Abstract
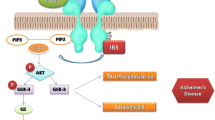
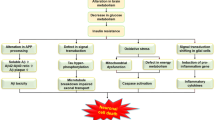
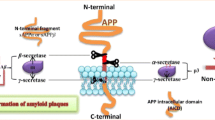
Relentless progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) poses a grave situation for the biomedical community to tackle. Agents starting as hot favorites in clinical trials have failed in later stages and it is time we reconsidered our approaches to intervene the disease. Quite some interesting work in the last decade has introduced a new school of thought which factors in neuronal glycemic imbalance as a major component for the development of AD. Insulin resistance in the brain has brought forward subsequent sequelae which might work towards amyloid accretion and/or tau hyperphosphorylation. It is also pointed out that insulin works by distributing iron to neuronal tissue and an insulin resistant state throws it off gear leading to iron overloading of neurons which is ultimately detrimental. A relatively recent investigation finds the role of c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK3) in AD which also seems to bear a link with insulin resistance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brookmeyer R, Jhonson E, Zieglr-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 3:186–191
Cllaway E (2012) Alzheimer’s drug take a new track. Nature 489:13–14
Burns JM, Donnelly JE, Anderson HS, Mayo MS, Spencer-Gardner L, Thomas G (2007) Peripheral insulin and brain structure in early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 69:1094–1104
Erol A (2008) An integrated and unifying hypothesis for the metabolic basis of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 13:241–253
Hopkins DFC, Williams G (1997) Insulin receptors are widely distributed in human brain and bind human and porcine insulin with equal affinity. Diabet Med 14:1044–1050
Adamo M, LeRoith D, Simon J, Roth J (1989) Effect of altered nutritional states on insulin receptors. Annu Rev Nutr 8:149–166
Russo VC, Gluckman PD, Feldman EL, Werther GA (2005) The insulin-like growth factor system and its pleiotropic functions in brain. Endocrinol Rev 26:916–943
Chiu SL, Cline HT (2010) Insulin receptor signalling in the development of neuronal structure and function. Neural Dev 5:1–18
Zhao W, Wu X, Xie H, Ke Y, Yung WH (2010) Permissive role of insulin in the expression of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus of immature rats. Neurosignals 18:236–245
Wang X, Zheng W, Xie JW, Wang T, Wang SL, Teng WP, Wang ZY (2010) Insulin deficiency exacerbates cerebral amyloidosis and behavioural deficits in an Alzheimer transgenic mouse model. Mol Neurodegener 2:46
Kahn CR, Suzuki R (2010) Diabetes, insulin and Alzheimer’s disease. In: Craft S, Christen Y (eds) Research and perspective in Alzheimer’s disease. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 1–21
Liu Y, Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX (2011) Deficient brain insulin signalling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J Pathol 225:54–62
Gasparini L, Netzer WJ, Greengard P, Xu H (2002) Does insulin dysfunction play a role in Alzheimer’s disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:288–293
Johnston AM, Pirola L, Van Obberghen E (2003) Molecular mechanisms of insulin receptor substrate protein-mediated modulation of insulin signalling. FEBS Lett 546:32–36
Van der Heide LP, Ramakers GMJ, Smidt MP (2006) Insulin signalling in the central nervous system: learning to survive. Prog Neurobiol 79:205–221
Johnston AM, Pirola L, Van Obberghen E (2003) Molecular mechanisms of insulin receptor substrate protein-mediated modulation of insulin signalling. FEBS Lett 546:32–36
McEwen BS, Reagan LP (2004) Glucose transporter expression in the central nervous system: relationship to synaptic function. Eur J Pharmacol 19:13–24
Cross DAE, Culbert AA, Chalmers KA, Facci L, Skaper SD, Reith AD (2001) Selective small-molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity protect primary neurones from death. J Neurochem 77:94–102
Phiel Christopher J, Wilson Christina A, Lee Virginia M-Y, Klein Peter S (2011) GSK-3α regulates production of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-β peptides. Nature 423:435–439
Gasparini L, Gouras GK, Wang R, Gross RS, Beal MF, Greengard P, Xu H (2001) Stimulation of beta amyloid precursor protein by insulin reduces intra neuronal beta amyloid and requires mitogen activated protein kinase signalling. J Neurosci 21:2561–2570
Dou JT, Chen M, Dufour F, Alkon DL, Zhao WQ (2005) Insulin receptor signalling in long-term memory consolidation following spatial learning. Learn Mem 12:646–655
