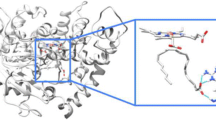
Abstract
CYP7B1 mutations have been linked directly with the neurodegenerative disease hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP), with mutations in the CYP7B1 gene identified as being directly responsible for autosomal recessive HSP type 5A (SPG5). To evaluate the potential impact of CYP7B1 mutations identified in SPG5 on binding and protein function, a comparative model of cytochrome P450 7B1 (CYP7B1) was constructed using human CYP7A1 as a template during model construction. The secondary structure was predicted using the PSIPRED and GOR4 prediction methods, the lowest energy CYP7B1 model was generated using MOE, and then this model was assessed in terms of stereochemical quality and the side chain environment using RAMPAGE, Verify3D and ProSA. Evaluation of the active site residues of the CYP7B1 model and validation of the active site architecture were performed via molecular docking experiments: the docking of the substrates 25-hydroxycholesterol and 27-hydroxycholesterol and the inhibitor 3α-Adiol identified structurally and functionally important residues. Mutational analysis of CYP7B1 amino acid mutations related to hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5 considered phosphorylation, ligand/substrate binding and the structural roles of mutated amino acid residues, with R112, T297 and S363 mutations expected to have a direct impact on ligand binding, while mutations involving R417 would indirectly affect ligand binding as a result of impairment in catalytic function.

A homology model for human CYP7B1 that provides valuable information on the active site architecture along with docking studies to analyze ligand-binding interactions are described. CYP7B1 mutations identified in SPG5 and their potential impact on binding and protein function were also evaluated






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myant NB, Mitropoulos KA (1977) Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res 18:135–153
Noshiro M, Nishimoto M, Morohashi K, Osuda K (1989) Molecular cloning of cDNA for cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase from rat liver microsomes nucleotide sequence. FEBS Lett 257:97–100
Noshiro M, Okuda K (1990) Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett 268:137–140
Stiles A, McDonald J, Bauman D, Russell D (2009) CYP7B1: one cytochrome P450, two human genetic diseases, and multiple physiological functions. J Biol Chem 284:28485–28489
Bjorkhem I, Andersson O, Diczfalusy U, Sevastik B, Xiu RJ, Dua C, Lund E (1994) Atherosclerosis and sterol 27-hydroxylase: evidence for a role of this enzyme in elimination of cholesterol from human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8592–8596
Wu Z, Martin KO, Javitt NB, Chiang JY (1999) Structure and functions of human oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase cDNAs and gene CYP7B1. J Lipid Res 40:2195–2203
Pettersson H, Lundqvist J, Norlin M (2010) Effects of CYP7B1-mediated catalysis on estrogen receptor activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1801:1090–1097
Tang W, Eggertse G, Chiang JY, Norlin M (2006) Estrogen-mediated regulation of CYP7B1: a possible role for controlling DHEA levels in human tissues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 100:42–51
Heverin M, Bogdanovic N, Lutjohann D (2004) Changes in the levels of cerebral and extracerebral sterols in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Lipid Res 45:186–193
Yau JL, Rasmuson S, Andrew R (2003) Dehydroepiandrosterone 7-hydroxylase CYP7B1: predominant expression I primate hippocampus and reduced expression in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 121:307–314
Attal-Khemis SV, Dalmeyda J, Michot L, Roudier M, Morfin R (1998) Increased total 7α-hydroxy-dehydroepiandrosterone in serum of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol 53:B125–B132
Li A, Bigelow JC (2010) The 7-hydroxylation of dehydroepiandrosterone in rat brain. Steroids 75:404–410
Chalbot S, Morfin R (2006) Dehydroepiandrosterone metabolites and their interactions in humans. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 22:1–23
Pettersson H, Lundqvist J, Oliw E, Norlin M (2009) CYP7B1-mediated metabolism of 5α-androstane-3α,17β-diol (3α-Adiol): a novel pathway for potential regulation of cellular levels of androgens and neurosteroids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791:1206–1215
Frye CA, van Keuren KR, Erskine MS (1996) Behavioral effects of 3α-androstanediol. I. Modulation of sexual receptivity and promotion of GABA-A stimulated chloride flux. Behav Brain Res 79:109–118
Tsaousidou M, Ouahchi K, Warner TT (2008) Sequence alterations within CYP7B1 implicate defective cholesterol homeostasis in motor-neuron degeneration. Am J Hum Genet 82:510–515
Goizet C, Boukhris A, Durr A, Beetz C, Truchetto J, Tesson C, Tsaousidou M, Forlani S, Guyant-Maréchal L, Fontaine B, Guimarães J, Isidor B, Chazouillères O, Wendum D, Grid D, Chevy F, Chinnery PF, Coutinho P, Azulay JP, Feki I, Mochel F, Wolf C, Mhiri C, Crosby A, Bricel A, Stevanin G (2009) CYP7B1 mutations in pure and complex forms of hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5. Brain 132:1589–1600
