.003
Mariotta L et al (2012) T-type amino acid transporter TAT1 (Slc16a10) is essential for extracellular aromatic amino acid homeostasis control. J Physiol 590:6413–6424. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.239574
Meier C, Ristic Z, Klauser S, Verrey F (2002) Activation of system L heterodimeric amino acid exchangers by intracellular substrates. EMBO J 21:580–589
Meier Y et al (2007) Regional distribution of solute carrier mRNA expression along the human intestinal tract. Drug Metab Dispos 35:590–594. doi:10.1124/dmd.106.013342
Naruhashi K, Sai Y, Tamai I, Suzuki N, Tsuji A (2002) PepT1 mRNA expression is induced by starvation and its level correlates with absorptive transport of cefadroxil longitudinally in the rat intestine. Pharm Res 19:1417–1423
Nishimura M, Naito S (2005) Tissue-specific mRNA expression profiles of human ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporter superfamilies. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20:452–477 JST.JSTAGE/dmpk/20.452
Palacin M et al (2005) The genetics of heteromeric amino acid transporters. Physiology 20:112–124. doi:10.1152/physiol.00051.2004
Pan X, Hussain MM (2009) Clock is important for food and circadian regulation of macronutrient absorption in mice. J Lipid Res 50:1800–1813. doi:10.1194/jlr.M900085-JLR200
Ramadan T, Camargo SM, Summa V, Hunziker P, Chesnov S, Pos KM, Verrey F (2006) Basolateral aromatic amino acid transporter TAT1 (Slc16a10) functions as an efflux pathway. J Cell Physiol 206:771–779. doi:10.1002/jcp.20531
Ristic Z et al (2006) Neutral amino acid transport mediated by ortholog of imino acid transporter SIT1/SLC6A20 in opossum kidney cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F880–F887. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00319.2005
Romeo E et al (2006) Luminal kidney and intestine SLC6 amino acid transporters of B0AT-cluster and their tissue distribution in Mus musculus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F376–F383
Scheppach W et al (1996) Effect of l-glutamine and n-butyrate on the restitution of rat colonic mucosa after acid induced injury. Gut 38:878–885
Seow HF, Broer S, Broer A, Bailey CG, Potter SJ, Cavanaugh JA, Rasko JE (2004) Hartnup disorder is caused by mutations in the gene encoding the neutral amino acid transporter SLC6A19. Nat Genet 36:1003–1007. doi:10.1038/ng1406
Singer D et al (2012) Defective intestinal amino acid absorption in Ace2 null mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol(ajpgi.00140.2012)
Takanaga H, Mackenzie B, Suzuki Y, Hediger MA (2005) Identification of mammalian proline transporter SIT1 (SLC6A20) with characteristics of classical system imino. J Biol Chem 280:8974–8984. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413027200
Terada T et al (2005) Expression profiles of various transporters for oligopeptides, amino acids and organic ions along the human digestive tract. Biochem Pharmacol 70:1756–1763 (S0006-2952(05)00635-0)
Tumer E, Broer A, Balkrishna S, Julich T, Broer S (2013) Enterocyte-specific regulation of the apical nutrient transporter SLC6A19 (B(0)AT1) by transcriptional and epigenetic networks. J Biol Chem 288:33813–33823. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.482760
Verrey F, Meier C, Rossier G, Kuhn LC (2000) Glycoprotein-associated amino acid exchangers: broadening the range of transport specificity. Pflugers Arch 440:503–512
Wehkamp J et al (2004) NOD2 (CARD15) mutations in Crohn’s disease are associated with diminished mucosal alpha-defensin expression. Gut 53:1658–1664. doi:10.1136/gut.2003.032805
Werner C, Poss J, Bohm M (2010) Optimal antagonism of the Renin-Angiotensin-aldosterone system: do we need dual or triple therapy? Drugs 70:1215–1230. doi:10.2165/11537910-000000000-00000
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mital Dave for cloning the human SIT1 cDNA. RNV was supported by a grant for the Doctorate of Medicine and of Philosophy (MD-PhD) students from the Swiss National Foundation. The laboratory of FV is supported by Grant 130471 of the Swiss National Foundation and the Swiss National Centre of Competence in Research Kidney Control of Homeostasis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuille-dit-Bille, R.N., Camargo, S.M., Emmenegger, L. et al. Human intestine luminal ACE2 and amino acid transporter expression increased by ACE-inhibitors. Amino Acids 47, 693–705 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1889-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1889-6