Abstract
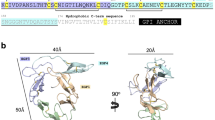
The P28 family of proteins are 28 kDa proteins expressed on the surface of sexual stages—zygote, ookinete and young oocyst stages—of Plasmodium species when the parasite resides inside the mosquito midgut. Together with P25 proteins, P28 proteins protect the parasite from the harsh proteolytic environment prevailing inside the mosquito midgut. Vaccines against these proteins induce antibodies in vertebrate hosts that are capable of inhibiting parasite development in the mosquito midgut, thus preventing transmission of the parasite from the mosquito to another human host. These transmission-blocking vaccines are helpful in reducing the burden caused by malaria, which affects 300–600 million, and kills 1–3 million, people annually. The purpose of this study was to structurally characterise six members of the P28 family of ookinete surface proteins with the help of homology modelling, to compare these proteins in terms of transmission blocking and host parasite interactions, and to analyse phylogenetic relationships within the P28 family and with the P25 family. Our results indicate that all the members of the P28 family studied have four EGF domains arranged in triangular fashion with a very big C loop present in EGF domain IV, which could serve as a diagnostic feature of the P28 family as this loop is absent in the P25 family of ookinete surface proteins. The models of the P28 family of ookinete surface proteins obtained may help in understanding the biology of the parasite inside the mosquito midgut, and in designing transmission-blocking vaccines against malaria in the absence of experimentally determined structures of these important surface proteins.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Snow RW, Guerra CA, Noor AM, Myint HY, Hay SI (2005) The global distribution of clinical episodes of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 434:214–217. doi:10.1038/nature03342
World Malaria Report Geneva. 2005 RBM/WHO/UNICEF, Geneva, Switzerland
Kumar N, Carter R (1985) Biosynthesis of two stage-specific membrane proteins during transformation of Plasmodium gallinaceum zygotes into ookinetes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 14:127–139. doi:10.1016/0166-6851(85)90032-5
Paton MG, Barker GC, Matsuoka H, Ramesar J, Janse CJ, Waters AP, Sinden RE (1993) Structure and expression of a post-transcriptionally regulated malaria gene encoding a surface protein from the sexual stages of Plasmodium berghei. Mol Biochem Parasitol 59:263–275. doi:10.1016/0166-6851(93)90224-L
Winger LA, Tirawanchai N, Nicholas NJ, Carter HE, Smith JE, Sinden RE (1998) Ookinete antigens of Plasmodium berghei. Appearance on the zygote surface of an Mr 21 kD determinant identified by transmission-blocking monoclonal antibodies. Parasite Immunol 10:193–207. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3024.1988.tb00214.x
Sinden RE, Winger L, Carter EH, Hartley RH, Tirawanchai N, Davies CS, Moore J, Sluiters JF (1987) Ookinete antigens of Plasmodium berghei: a light and electron-microscope immunogold study of expression of the 21 kDa determinant recognized by a transmission-blocking antibody. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 230:443–458. doi:10.1098/rspb.1987.0028
Duffy PE, Pimenta P, Kaslow D (1993) C: Pgs28 belongs to a family of epidermal growth factor-like antigens that are targets of malaria transmission-blocking antibodies. J Exp Med 177:505–510. doi:10.1084/jem.177.2.505
Tomas AM, Margos G, Dimopoulos G, van Lin LH, Koning-Ward TF, Sinha R, Lupetti P, Beetsma AL, Rodriguez MC, Karras M, Hager A, Mendoza J, Butcher GA, Kafatos F, Janse CJ, Waters AP, Sinden RE (2001) P25 and P28 proteins of the malaria ookinete surface have multiple and partially redundant functions. EMBO J 20:3975–3983. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.15.3975
Tsuboi T, Kaslow DC, Gozar MM, Tachibana M, Cao YM, Torii M (1998) Sequence polymorphism in two novel Plasmodium vivax ookinete surface proteins, Pvs25 and Pvs28 that are malaria transmission-blocking vaccine candidates. Mol Med 4:772–782
Carter R, Graves PM, Quakyi IA, Good MF (1989) Restricted or absent immune responses in human populations to Plasmodium falciparum gamete antigens that are targets of malaria transmission blocking antibodies. J Exp Med 169:135–147. doi:10.1084/jem.169.1.135
Yoshida S, Ioka D, Matsuoka H, Endo H, Ishii A (2001) Bacteria expressing single-chain immunotoxin inhibit malaria parasite development in mosquitoes. Mol Biochem Parasitol 113:89–96. doi:10.1016/S0166-6851(00)00387-X
Kaslow DC (1996) Transmission-blocking vaccine. In: Hoffman SL (ed) Malaria vaccine development: a multi-immune response approach. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 181–227