Schule R, Suddique T, Deng HX, Yang Y, Donkervoort HM, Madrid RE, Siddique N, Schols L, Bjorkhem I (2010) Marked accumulation of 27-hydroxycholesterol in SPG5 patients with hereditary spastic paresis. J Lipid Res 51:819–823
Erichsen AK, Koht J, Stray-Pedersen A, Abdelnoor M, Tallaksen ME (2009) Prevelance of hereditary ataxia and spastic paraplegia in southeast Norway: a population-based study. Brain 132:1577–1588
Setchell KDM, Schwarz NC, O’Connell EG, Lund DL, Davis R, Lathe HR, Thompson R, Tyson W, Sokol RJ, Russell DW (1998) Identification of a new inborn error in bile acid synthesis: mutation of the oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase gene causes severe neonatal liver disease. J Clin Invest 102:1690–1703
Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (2009) ExPASy (Expert Protein Analysis System) Proteomics Server. http://ca.expasy.org
Worldwide Protein Data Bank (2011) RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB). http://www.rcsb.org/pdb
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie JM, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W465–W469. http://www.phylogeny.fr/
Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw
Jonassen I (1997) Efficient discovery of conserved patterns using a pattern graph. Comput Appl Biosci 13:509–522
Chemical Computing Group Inc. (2008) Molecular Operating Environment 2008.09 (MOE). http://www.chemcomp.com
Weiner SJ, Kollman PA, Nguyen DT (1986) An all atom forcefield for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids. J Comput Chem 7:230–252
Strushkevich NV, Tempel W et al. Crystal structure of human CYP7A1, Protein Data Bank. doi:10.2210/pdb3dax/pdb
de Bakker P, Lovell S, Richardson Lab at Duke University (2011) RAMPAGE server. http://mordred.bioc.cam.ac.uk/~rapper/rampage.php
Bowie JU, Luthy R, Eisenberg D (1991) A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 253:164–170
Wiederstein M, Sippl M (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W407–W410
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Gotoh O (1992) Substrate recognition sites in cytochrome P450 family 2 (CYP2) proteins inferred from comparative analyses of amino acid and coding nucleotide sequences. J Biol Chem 267:83–90
Lewis DFV (2001) Guide to cytochromes P450 structure and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hasemann CA, Kurumbail RG, Boddupalli SS, Peterson JA, Deisenhofer J (1995) Structure and function of cytochromes P450: a comparative analysis of three crystal structures. Structure 3:41–62
Garnier J, Gibrat JF, Robson B (1996) GOR method for predicting protein secondary structure from amino acid sequence. Meth Enzymol 266:540–554
Allen SW, Raucy JL (2001) Recent advances in P450 research. Pharmacogenomics J 1:178–186
Kim D, Heo YS, de Montellano PRO (2008) Efficient catalytic turnover of cytochrome P450(cam) is supported by a T252N mutation. Arch Biochem Biophys 474:150–156
Graham SE, Peterson JA (2002) Sequence alignments, variabilities and vagaries. Meth Enzymol 357:15–28
Chiang CW, Chan NL, Yeh HC, Wang LH (2006) Crystal structure of the human prostacyclin synthase. J Mol Biol 364:266–274
UCLA-DOE Institute for Genomics & Proteomics (2011) Server. http://www.doe-mbi.ucla.edu/Services
Pikuleva IA (2006) Cytochrome P450s and cholesterol homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther 112:761–773
Mast N, Graham SE, Andersson U, Bjorkhem I, Hill C, Peterson J, Pikuleva IA (2005) Cholesterol binding to cytochrome P450 7A1, a key enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. Biochemistry 44:3259–3271
Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S (1999) Sequence- and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J Mol Biol 294:1351–1362
Pikuleva IA, Cao C, Waterman MR (1999) An additional electrostatic interaction between adrenodoxin and P450c27 (CYP27A1) results in tighter binding than between adrenodoxin and P450scc (CYP11A1). J Biol Chem 274:2045–2052
Zheng YM, Baer BR, Kneller MB, Henne KR, Kunze KL, Rettie AE (2003) Covalent heme binding to CYP4B1 via Glu310 and a carbocation porphyrin intermediate. Biochemistry 42:4601–4606
Pullingr CR, Eng C, Salen G, Shefer S, Batta AK, Erickson SK, Verhagen A, Rivera CR, Mulvihill SJ, Malloy MJ, Kane JP (2002) Human cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) deficiency has a hypercholesterolemic phenotype. J Clin Invest 110:109–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 74 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siam, A., Brancale, A. & Simons, C. Comparative modeling of 25-hydroxycholesterol-7α-hydroxylase (CYP7B1): ligand binding and analysis of hereditary spastic paraplegia type 5 CYP7B1 mutations. J Mol Model 18, 441–453 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1084-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-011-1084-6