Abstract
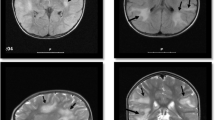
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and coeliac disease (CD) are an uncommon association. Recently “MS-like illness and CNS white-matter abnormalities” have been demonstrated in patients with CD. We report the case of a 19-year-old female with MS, who presented an episode of headache at onset of disease and developed acute hepatitis (AH) 14 months later. After the diagnosis of AH, an occult CD, confirmed by jejunal biopsy, was disclosed. Constipation was the only gastrointestinal symptom. A serum sample collected before onset of MS was positive for CD. Anti-central nervous system antibodies were negative in both retrospective and current serum samples. Conclusions The concomitant presence of MS with atypical onset, AH and CD likely represents an unusual chance association in our patient but inflammatory immune-mediated damage of the central nervous system triggered by gluten could not be excluded.
Sommario
L’associazione di sclerosi multipla e celiachia non è frequente. Recentemente, “casi simili alla sclerosi multipla (MS-like) ed alterazioni della sostanza bianca del sistema nervoso centrale” sono stati descritti in pazienti affetti da celiachia. Riportiamo il caso di una ragazza di 19 anni affetta da sclerosi multipla esordita con un episodio di cefalea cui ha fatto seguito, dopo 14 mesi, l’esordio di un’epatite acuta. Confermata l’origine autoimmune dell’epatite auto-immune, è stata diagnosticata una celiachia silente, confermata da una biopsia intestinale. L’unico disturbo gastrointestinale riferito dalla paziente era la stipsi. Un campione di siero della paziente raccolto all’esordio della sclerosi multipla è risultato positivo per celiachia. La ricerca degli anticorpi anti-sistema nervoso centrale è risultata negativa sia all’esordio della sclerosi multipla che in una fase successiva. Conclusioni La presenza contemporanea nella nostra paziente di una sclerosi multipla ad esordio atipico, di un’epatite autoimmune e di una celiachia anche se non frequente è probabilmente del tutto occasionale, pur non potendosi comunque escludere un danno immunomediato del sistema nervoso centrale innescato dal glutine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Green PH, Jabri B (2003) Coeliac disease. Lancet 362:383–391
Pengiran Tengah D, Lock RJ et al (2004) Multiple sclerosis and occult gluten sensitivity. Neurology 62:2326–2327
Hadjivassiliou M, Grunewald RA, Laweden M et al (2001) Headache and CNS white matter abnormalities associated with gluten sensitivity. Neurology 56:385–388
Hafler DA, Weiner HL (1989) MS: a CNS and systemic autoimmune disease. Immunol Today 10:104–107
Bateson MC, Hopwood D, Mac Gillivray JB (1979) Jejunal morphology in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1:1108–1110
Kieslich M, Errazuriz G, Posselt HG et al (2001) Brain-white-matter lesions in celiac disease: a prospective study of 75 diet-treated patients. Pediatrics 108:E21
Hadjivassiliou M, Grunewald RA, Davies-Jones GAB (2005) Gluten sensitivity as a neurological illness. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:560–563
Hadjivassiliou M, Boscolo S, Davies-Jones GAB et al (2002) The humoral response in the pathogenesis of gluten ataxia. Neurology 58:1221–1226
Hadjivassiliou M, Maki M, Sanders DS et al (2006) Autoantibody targeting of brain and intestinal transglutaminase in gluten ataxia. Neurology 66:373–377
Mohan K, Pinto D, Issekuts TB (2003) Identification of tTG as a novel molecule involved in human CD8+T cell transendothelial migration. J Immunol 171:3179–3186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrò, M.T., Franciotta, D., Riccardi, T. et al. A case of multiple sclerosis with atypical onset associated with autoimmune hepatitis and silent coeliac disease. Neurol Sci 29, 29–31 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-008-0855-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-008-0855-z