Sheng M, Kim MJ (2002) Postsynaptic signalling and plasticity mechanisms. Science 25:776–780
Park CR (2001) Cognitive effects of insulin in the central nervous system. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:311–323
Zhao WQ, Chen H, Quon MJ, Alkon DL (2004) Insulin and insulin receptors in experimental models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 490:71–81
Katakam PV, Tulbert CD, Snipes JA, Erdos B, Miller AW, Busija DW (2005) Impaired insulin induced vasodilatation in small coronary arteries of Zucker obese rats is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H854–H860
Craft S (2009) The role of metabolic disorders in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia: two roads converged. Arch Neurol 66:300–305
Zao WQ, Dl Alkon (2001) Role of insulin and insulin receptor in learning and memory. Mol Cell Endocrinol 177:125–134
Dou JJ, Chen M, Dufour F, Alkon DL, Zao WQ (2005) Insulin receptor signalling in long term memory consolidation following spatial learning. Learn Mem 12:646–655
Scautam D, Surjo D, Ueki K, Baudler S, Schubert D et al (2004) Role for neuronal insulin resistance in neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Nat Acad Sci 101:3100–3105
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ (2011) The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus—present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:228–236
McCrimmon RJ, Ryan CM, Frier BM (2012) Diabetes and cognitive dysfunction. Lancet 379:2291–2299
Rönnemaa E, Zethelius B, Sundelöf J, Sundström J, Degerman-Gunnarsson M, Berne C, Lannfelt L, Kilander L (2008) Impaired insulin secretion increases the risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 71:1065–1071
Hassing LB, Hofer SM, Nilsson SE, Berg S, Pedersen NL, McClearn G, Johansson B (2004) Comorbid type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension exacerbates cognitive decline: evidence from a longitudinal study. Age Ageing 33:355–361
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV (2009) Hypoglycaemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 301:1565–1572
Weiss R, Dufour S, Taksali SE, Tambortlane WV, Petersen KF, Bonadonna RC, Boselli L, Barbetta G, Alle K, Rife F, Savoye M, Dziura J, Sherwin R, Shulman R, Caprio S (2003) Prediabetes in obese youth: a syndrome of impaired glucose tolerance, severe insulin resistance, and altered myocellular and abdominal fat partitioning. Lancet 362:951–957
Small GW, Ercoli LM, Silverman DH et al (2000) Cerebral metabolic and cognitive decline in persons at genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(11):6037–6042
Rasgon NL, Kenna HA, Wroolie TE et al (2011) Insulin resistance and hippocampal volume in women at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 32:1942–1948
Forlich L, Blum- Degen D, Bernstein HG, Engelsberger S, Humrich J, Lauffer S, Muschner D et al (1998) Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 105:423–438
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Hoyer S (2007) Central insulin resistance as a trigger for sporadic Alzheimer-like pathology: an experimental approach. J Neural Transm Suppl 72:217–233
Unoki H, Yamagishi S (2008) Advanced glycation end products and insulin resistance. Curr Pharm Des 14:987–989
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 330:1774
Pahnke J, Walker LC, Scheffler K, Krohn M (2009) Alzheimer’s disease and blood-brain barrier function—why have anti-β-amyloid therapies failed to prevent dementia progression? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2009(33):1099–1108
Vogelgesang S et al (2002) Deposition of Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid is inversely correlated with P-glycoprotein expression in the brains of elderly non-demented humans. Pharmacogenetics 12:535–541
Cirrito JR, Deane R, Fagan AM, Spinner ML, Parsadanian M, Finn MB et al (2005) P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood–brain barrier increases amyloid-β deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest 115:3285–3290
Ling S, Zou J, Rudd JA, Hu Z, Fang M (2011) The recent approaches of therapeutic approaches against Aβ for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Anat Rec 294:1307–1318
Carter TL, Pedrini S, Ghiso J, Ehrlich ME, Gandy S (2006) Brain neprilysin activity and susceptibility to transgene-induced Alzheimer amyloidosis. Neurosci Lett 392:235–239
Hellstrom-Lindahl E, Ravid R, Nordberg A (2006) Age-dependent decline of neprilysin in Alzheimer’s disease and normal brain: inverse correlation with Aβ levels. Neurobiol Aging 29(2):210–221