Han YS, Thompson J, Kafatos FC, Barillas-Mury C (2000) Molecular interactions between Anopheles stephensi midgut cells and Plasmodium berghei: the time bomb theory of ookinete invasion of mosquitoes. EMBO J 19:6030–6040. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.22.6030
Tsuboi T, Cao YM, Hitsumoto Y, Yanagi T, Kanbara H, Torii M (1997) Two antigens on zygotes and ookinetes of Plasmodium yoelii and Plasmodium berghei that are distinct targets of transmission blocking immunity. Infect Immun 65:2260–2264
Yoshida S, Matsuoka H, Luo E, Iwai K, Arai M, Sinden RE, Ishii A (1999) A single-chain antibody fragment specific for the Plasmodium berghei ookinete protein Pbs21 confers transmission blockade in the mosquito midgut. Mol Biochem Parasitol 104:195–204. doi:10.1016/S0166-6851(99)00158-9
Duffy PE, Kaslow DC (1997) A novel malaria protein, Pfs28, and Pfs25 are genetically linked and synergistic as falciparum malaria transmission-blocking vaccines. Infect Immun 65:1109–1113
Saxena AK, Singh K, Su HP, Klein MM, Stower AW, Saul AJ, Long C, Garboczi DN (2006) Plasmodium P25 and P28, essential proteins for survival of the malaria parasite in the mosquito, are tile-like triangular prism. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:90–91. doi:10.1038/nsmb1024
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, Ivanyi I, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg563
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 15:403–410
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Ramu C, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the Clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3497–3500. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg546
Sali A, Blundell T (1993) L: Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1626
András F, Andrej S (2003) ModLoop: automated modeling of loops in protein structures. Bioinformatics 19:2500–2501. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg362
Fiser A, Kinh Gian Do R, Andrej S (2000) Ali: Modeling of loops in protein structures. Protein Sci 9:1753–1773
Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 10:1093. doi:10.1093/nar/10.3.1093
Sippl MJ (1993) Recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Proteins 17:355–362. doi:10.1002/prot.340170404
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton J (1993) M: PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Cryst 26:283–291. doi:10.1107/S0021889892009944
Vriend G (1990) WHAT IF: a molecular modeling and drug design program. J Mol Graph 8:52–56. doi:10.1016/0263-7855(90)80070-V
Hooft RWW, Vriend G, Sander C, Abola EE (1996) Errors in protein structures. Nature 381:272–272. doi:10.1038/381272a0
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD—visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14:33–38. doi:10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5
Laskowaski RA (2001) PDBsum: summaries and analyses of PDB structures. Nucleic Acids Res 29:221–222. doi:10.1093/nar/29.1.221
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599. doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) Weblogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14:1188–1190. doi:10.1101/gr.849004
Schneider TD, Stephens R (1990) M: Sequence Logos: a new way to display consensus sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6097–6100. doi:10.1093/nar/18.20.6097
Tsuboi T, Kaslow DC, Gozar MM, Tachibana M, Cao YM, Torii M (1998) Sequence polymorphism in two novel Plasmodium vivax ookinete surface proteins, Pvs25 and Pvs28 that are malaria transmission-blocking vaccine candidates. Mol Med 4:772–782
White NJ (2008) Plasmodium knowlesi: the fifth human malaria parasite. Clin Infect Dis 46:172–173. doi:10.1086/524889
Waters AP, Higgins DG, McCutchan TF (1991) Plasmodium falciparum appears to have arisen as a result of lateral transfer between avian and human hosts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3140–3144. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.8.3140
Acknowledgements
B.S. thanks CSIR (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research) for providing a fellowship. I thank my supervisor Dr. A. K. Saxena for allowing me to design and implement the protocols for this study independently.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00894-009-0483-4
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B., Ambedkar, R.D. A very large C-loop in EGF domain IV is characteristic of the P28 family of ookinete surface proteins. J Mol Model 15, 309–321 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-008-0392-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-008-0392-y