Devi L, Alldred Melissa J, Ginsberg SD, Ohno M (2012) Mechanisms underlying insulin deficiency-induced acceleration of β-amyloidosis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 7:e32792
Gong CX, Liu F, Grundke-iqbal I, Iqbal K (2006) Impaired brain glucose metabolism leads to Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration through a decrease in tau O-GlcNAcylation. J Alzheimer’s Dis 9(1):1–12
Goto I, Taniwaki T, Hosokawa S, Otsuka M, Ichiya Y, Ichimiya A (1993) Positron emission tomographic (PET) studies in dementia. J Neurol Sci 114:1–6
Loring JF, Wen X, Lee JM, Seilhamer J, Somogyi R (2001) A gene expression profile of Alzheimer’s disease. DNA Cell Biol 20:683–695
Gerozissis K (2003) Brain insulin: regulation, mechanisms of action, and functions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23(4–5):873–874
Ishiguro K, Shiratsuchi A, Sato S et al (1993) Glycogen synthase kinase 3β is identical to tau protein kinase I generating several epitopes of paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett 325:167–172
Hong M, Lee VMY (1997) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 regulate tau phosphorylation in cultured human neurons. J Biol Chem 272:19547–19553
Wells L, Whelan SA, Hart GW (2003) O-GlcNAc: a regulatory post-translational modification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:435–441
Gong CX, Liu F, Iqbal IG, Iqbal K (2006) Impaired brain glucose metabolism leads to Alzheimer’s neurofibrillary neurodegeneration through a decrease in Tau-O-GlcNacylation. J Alzheimers Dis 9:1–12
Jahanshad N, Kohannim O, Hibar DP, Stein JL, McMahon KL, de Zubicaray GI, Medland SE, Montgomery GW, Whitfield JB, Martin NG, Wright MJ, Toga AW, Thompson PM (2012) Brain structure in healthy adults is related to serum transferrin and the H63D polymorphism in the HFE gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 3(109):E851–E859
Connor JR, Menzies SL, St Martin SM, Mufson EJ (1992) A histochemical study of iron, transferrin, and ferritin in Alzheimer’s diseased brains. J Neurosci Res 31:75–83
O’Donnell MJ, Watson J, Martin P, Chapman C, Barnett AH (1991) Transferrinuria in type 2 diabetes: the effect of glycaemic control. Ann Clin Biochem 28:174–178
Swaminathan S, Alam MG, Fonseca VA, Shah SV (2007) The role of iron in diabetes and its complications. Diabetes Care 30:1926–1933
Fernández-Real JM (2008) Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. The impact of oxidative stress on endothelial function. Rev Esp Cardiol 8(Suppl C):42–49
Tanner LI, Lienhard GE (1987) Insulin elicits a redistribution of transferrin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through an increase in the rate constant for receptor externalization. J Biol Chem 262:8975–8980
Jehn ML, Guallar E, Clark JM, Couper D, Duncan BB, Ballantyne CM et al (2007) A prospective study of plasma ferritin level and incident diabetes. Am J Epidemiol 165:1047–1054
Choi KM, Lee KW, Kim HW et al (2005) Association among serum ferritin, alanine aminotransferase levels, and metabolic syndrome in Korean postmenopausal women. Metabolism 54:1510–1514
Abdelli S, Abderrahmani A, Hering BJ, Beckmann JS, Bonny C (2007) The c-Jun N-terminal kinase JNK participates in cytokine- and isolation stress-induced rat pancreatic islet apoptosis. Diabetologia 50:1660–1669
Gupta S, Barrett T, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Sluss HK et al (1996) Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors. EMBO J 15:2760–2770
Davis RJ (2000) Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103:239–252
Fowler AE, da Silva NF, Burman C, Harte AL, McTernan PG, Kumar S (2004) Increased C-jun N terminal kinase (JNK) activity may link insulin resistance and inflammation in human central obesity. Endocr Abstr 7:49
Yoon SO, Park DJ, Ryu JC, Ozer HC, Tep C, Shin YJ et al (2012) JNK3 perpetuates metabolic stress induced by Aβ peptides. Neuron 75:824–837
Duarte AI, Moreira PI, Oliveira CR. (2012) Insulin in CNS: more than just a peripheral hormone. J Aging Res 1–21
Salkovic Petrisic M, Laekovic Z (2003) Intracerebroventricular administration of betacytotoxics alters expression of brain monoamine transporter genes. J Neural Transm 110:15–29
Talbot K, Wang HY, Kazi M, Han LY, Bakshi KP, Stucky A, Rl Fuino (2012) Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF 1 resistance, IRS 1 dysfunction, cognitive decline. J Clin Investig 122:1316–1338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medhi, B., Chakrabarty, M. Insulin resistance: an emerging link in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci 34, 1719–1725 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1454-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-013-1454-1